- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
Myocardial Infarction Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs has been at the forefront of preclinical drug development, leveraging profound expertise to offer a comprehensive suite of well-established and highly predictive MI models. These models are meticulously designed to empower researchers in accurately evaluating the efficacy of drug therapies and fostering a deeper understanding of MI pathogenesis.
Introduction
Myocardial Infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, stands as a critical global health challenge, driving significant morbidity and mortality. This acute cardiac event, characterized by damage to the heart muscle and subsequent pathological remodeling, necessitates the development of innovative therapeutic strategies.
Available Myocardial Infarction Models at Creative Biolabs
Robust experimental models are foundational to deciphering the intricate mechanisms underlying MI and evaluating the efficacy of potential therapeutic agents. The careful selection and meticulous construction of these models are paramount to generating translatable data that truly reflects human pathology. Creative Biolabs specializes in developing and implementing models that provide controlled, reproducible environments for studying acute cardiac injury, chronic remodeling, and various interventional strategies. Our approach to model construction ensures relevance to specific research questions, from detailed molecular analysis in in vitro systems to comprehensive functional assessment in in vivo preclinical settings.
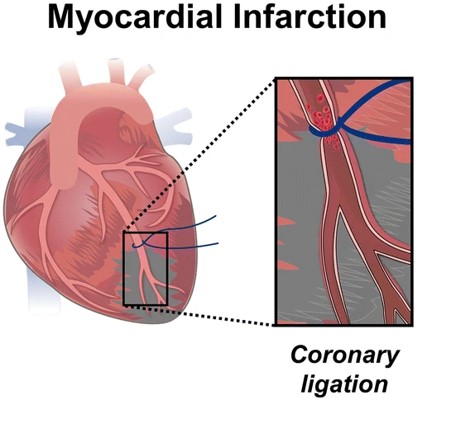 Fig.1 Illustration of MI model.1,4
Fig.1 Illustration of MI model.1,4
We provide the following acute and chronic MI models, each meticulously established and validated to meet the highest scientific standards:
-
Ischemia-Reperfusion (I/R) Myocardial Infarction Model
- Modeling: This model is induced by transient ligation of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery, followed by reperfusion. It precisely mimics the clinical scenario of an MI followed by angioplasty, making it indispensable for studying reperfusion injury, infarct size limitation, and early cardiac remodeling. Our refined surgical techniques ensure consistent duration of ischemia and controlled reperfusion.
- Animal species: Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Dog, NHPs.
-
Permanent Ischemic Myocardial Infarction Model
- Modeling: Achieved through permanent ligation of the LAD coronary artery, this model creates a sustained, larger infarction. It is ideally suited for investigating long-term post-infarction remodeling, chronic heart failure progression, and the efficacy of therapies aimed at scar reduction or cardiac regeneration over extended periods. We employ advanced surgical protocols to maximize animal survival and model reproducibility.
- Animal species: Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Dog, NHPs.
-
Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction Model
- Modeling: This non-surgical model involves administering a chemical agent (isoproterenol) to induce acute myocardial damage. It offers advantages such as lower mortality rates and a simpler experimental procedure, making it valuable for initial screening of cardioprotective compounds and studies focusing on broad myocardial injury and repair mechanisms.
