- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
Diabetic Complication Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Diabetic complications represent a severe and growing public health challenge, stemming from prolonged hyperglycemia and metabolic dysregulation. These conditions can lead to debilitating outcomes such as diabetic cardiomyopathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy, significantly impacting patient quality of life and imposing immense healthcare costs. Developing effective therapeutic strategies requires a deep understanding of these complex disease mechanisms.
Creative Biolabs, leveraging extensive expertise, provides a comprehensive suite of well-established rodent models for the rigorous evaluation of novel therapies targeting these complications.
Available Diabetic Complication Models at Creative Biolabs
Role and Importance of Diabetic Complication Models
Diabetic complication models are fundamental for advancing research into diabetic complications, providing a controlled and reproducible environment to unravel the intricate molecular and cellular pathways driving disease progression, from initial metabolic disturbances to organ-specific damage. They are indispensable for identifying and validating novel therapeutic targets, serving as crucial platforms for preclinical efficacy and safety testing of potential drug candidates. Additionally, longitudinal studies in these models offer invaluable insights into the natural history of complications and the impact of interventions over time.
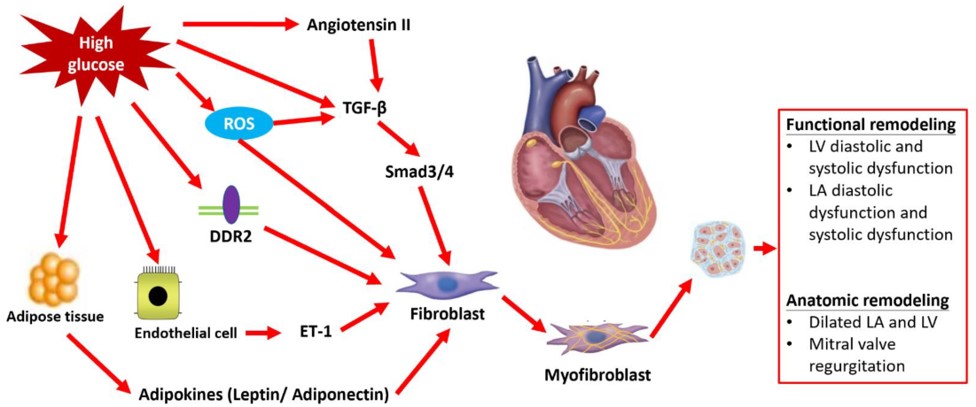 Fig.1 Pathologic myocardial fibrosis of diabetic cardiomyopathy.1,3
Fig.1 Pathologic myocardial fibrosis of diabetic cardiomyopathy.1,3
Methods and Strategies for Model Construction
Creative Biolabs employs diverse strategies to construct rodent diabetic complication models, each carefully chosen to recapitulate specific aspects of human disease:
Genetic Models: These models, such as the db/db mouse or Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rat, spontaneously develop Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) and associated complications due to inherent genetic mutations (e.g., leptin receptor deficiency). They are highly valuable for investigating long-term complications and genetic predispositions.
Chemically-Induced Models: The streptozotocin (STZ)-induced model is widely utilized. STZ selectively targets pancreatic beta cells, leading to their destruction and inducing type 1 diabetes (T1D) or severe T2D phenotypes depending on the dosage. These models offer high reproducibility and are extensively used for both acute and chronic complication studies.
Diet-Induced Models: High-fat diet (HFD) or high-fat/high-sucrose diet models are employed to induce insulin resistance, obesity, and subsequent T2D, closely mimicking the metabolic syndrome seen in humans. These are particularly effective for studying complications linked to metabolic dysfunction, inflammation, and cardiovascular issues.
Combined Models: Often, a combination of genetic factors and dietary interventions is used to create more nuanced and clinically relevant models that better reflect the multifactorial etiology of human diabetic complications, providing a robust platform for complex research questions.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs' state-of-the-art evaluation platform integrates a wide array of biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and advanced imaging instruments and tests. Our comprehensive assessment includes:
- Metabolic Parameters: Blood glucose, insulin, HbA1c, lipid profiles, glucose tolerance tests.
- Cardiac Function: Echocardiography (E/A ratio, LV mass, ejection fraction), hemodynamic measurements.
- Renal Function: Albuminuria/proteinuria, creatinine clearance, BUN, kidney weight/histology.
- Vascular Function: Endothelial-dependent vasodilation, arterial stiffness.
- Neuropathy Assessment: Nerve conduction velocity, thermal/mechanical sensitivity, motor coordination.
- Ocular Assessment: Retinal imaging, fundus photography, electroretinography.
- Histopathology: H&E staining, Masson's trichrome (fibrosis), immunohistochemistry for specific markers.
- Molecular Analysis: Gene expression (RT-qPCR), protein expression (Western blot, ELISA), oxidative stress markers.
Applications
Disease Simulation: These models accurately simulate various human diabetic complications, including diabetic cardiomyopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and peripheral vascular disease, enabling detailed mechanistic studies.
Drug Evaluation: They are routinely used for the preclinical evaluation of novel therapeutic agents, including anti-diabetic drugs, anti-inflammatory compounds, anti-fibrotic agents, antioxidants, and compounds targeting specific organ damage pathways.
Treatment Modality Assessment: Our platforms support the assessment of diverse treatment modalities, encompassing pharmacological interventions, gene therapies, cell-based therapies, and the impact of lifestyle modifications on complication progression and reversal.
