Acetylcholine induced Atrial Fibrillation Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) stands as the most prevalent sustained cardiac arrhythmia globally, significantly elevating risks of stroke, heart failure, and mortality. Its complex and diverse underlying mechanisms present substantial challenges for developing effective and safe therapeutic interventions.
Recognizing this critical need, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of well-established preclinical models, including the acetylcholine-induced AF model, specifically designed to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of novel antiarrhythmic strategies.
Acetylcholine-Induced AF Model
The acetylcholine (ACh)-induced AF model is a highly valuable and physiologically relevant preclinical tool, specifically engineered to mimic forms of human AF driven by increased vagal tone, such as paroxysmal or vagally-mediated AF. This model precisely recapitulates the electrophysiological conditions observed during parasympathetic activation, making it ideal for dissecting the intricate pathophysiology of AF and for the robust evaluation of novel antiarrhythmic compounds, particularly those targeting ion channels or autonomic modulation.
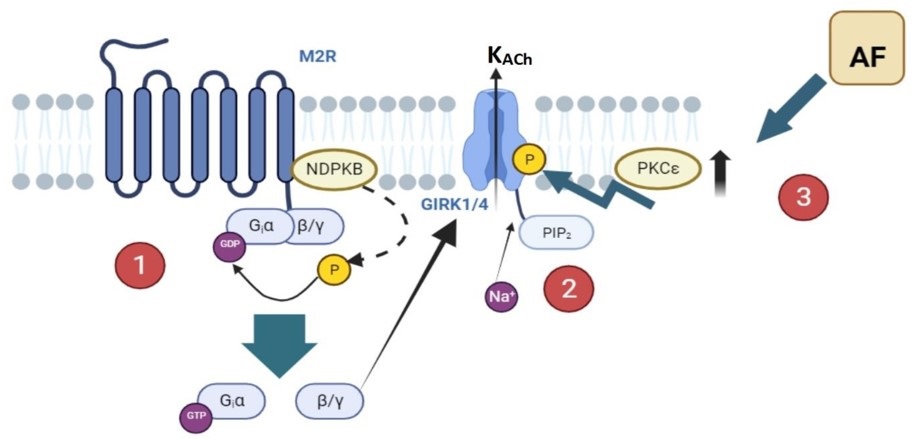 Fig.1 Regulation mechanisms of constitutive KACh in AF.1,3
Fig.1 Regulation mechanisms of constitutive KACh in AF.1,3
Model Construction Steps
The core strategy for constructing this model involves the exogenous administration of ACh, often in combination with calcium chloride, to induce a controlled and reproducible arrhythmogenic substrate. This approach reliably shortens atrial refractoriness and promotes electrical heterogeneity, facilitating the onset of AF.
01Animal Preparation
Rodents, commonly rats or mice, are anesthetized to ensure stability and minimize stress throughout the procedure.
02Surgical Access
A catheter is carefully inserted into a peripheral vein, such as the jugular vein, to allow for precise intravenous infusion of pharmacological agents.
03Electrophysiological Monitoring
Electrocardiogram (ECG) leads are meticulously positioned to continuously record cardiac electrical activity, enabling real-time detection and characterization of arrhythmias.
04ACh Infusion
Acetylcholine, often accompanied by calcium chloride (ACh-CaCl2) to enhance arrhythmogenicity and ensure consistent AF induction, is infused intravenously at a controlled rate and concentration.
05AF Induction and Assessment
The onset and duration of AF episodes are meticulously monitored via ECG. Programmed electrical stimulation (PES) may also be employed to confirm AF inducibility and assess the stability of the arrhythmogenic substrate.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- Physiological Relevance: Accurately mimics vagally-mediated and paroxysmal AF in humans, providing a strong translational link.
- High Reproducibility: Offers excellent experimental control, allowing for consistent and repeatable AF induction, crucial for reliable drug screening.
- Responsiveness to Drugs: Demonstrates predictable responses to known antiarrhythmic agents, validating its utility for novel compound evaluation.