- Animal species: Mouse
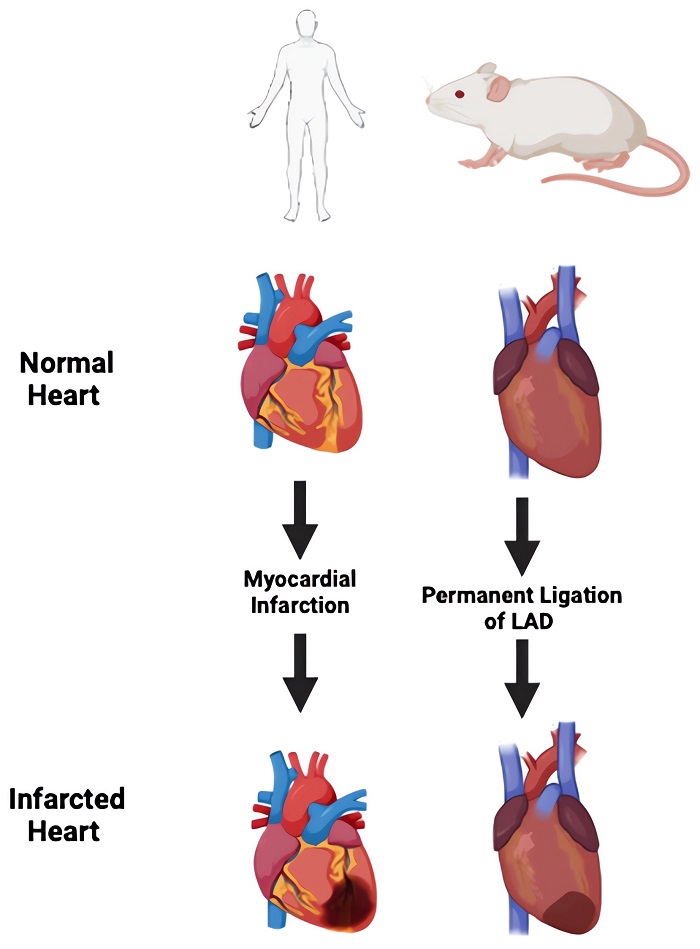 Fig.2 Injury models in the mouse model to mimic MI.2,4
Fig.2 Injury models in the mouse model to mimic MI.2,4
Evaluation Platform
Our state-of-the-art evaluation platform integrates a wide array of biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and imaging techniques to provide a holistic understanding of MI progression and therapeutic efficacy. We employ advanced instruments and validated assays to capture critical endpoints. These assessments include but are not limited to:
- Biochemical: Serum cardiac enzymes (e.g., troponin I, CK-MB), inflammatory markers (e.g., cytokines), oxidative stress markers.
- Molecular: Gene expression (RT-qPCR), protein expression (Western blot, ELISA) related to remodeling, inflammation, and survival pathways.
- Cellular: Flow cytometry for immune cell infiltration, cardiomyocyte viability assays.
- Histopathological: Infarct size determination (e.g., TTC staining), fibrosis quantification (e.g., Masson's trichrome), cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, capillary density, and accurate assessment of cardiac rupture via systematic serial sectioning.
- Imaging & Functional Assessment: Echocardiography (e.g., ejection fraction, fractional shortening, LV dimensions), pressure-volume loop analysis (e.g., dP/dt max/min), electrocardiogram (ECG) for immediate MI confirmation (e.g., ST segment elevation) and arrhythmia analysis.
Applications
Simulating Diseases: Precisely simulating acute MI, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and chronic heart failure, encompassing cardiac remodeling and arrhythmias. This enables in-depth investigation of disease mechanisms and identification of critical intervention windows.
Evaluating Drugs: Rigorously evaluating a broad spectrum of therapeutic agents, including cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and pro-angiogenic compounds designed to limit injury, mitigate adverse responses, prevent scar formation, and restore blood supply. We also assess anti-remodeling agents.
Assessing Treatments: Assessing advanced interventions such as stem cell, gene, and exosome-based therapies, along with novel medical devices, all aimed at comprehensive cardiac repair and functional restoration.
Related Cardiovascular Models
Our Advantages
- Extensive Species Diversity: Access to a wide range of animal species, including various rodent strains and large animal models, for optimal research translation.
- Integrated One-Stop Solutions: Comprehensive in vivo and in vitro evaluation capabilities, offering seamless progression from early discovery to preclinical validation.
- Expert Team & Quality Systems: A highly professional team of experienced biologists and veterinarians, supported by a perfect quality management system, ensures rigorous study design and execution.
Work with Us
Inquiry Stage
Project Start
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
Project Progress
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
Project Completion
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
After-Sales Support
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Partnering with us means gaining access to unparalleled expertise in MI models. Let our dedicated team and advanced platforms accelerate your discoveries. Contact us today to discuss your specific research needs.
FAQs
-
Q1: How do you ensure the reproducibility of your MI models?
A: We prioritize model consistency. We achieve high reproducibility by adhering to stringent standardized operating procedures, employing highly trained surgical teams, and utilizing robust internal validation methods, including physiological and biochemical confirmation of MI induction, such as ECG changes and enzyme levels.
-
Q2: Can you customize the MI model to fit my specific research question?
A: Absolutely. Our approach is highly flexible. We work closely with each client to understand their unique objectives, enabling us to tailor parameters like ischemia duration, reperfusion protocols, and animal strain selection to precisely match the demands of their study.
-
Q3: Can you perform studies on both acute and chronic phases of MI?
A: Yes, our expertise spans both acute and chronic phases of MI. We design studies to investigate immediate post-ischemic injury responses, as well as long-term cardiac remodeling, fibrosis, and functional deterioration, providing comprehensive insights into the disease continuum.
