HBV Infection & Liver Fibrosis Combination Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established rodent models for studying HBV infection and liver fibrosis. These models accurately replicate human HBV infection and fibrosis progression, providing valuable insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. Our models are designed for preclinical testing of antiviral drugs, immune modulators, and anti-fibrotic agents. We also provide detailed assessments, including histological examination, serum biomarker analysis, viral load measurement, and fibrosis scoring. Our team is committed to supporting your research from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring effective and reliable results.
Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major global health concern that affects the liver and can lead to both acute and chronic conditions. In chronic infection, the body's immune response to persistent HBV replication leads to liver inflammation, which over time can result in liver fibrosis—a progressive buildup of scar tissue. If left untreated, liver fibrosis can advance to cirrhosis and, in some cases, lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The progression from HBV infection to liver fibrosis and further liver damage is influenced by various factors, including the viral genotype, immune response, and co-infection with other viruses like hepatitis C or HIV.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established rodent models for studying the combination of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and liver fibrosis. These models are carefully designed to simulate the progression of chronic HBV infection leading to liver fibrosis, closely mimicking the complex human disease spectrum. The models include both acute and chronic HBV infection with varying stages of liver fibrosis, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of therapeutic candidates targeting viral replication, immune response modulation, and fibrosis attenuation. Our team of experienced scientists will collaborate with you throughout your project, from model selection and experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring the generation of high-quality and reliable results. To learn more about the rodent HBV infection and liver fibrosis models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
 Fig. 1 HBV-TAA/EtOH induced hepatic fibrosis.1
Fig. 1 HBV-TAA/EtOH induced hepatic fibrosis.1
| Model | Simulated Disease | Drug Evaluation Focus |
| HBV Transgenic & CCl4 induced Liver Fibrosis Model | Chronic Hepatitis B (HBV), liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis | Antiviral agents, anti-fibrotic drugs, liver regeneration therapies, hepatoprotective agents, anti-inflammatory drugs |
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent HBV infection and liver fibrosis combination models, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
General observations: Body weight, liver size, mortality rate, jaundice, and general health status.
Histopathological analysis: Liver tissue sections stained with H&E, Masson's trichrome, and Sirius Red for assessing liver architecture, fibrosis stages, and inflammation.
Immunohistochemistry: Detection of HBV antigens (HBsAg, HBcAg) and infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in liver tissues.
Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and other fibrosis-related cytokines.
Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Measurement of liver enzymes (e.g., ALT, AST), bilirubin levels, collagen deposition (hydroxyproline), and viral load (HBV DNA).
Gene/protein expression profiling via RT qPCR and Western blot techniques: Quantification of key genes involved in HBV replication (e.g., HBV polymerase), fibrosis (e.g., Collagen I, TGF-β), immune response (e.g., MxA, IL-10), and liver injury (e.g., α-SMA).
In addition to these established HBV infection and liver fibrosis models, we also offer the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research objectives, guided by literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to the HBV infection and liver fibrosis combination model, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Advantages
- Expertise in Hepatitis B and Liver Fibrosis: We specialize in providing high-quality rodent models for studying Hepatitis B infection and liver fibrosis. Our team has extensive experience in viral pathogenesis, liver injury mechanisms, and fibrosis progression, enabling us to offer invaluable insights for your research.
- Comprehensive Model Solutions: We offer a range of well-established models that replicate both HBV infection and liver fibrosis, along with models for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These models are ideal for preclinical evaluation of therapeutic candidates targeting viral replication, fibrosis, inflammation, and liver protection.
- Advanced Technologies for Accurate Results: Our models are complemented by advanced technologies for in-depth analysis, including histological evaluation, serum biomarkers, cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA), gene/protein expression analysis (e.g., RT qPCR, Western blot), and immune response assessment. This comprehensive approach enables reliable, reproducible data.
- Tailored Solutions for Specific Research Needs: Every research project is unique. We provide customized model development based on your specific goals, whether it's testing antiviral agents, immune modulators, or anti-fibrotic treatments. We ensure that the models are designed to meet the unique needs of your study.
- Full Support Across All Stages: From model selection and experimental design to data analysis and interpretation, our scientific team provides expert support throughout the entire research process. We work closely with you to ensure high-quality, consistent results that align with your project objectives.
- High-Quality, Reproducible Results: We prioritize the accuracy and reproducibility of results. Our models are rigorously validated to ensure consistent performance, giving you confidence in the data you collect for your research.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of HBV infection and liver fibrosis models do you offer?
We offer a range of rodent models for HBV infection and liver fibrosis, including both acute and chronic HBV infection models, liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) models. These models are designed to replicate the human disease progression, allowing for comprehensive therapeutic evaluations.
-
2. Can I customize the HBV infection and liver fibrosis models for my research?
Yes, our models can be fully customized based on your specific research needs. Whether you are investigating antiviral therapies, immune modulators, anti-fibrotic drugs, or liver regeneration therapies, we can tailor the model to suit your study goals.