Related Cardiovascular Models
Our Advantages
- Multiple Animal Species: Offering a wide selection of well-characterized mouse and rat strains to best suit specific research objectives.
- One-Stop In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluation: Providing integrated services from model selection and establishment to comprehensive phenotyping and data analysis.
- Professional Team and Complete Management System: Our highly experienced scientists and robust quality management systems ensure the highest standards of experimental rigor and data integrity.
Work with Us
Inquiry Stage
Project Start
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
Project Progress
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
Project Completion
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
After-Sales Support
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs's two decades of expertise and advanced modeling platforms to accelerate your research into diabetic complications. Our commitment to scientific excellence ensures reliable and translatable data for your therapeutic development. Contact us today to discuss your specific research needs and how we can support your next breakthrough.
FAQs
-
Q1: How do I choose the most appropriate rodent model for my specific diabetic complication research?
A: Selecting the ideal model depends heavily on your research focus, whether it's Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, the specific complication of interest (e.g., nephropathy, cardiomyopathy), and the stage of disease you wish to study. Our scientific team offers detailed consultations to guide you through the various genetic, chemically-induced, and diet-induced models, ensuring the chosen model aligns perfectly with your experimental goals.
-
Q2: What are the key differences between STZ-induced and diet-induced diabetic models?
A: STZ-induced models typically mimic T1D by destroying pancreatic beta cells, leading to severe insulin deficiency and hyperglycemia. Diet-induced models, often involving high-fat diets, induce insulin resistance and obesity, closely resembling Type 2 diabetes. Each model presents distinct metabolic profiles and complication development patterns, making them suitable for different research questions.
-
Q3: Can you help with custom model development if standard models don't fit my needs?
A: Absolutely. While we offer a wide array of established models, our expertise extends to developing custom models tailored to unique research requirements. This might involve specific genetic modifications, combined induction methods, or specialized dietary interventions to create a model that precisely reflects your experimental objectives.
-
Q4: What is the typical sample size for studies using these models?
A: Sample size determination is a critical aspect of study design, influenced by the variability of the chosen model, the expected effect size of the intervention, and statistical power requirements. Our biostatisticians can assist in calculating the appropriate sample size to ensure your study is adequately powered to detect statistically significant differences, maximizing the robustness of your findings.
-
Q5: Can I get real-time updates on my study's progress?
A: Yes, Creative Biolabs is committed to transparent communication. We provide regular updates on your study's progress, including interim data reports and scheduled meetings with our project managers and scientific leads. Our goal is to keep you fully informed every step of the way, ensuring a collaborative and efficient research partnership.
-
Q6: How do you ensure the reproducibility of results from these models?
A: Reproducibility is paramount to our operations. We achieve this through stringent standardization of our animal models, meticulously controlled environmental conditions, consistent experimental protocols, and rigorous quality control measures. Our experienced technicians and scientists follow validated procedures, ensuring the reliability and consistency of your research outcomes.
Published Data
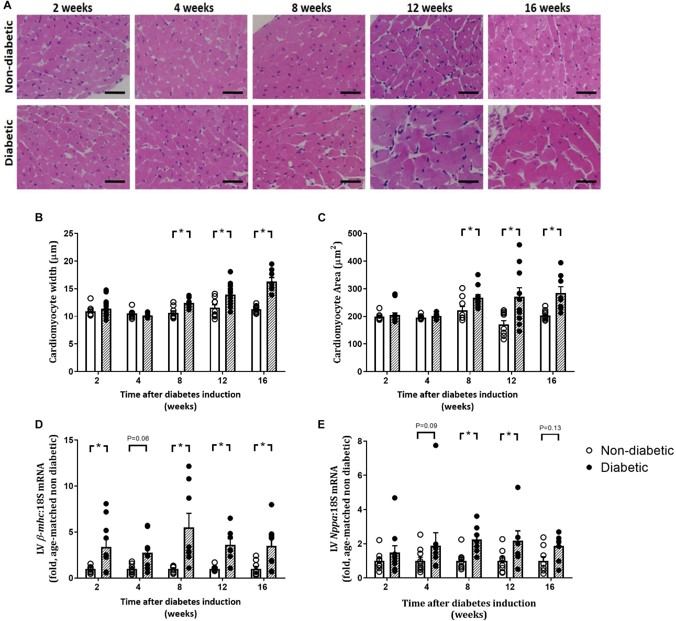 Fig.2 Progression of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.2,3
Fig.2 Progression of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.2,3
In this study, researchers utilized a STZ-induced T1D mouse model (FVB/N strain) to meticulously track the time course of diabetic cardiomyopathy development over 16 weeks. They observed significant elevations in blood glucose and HbA1c by two weeks, followed by a decline in left ventricular diastolic function (reduced E/A ratio) from four weeks onward. This comprehensive study elucidated the progression of cardiac dysfunction and identified multiple contributing pathways at various time points, providing critical insights for therapeutic intervention strategies. This work underscores the power of well-characterized rodent models in dissecting complex disease progression.
References
- Pan, Kuo-Li et al. "The Role of Cardiac Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Diagnostic Tools." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 24,10 8604. 11 May. 2023, doi:10.3390/ijms24108604.
- De Blasio, Miles J et al. "Defining the Progression of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in a Mouse Model of Type 1 Diabetes." Frontiers in physiology vol. 11 124. 20 Feb. 2020, doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00124.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
