Chronic Hepatitis B Woodchuck Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs provides a range of advanced animal models tailored to evaluate the efficacy of Hepatitis B therapies. These models help in preclinical testing by simulating various stages of infection and disease progression, ensuring accurate assessment of potential treatments for Hepatitis B.
Introduction
Hepatitis B (HBV) is a serious liver infection caused by the Hepatitis B virus. It is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person, including through sexual contact, sharing needles, or from mother to child during birth. HBV can cause both acute and chronic infections, with the latter potentially leading to severe complications such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). Chronic Hepatitis B (CHB) is a major global health issue, affecting more than 250 million people worldwide. The virus primarily targets liver cells, and its long-term persistence in the body can lead to chronic inflammation and progressive liver damage. The clinical presentation of Hepatitis B can vary, with some individuals remaining asymptomatic for years, while others develop acute or chronic liver disease. Chronic infection is particularly concerning because it often leads to long-term liver damage without obvious symptoms until significant liver dysfunction occurs. Currently, antiviral treatments such as nucleos(t)ide analogs and interferons are used to manage the virus, but there is no cure, and treatments primarily aim to suppress viral replication and prevent liver damage.
Disease Models and Applications
The Chronic Hepatitis B in Woodchucks model is an essential preclinical tool for evaluating potential therapeutic strategies for HBV infection. This model is established by infecting woodchucks with the woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV), a close relative of HBV, leading to chronic infection and liver disease similar to human chronic hepatitis B. Woodchucks naturally develop HBV-like infections, offering a realistic representation of human HBV pathology, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. One key advantage of this model is its similarity to human disease progression, allowing for accurate drug evaluation. However, the model is limited by the availability of the woodchuck species and the potential variability in response to infection. Despite these limitations, the woodchuck model provides valuable insights into antiviral drug development, particularly for studying long-term chronic infections and their complications.
Simulates: This model simulates Chronic Hepatitis B, including both acute and chronic phases of infection. Closely mimicking the natural history of HBV in humans allows for the observation of disease progression from initial infection to the development of liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potential carcinogenesis.
Evaluates Drugs: The woodchuck model is used to evaluate the efficacy of antiviral therapies, including nucleos(t)ide analogs, immune modulators, and novel HBV-targeted agents. It is particularly useful for assessing the impact of drugs on viral replication, liver inflammation, and fibrosis. This model is also employed in testing combination therapies aimed at achieving a functional cure for HBV infection.
 Fig. 1 Pictures of eastern woodchuck M. monax.1
Fig. 1 Pictures of eastern woodchuck M. monax.1
Measurements
For evaluating drug efficacy in the Chronic Hepatitis B in Woodchucks model, we employ several advanced measurement techniques, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Weight changes, liver enlargement, and overall health.
- Histopathology: Liver tissue analysis via H&E and Masson's trichrome staining to assess inflammation and fibrosis.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in the liver.
- Cytokine profiling: Measurement of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) using ELISA.
- Viral load quantification: Real-time PCR to measure WHV DNA levels in serum and liver tissue.
- Liver function tests: Assessment of serum markers, including ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels.
- Gene/protein expression: Profiling using RT qPCR and Western blot to evaluate changes in HBV-related genes and proteins.
In addition, our team provides guidance in experimental design, helping to tailor the model and measurements to specific research needs, ensuring precise and meaningful results.
Related Services
In addition to the established woodchuck model, we offer other methods for inducing Chronic Hepatitis B in woodchucks. These models are valuable for evaluating therapeutic candidates under different infection conditions. With our extensive knowledge in model development, we ensure the most appropriate approach for your research needs.
- AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Model
- HBV Transgenic Mouse Model
- Hydrodynamic Injection HBV Model
- Hepatitis B Humanized Mouse Model
Advantages
- Expertise: Our team has extensive experience in HBV model development and drug evaluation.
- Customizability: We offer tailored solutions, adjusting models to meet specific research objectives.
- State-of-the-art facilities: Our labs are equipped with the latest technology for accurate, reliable data.
- Comprehensive support: From model selection to data analysis, we provide full-service support throughout the project.
- Quick turnaround: We deliver timely results, ensuring that your research progresses efficiently.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the advantage of using the woodchuck model for HBV research?
The woodchuck model is one of the few that accurately replicates chronic HBV infection in humans, providing essential insights into drug efficacy and disease progression.