-
3. How is the severity of liver fibrosis and HBV infection assessed in these models?
The severity of liver fibrosis and HBV infection is assessed using histopathological techniques, serum biomarkers, viral load measurement, cytokine levels, and fibrosis scoring systems (e.g., Ishak score). We also evaluate liver function through liver enzyme levels (ALT, AST).
-
4. What therapeutic interventions can be tested in HBV infection and liver fibrosis models?
Our models are ideal for testing antiviral therapies, immune modulators, anti-inflammatory agents, liver-protective drugs, and anti-fibrotic treatments. These models allow for detailed investigation of drug efficacy in preventing HBV-related liver damage and fibrosis progression.
-
5. How long does it take to obtain results from your HBV infection and liver fibrosis models?
The timeline for obtaining results depends on the model and study goals. Preliminary data (e.g., liver function and viral load) can be obtained in a few weeks, while comprehensive results, including histology and gene expression analysis, may take several weeks to months.
Published Data
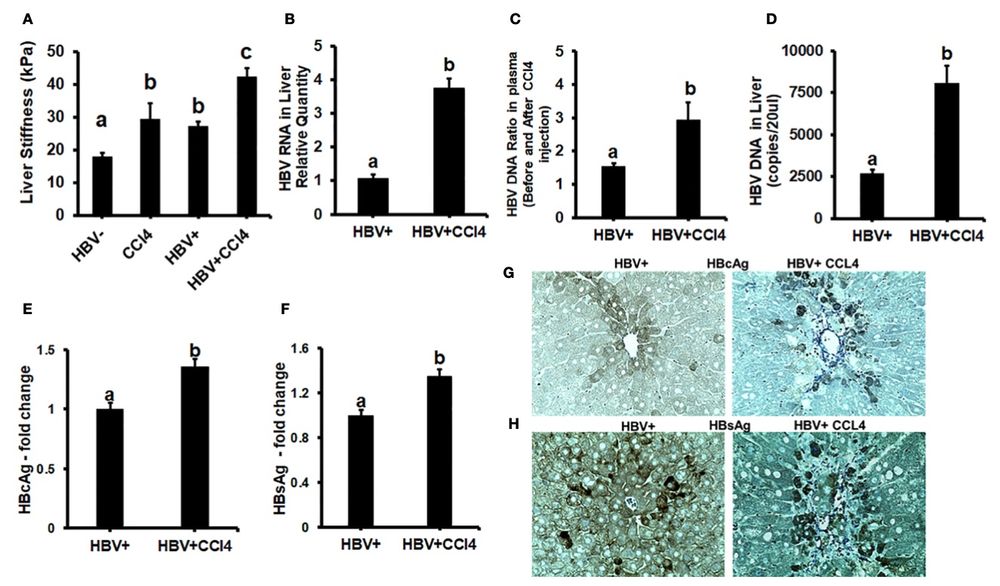 Fig. 2 Increased liver tissue stiffness regulates HBV replication/enhanced expression of HBV markers in livers of CCl4-administered HBV+ transgenic mice.2
Fig. 2 Increased liver tissue stiffness regulates HBV replication/enhanced expression of HBV markers in livers of CCl4-administered HBV+ transgenic mice.2
This article examined the mechanical properties of liver tissue stiffness in control and HBVTg mice under CCl4 induced liver injury conditions. As shown in Figure 2A, the ex vivo liver tissue stiffness of control mice was measured at 17 kPa. It is important to note that mechanical properties can change due to factors like perfusion pressure, tissue degradation, and boundary conditions in ex vivo tissue, which may differ from the in vivo environment. The results also indicate that the tissue stiffness can change drastically within minutes postmortem. To account for these variations, all tissue conditions were processed on the same day to ensure consistency when measuring stiffness, and comparisons between groups were made to evaluate changes under different treatment conditions. The liver tissue stiffness of wild-type control mice represents the stiffness of a healthy liver, while the increased stiffness observed in CCl4-treated mice correlates with fibrotic changes. Interestingly, control HBVTg mice exhibited higher liver stiffness compared to wild-type controls. To investigate the potential link between increased liver stiffness and HBV infection markers, we measured HBV RNA and DNA in the liver tissues of CCl4-treated HBVTg mice. Additionally, serum HBV DNA levels were assessed using the COBAS Amplicor HBV monitor test, and immunohistochemistry was performed to detect HBV markers such as HBcAg and HBsAg in liver tissues (Figures 2B-H). These markers were significantly elevated in the livers of CCl4-treated HBVTg mice, suggesting a correlation between liver stiffness and HBV infection progression.
References
- Poilil Surendran, Suchithra et al. "Effect of hepato-toxins in the acceleration of hepatic fibrosis in hepatitis B mice." PloS one vol. 15,5 e0232619. 19 May. 2020, DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0232619. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Bybee, Grace et al. "Increased liver stiffness promotes hepatitis B progression by impairing innate immunity in CCl4 induced fibrotic HBV+ transgenic mice." Frontiers in immunology vol. 14 1166171. 3 Aug. 2023, DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166171. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