- Integration with Remodeling: Can be combined with models of atrial fibrosis to study the interplay between electrical and structural remodeling, as demonstrated by studies showing exacerbated AF in fibrotic atria.
Limitations:
- Acute Nature: Primarily an acute model, which may not fully capture the complexities of chronic or persistent AF unless combined with long-term remodeling interventions.
- Species Differences: Physiological variations in vagal innervation and atrial electrophysiology across species may influence direct translatability.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs' state-of-the-art evaluation platform is equipped with advanced instrumentation for comprehensive analysis of antiarrhythmic efficacy and underlying mechanisms. We integrate a range of biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and imaging techniques to provide a holistic understanding of drug effects.
Key Test Indicators:
- Electrophysiological Parameters: AF inducibility, AF duration, atrial action potential duration (APD), effective refractory period (ERP), conduction velocity, and dispersion of refractoriness.
- Histopathological Assessments: Quantification of atrial fibrosis (e.g., collagen I, collagen III, TGF-β1, CTGF, fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin), inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Molecular Analysis: Gene and protein expression levels of ion channels (e.g., KCNJ3/5 for IK,ACh), fibrosis markers, and relevant microRNAs (e.g., miR-101a-3p, EZH2).
- Cellular Electrophysiology: Patch-clamp studies on isolated atrial cardiomyocytes to assess specific ion currents (e.g., IK,ACh) and action potential characteristics.
- Cardiac Imaging: Echocardiography for assessment of atrial size, function, and overall cardiac morphology.
Applications
- Diseases Simulation: Primarily used to simulate paroxysmal AF, vagally-mediated AF, and AF exacerbated by underlying atrial fibrosis and remodeling.
- Drugs Evaluation: Ideal for assessing the efficacy of traditional antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., Class I, II, III, IV agents), novel compounds targeting the IK,ACh channel, autonomic nervous system modulators, and anti-fibrotic therapies.
- Treatment Modalities: Applicable for evaluating pharmacological interventions, as well as exploring the impact of non-pharmacological strategies like specific exercise regimens on AF susceptibility and progression.
- Mechanistic Studies: Provides a robust platform for unraveling the precise molecular and cellular mechanisms contributing to AF initiation and perpetuation.
- Target Validation: Essential for validating novel molecular targets implicated in the pathogenesis of vagally-mediated AF and its associated remodeling.
Related Atrial Fibrillation Models
Our Advantages
- Customized Solutions: We design bespoke study protocols meticulously tailored to your unique research objectives and compound characteristics.
- High-Quality Data: Our rigorous experimental protocols and quality control measures ensure the generation of robust, reproducible, and reliable data.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Integration of multi-omics approaches and advanced analytical techniques provides deep mechanistic insights.
- Accelerated Timelines: Our efficient project management and streamlined workflows are designed to expedite your discovery and development process.
- Expert Interpretation: Our seasoned scientific team provides insightful data interpretation and strategic guidance, translating complex results into actionable conclusions.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs stands as your premier partner in advancing AF research. By leveraging our profound expertise and the highly relevant ACh-induced AF model, we are committed to providing unparalleled services that guide your therapeutic development. We invite you to connect with our team to explore how our capabilities can accelerate your next breakthrough.
FAQs
-
Q1: Can this model be used to study the interplay between electrical and structural remodeling in AF?
A: Absolutely. While primarily an acute electrical model, it can be effectively combined with interventions that induce structural remodeling, such as chronic disease states leading to fibrosis. Our studies have shown that the arrhythmogenic effects of ACh are significantly enhanced in the presence of atrial fibrosis, making it a powerful tool to investigate therapies that target both electrical and structural components of AF.
-
Q2: How do you ensure the reproducibility and reliability of AF induction in this model?
A: Reproducibility is paramount at Creative Biolabs. We achieve this through stringent standardization of our experimental protocols, including precise titration of ACh concentrations, consistent routes of administration, and continuous, high-fidelity ECG monitoring. Our experienced scientists are trained to maintain consistent experimental conditions, ensuring the reliability of your study results.