-
Q4: How do you manage potential challenges like high mortality rates in surgical models?
A: We mitigate potential mortality risks through highly refined surgical techniques, extensive pre- and post-operative care protocols, and continuous monitoring of animal health. Our experienced surgical teams are adept at minimizing invasive impact, leading to superior survival rates and more robust data.
-
Q5: What measures do you take to ensure the translational relevance of your models?
A: We meticulously select models that best recapitulate key aspects of human MI pathophysiology, such as the use of reperfused models to mimic clinical interventions. We also integrate human-derived cellular models where appropriate, aiming to bridge the gap between preclinical findings and clinical applicability.
-
Q6: Can you assist with subsequent in vitro or molecular analyses based on in vivo findings?
A: Absolutely. Our integrated capabilities mean we can seamlessly transition from in vivo studies to follow-up in vitro or molecular analyses. This includes cell culture assays, gene expression profiling, proteomics, and advanced histological staining, providing a deeper mechanistic understanding of your observed in vivo effects.
Published Data
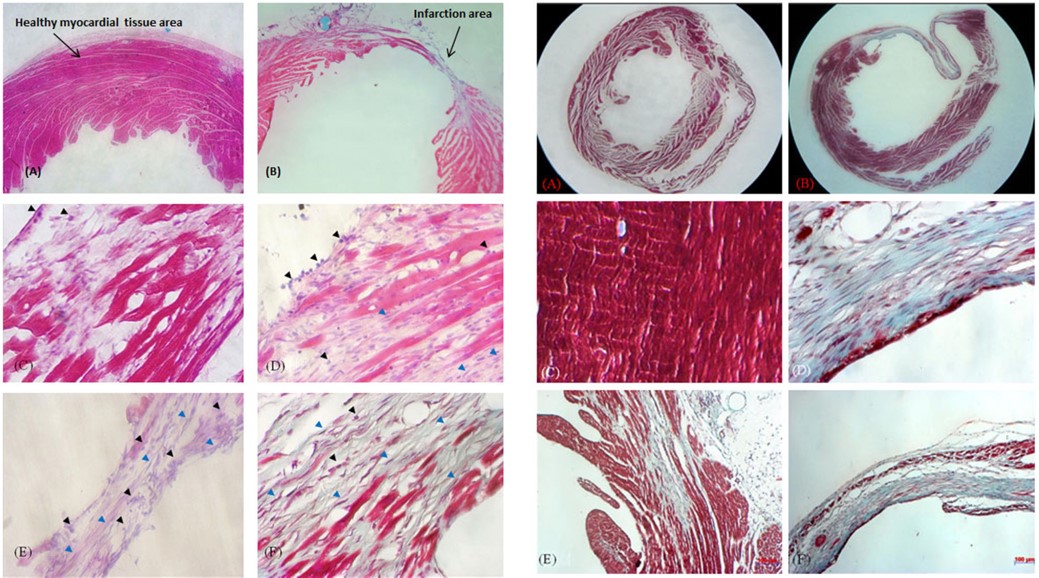 Fig.3 Histopathology analysis of mouse model for myocardial injury.3
Fig.3 Histopathology analysis of mouse model for myocardial injury.3
In a study establishing a reproducible mouse model for myocardial injury induced by ischemia, researchers successfully created a model via LAD ligation. This model was then effectively utilized to evaluate the potential of novel therapies for heart disease, including new drug development and cell therapy, demonstrating its versatility and utility in preclinical studies. Histopathological assessments further confirmed the myocardial damage and cell death, validating the model's effectiveness for therapeutic evaluation.
References
- Lai, Shih-Lei et al. "Immune responses in cardiac repair and regeneration: a comparative point of view." Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS vol. 76,7 (2019): 1365-1380. DOI:10.1007/s00018-018-2995-5.
- Kar, Riya, Debabrata Mukhopadhyay, and Ramcharan Singh Angom. "Progress in disease modeling for myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease: bridging in vivo and in vitro approaches." Hearts 5.4 (2024): 429-447. DOI: 10.3390/hearts5040031.
- Pham, T., Nguyen, D., Nguyen, O., Nguyen, T., & Pham, P. (2014). Mouse model for myocardial injury caused by ischemia. Biomedical Research and Therapy, 1(05), 152-166. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. DOI: 10.7603/s40730-014-0023-4.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
