Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes (T2D) Rat Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established animal models for Type II Diabetes, including the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rat Model, to help evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic interventions. Our models are specifically designed to aid researchers in evaluating novel drugs and therapies for managing this widespread disease.
Introduction
Type II Diabetes (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, and elevated blood glucose levels. Unlike Type I Diabetes, where the body cannot produce insulin, Type II Diabetes occurs when the body's cells no longer respond effectively to insulin. Over time, this leads to β-cell dysfunction and increased blood sugar. T2D is primarily associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. It is a leading cause of cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, and blindness, and its prevalence has risen sharply in recent decades, particularly in developed countries. Early diagnosis and effective management are critical for reducing the risk of severe complications. Treatment strategies for Type II Diabetes include lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
Disease Models and Applications
The Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rat Model is a genetic model of Type II Diabetes that is widely used in research. ZDF rats are leptin receptor-deficient, making them genetically prone to developing obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia, all key features of Type II Diabetes. This model is ideal for studying the metabolic disturbances associated with the disease, including impaired insulin signaling, β-cell dysfunction, and the development of cardiovascular and renal complications. The model is created by using ZDF rats that have been selectively bred to exhibit these characteristics, making it a reliable and reproducible option for long-term studies. Its advantages include the ability to mimic human Type II Diabetes closely, particularly in terms of obesity-induced insulin resistance. However, one limitation is that the model predominantly develops disease-related features after a prolonged period, which may not fully replicate the rapid onset seen in some human cases.
- Simulates: The ZDF Type II Diabetes Rat Model simulates human Type II Diabetes, particularly the insulin resistance and obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction seen in patients. It is an ideal model for studying the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications, including cardiovascular and renal diseases.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate drugs that target insulin resistance, β-cell function, and glucose metabolism. It is particularly useful for assessing the effectiveness of therapies aimed at improving insulin sensitivity, controlling hyperglycemia, and mitigating complications associated with obesity-related diabetes.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, blood glucose levels, food and water intake, and activity levels.
- Glucose tolerance test (GTT): Assessment of insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
- Hematology analysis: Measurement of blood parameters, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Serum biomarkers: Insulin levels, HbA1c, and other metabolic markers.
- Histopathology: Examination of pancreatic, liver, and kidney tissues for signs of diabetic complications such as β-cell loss, steatosis, and nephropathy.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Quantification of key molecules involved in glucose metabolism and insulin signaling via RT-qPCR and Western blot.
Our scientific team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a tailored approach to your research project.
Related Services
In addition to the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model, we also provide other diabetes models. These models allow for the investigation of different aspects of Type II Diabetes pathophysiology and drug efficacy.
- Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes Model
- Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model
- db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model
- Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model
- STZ-NA induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Combined Spleen & Partial Pancreas Resection & Glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model
Advantages
- Specialized Expertise: We specialize in providing reliable and reproducible diabetes models, including the ZDF rat model, tailored for Type II Diabetes research.
- Comprehensive Model Portfolio: We offer a wide range of well-established models to study various aspects of Type II Diabetes, allowing for flexible and comprehensive research options.
- Cutting-edge Technology: Our advanced technologies for glucose metabolism analysis, histopathology, and gene expression profiling ensure precise and accurate data collection.
- Customizable Solutions: We provide fully customizable research designs to suit your specific study needs, whether you're focusing on drug efficacy, disease pathogenesis, or complications.
- Expert Support: Our experienced scientific team offers full support throughout your project, from experimental design and model selection to data analysis, ensuring successful outcomes.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What are the key advantages of using the ZDF rat model for Type II Diabetes research?
A: The ZDF model closely mimics human Type II Diabetes, especially in terms of obesity-induced insulin resistance and the development of related complications, making it ideal for drug testing.
-
Q: How long does it take for ZDF rats to develop diabetes?
A: ZDF rats typically develop diabetes around 10–12 weeks of age, making it suitable for both short- and long-term studies.
-
Q: Can your models be used to study diabetic complications like nephropathy or cardiovascular disease?
A: Yes, the ZDF model is excellent for studying diabetic complications, including kidney damage and cardiovascular dysfunction, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of potential therapies.
-
Q: Do you offer any post-study services or follow-up support?
A: Yes, we provide post-study support, including data analysis and reporting services, ensuring that your findings are thoroughly analyzed and documented for publication or further research.
Published Data
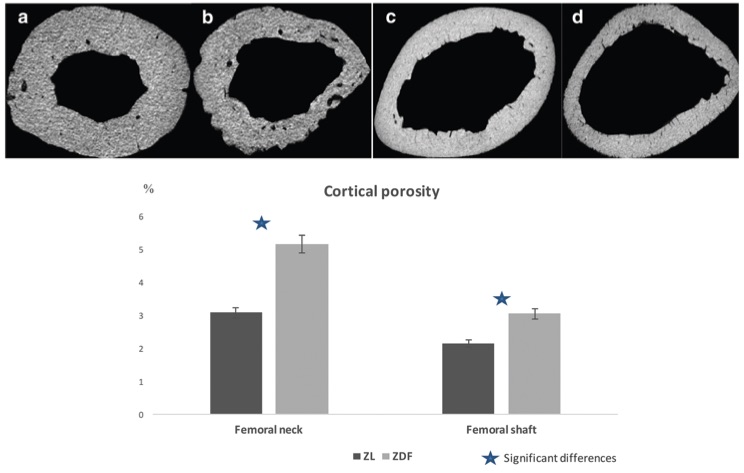 Fig. 1 Comparison of cortical porosity between a Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat and a Zucker lean ZL rat.1
Fig. 1 Comparison of cortical porosity between a Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat and a Zucker lean ZL rat.1
To investigate bone fragility in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and assess the role of microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) in evaluating bone microarchitecture and vascularization, we conducted an in vitro preliminary study using femurs from Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats and Zucker lean (ZL) rats. The study focused on comparing cortical porosity between the two groups. Micro-CT axial images of the femoral neck and femoral shaft were obtained for both ZL and ZDF rats. As shown in the images, cortical porosity was significantly higher in the ZDF rats compared to the ZL rats at both the femoral neck and shaft locations. These findings highlight the increased bone fragility associated with diabetes and demonstrate the utility of micro-CT in assessing changes in bone microarchitecture in diabetic models.
Reference
- Zeitoun, David et al. "Microcomputed tomography of the femur of diabetic rats: alterations of trabecular and cortical bone microarchitecture and vasculature-a feasibility study." European radiology experimental vol. 3,1 17. 11 Apr. 2019, DOI:10.1186/s41747-019-0094-5. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