-
Q3: Is it possible to evaluate compounds that target novel mechanisms beyond traditional ion channel blockade in this model?
A: Yes, definitely. The ACh-induced AF model is highly adaptable for exploring novel therapeutic mechanisms. For instance, recent research has utilized this model to investigate the role of microRNAs in regulating atrial fibrosis and their impact on AF susceptibility. This allows for the evaluation of compounds that modulate gene expression, anti-fibrotic pathways, or other non-traditional targets.
-
Q4: Can this model differentiate between compounds that prevent AF initiation versus those that terminate ongoing AF?
A: Yes, the model can be designed to assess both aspects. By carefully controlling the timing of compound administration relative to ACh infusion or programmed electrical stimulation, we can evaluate a drug's ability to prevent AF onset or to terminate an established episode of AF. This provides critical insights into the therapeutic potential of your compounds.
-
Q5: How do you account for potential proarrhythmic effects of test compounds in this model?
A: Assessing proarrhythmic risk is an integral part of our safety pharmacology evaluations. While primarily focused on antiarrhythmic efficacy, we meticulously monitor for any signs of proarrhythmia, such as prolonged QT intervals or the induction of ventricular arrhythmias, during the study. This comprehensive monitoring helps to characterize the overall safety profile of your compounds.
Published Data
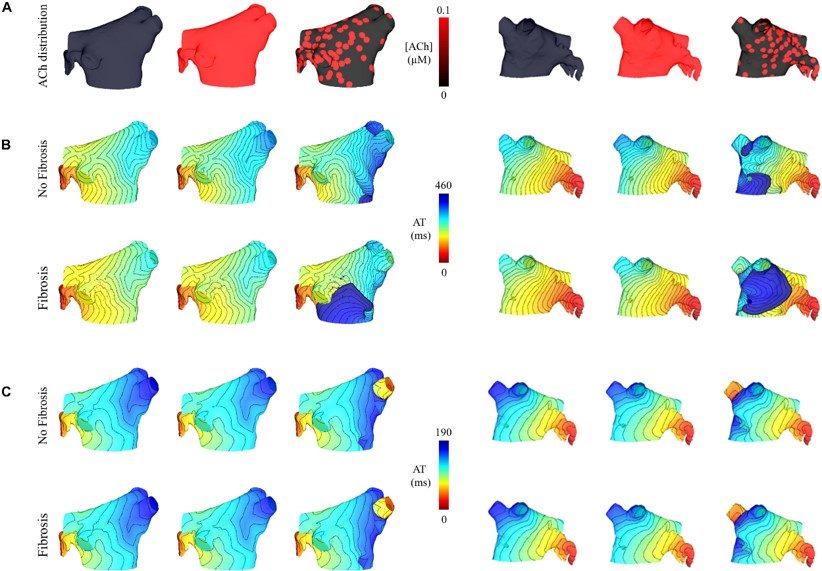 Fig.2 Effect of heterogeneous ACh in AF.2,3
Fig.2 Effect of heterogeneous ACh in AF.2,3
This research utilized computational, experimental, and clinical approaches to elucidate how ACh delays atrial activation, thereby facilitating AF, particularly in the context of interstitial fibrosis. The study revealed that ACh not only shortens APD but also significantly slows conduction, promoting unidirectional block and reentry in fibrotic atria. This comprehensive investigation underscored the critical interaction between vagal tone and structural remodeling in AF, validating the importance of models like the ACh-induced AF model for understanding complex disease mechanisms and identifying therapeutic targets.
References
- Mitrokhin, Vadim et al. "The Role of KACh Channels in Atrial Fibrillation." Cells vol. 13,12 1014. 10 Jun. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13121014
- Bayer, Jason D et al. "Acetylcholine Delays Atrial Activation to Facilitate Atrial Fibrillation." Frontiers in physiology vol. 10 1105. 4 Sep. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01105
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