-
2. How does this model simulate chronic HBV infection?
The woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) shares significant similarities with HBV, allowing for the study of chronic infection, liver inflammation, and complications like cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
3. What types of drugs can be evaluated using this model?
Antiviral drugs, immune modulators, and novel therapies aimed at achieving a functional cure for HBV can be tested in this model.
-
4. Are the results from the woodchuck model directly translatable to human patients?
While there are differences between species, the woodchuck model is the closest available option to human HBV infection and provides valuable predictive insights into human responses to therapies.
-
5. What measurement techniques are used to assess treatment efficacy?
We utilize a range of techniques, including histopathology, cytokine profiling, gene expression analysis, and viral load quantification, to assess drug impact in this model.
Published Data
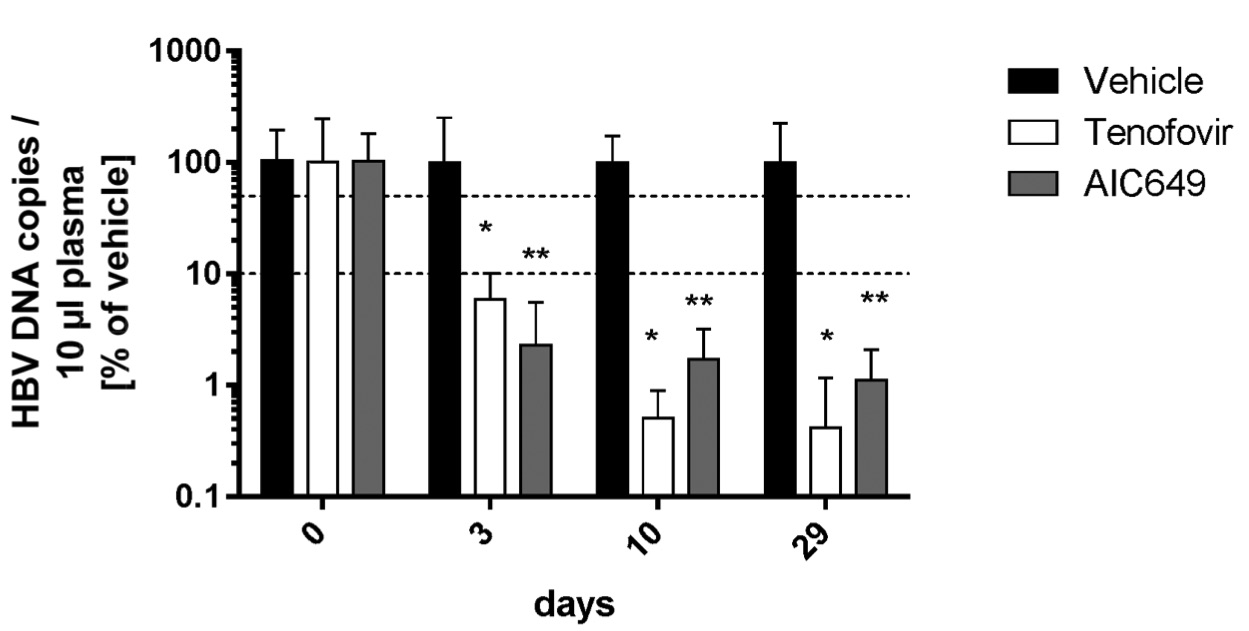 Fig. 2 AIC649 reduces the HBV titer in HBV tg mice as effective as Tenofovir.2
Fig. 2 AIC649 reduces the HBV titer in HBV tg mice as effective as Tenofovir.2
The immunomodulator AIC649 was evaluated for its ability to reduce HBV titer in comparison to potent direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), including the "gold standard" Tenofovir. In the experiment, HBV transgenic (tg) mice were treated for 29 days with either AIC649 twice weekly, Tenofovir twice daily, or a vehicle control. Both treatment regimens led to a significant reduction in HBV titer compared to the control group (Fig. 1). Notably, the antiviral effect of AIC649 administered twice weekly was found to be comparable to that of Tenofovir administered twice daily.
References
- Kosinska, Anna D et al. "Therapeutic vaccination and immunomodulation in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: preclinical studies in the woodchuck." Medical microbiology and immunology vol. 204,1 (2015): 103-14. DOI:10.1007/s00430-014-0379-5. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Paulsen, Daniela et al. "AIC649 Induces a Bi-Phasic Treatment Response in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B." PloS one vol. 10,12 e0144383. 14 Dec. 2015, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144383. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
