Allergic Rhinitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Allergic Rhinitis (AR) is a common chronic respiratory disease, and driven by IgE. Risk factors include genetics, urbanization, smoking, and obesity. The main pathological features are sneezing, runny nose, nasal itching, and nasal congestion. The prevalence exceeds 40% globally and is increasing year by year. Creative Biolabs' AR models can simulate acute and chronic allergic symptoms in humans to facilitate mechanism analysis and preclinical drug development, such as antibodies, receptor antagonists, and new therapies.
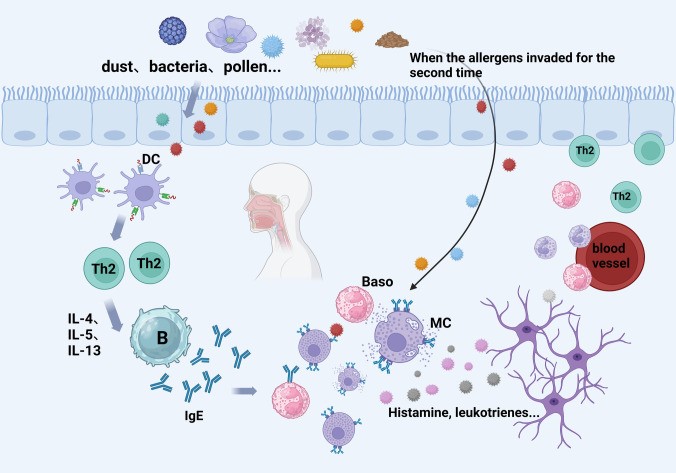 Fig.1 Pathogenesis of AR.1
Fig.1 Pathogenesis of AR.1
Available Allergic Rhinitis Models
With years of experience, we have two models with clear characteristics that are essential for allergic rhinitis development.
| Allergic Rhinitis Models | Simulates | Applicable Drug Evaluation Focus | Animal Species |
| OVA-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Model | Simulates Systemic IgE-mediated acute allergy, reflecting an allergic disposition. Often used for seasonal allergy or acute exacerbation research. | High-throughput screening: Such as Antihistamines (e.g., Cetirizine), Hormone/Corticosteroid Drugs (e.g., Budesonide), and agents targeting acute inflammatory signals. | Mouse, Rat, NHPs |
| HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Model | Simulates Perennial Allergic Rhinitis induced by a natural aeroallergen. | Preclinical efficacy verification: Targeted Therapeutic Drugs (e.g., Anti-IgE antibody Omalizumab or anti-cytokine biologics), and Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) (e.g., sublingual or subcutaneous immunotherapies). | Mouse, Guinea Pig, NHPs |
Evaluation Platform
We guarantee premium service quality by using precise methods and advanced instruments for in-depth indicator analysis.
- Behavioral Analysis: High-definition cameras and specialized software are used for quantitative measurement of sneezing and nasal rubbing counts, assessing drug efficacy and clinical relevance against acute symptoms.
- Molecular Biology Detection: Western blot, qPCR, and gene sequencing are used for in-depth analysis of inflammatory signaling activation, evaluating compound influence on genetic and protein-level inflammatory mechanisms (e.g., mitochondrial function).
- Immunology Analysis: ELISA, MSD, and flow cytometry are used for precise measurement of total/specific IgE, key TH2 cytokines, and immune cell ratios, reflecting the intensity and type of the allergic immune response.
- Histopathology: H&E, PAS, and immunohistochemistry are used for morphological analysis and quantification of inflammatory/secretory cells (e.g., eosinophils, mast cells), assessing compound effects on tissue inflammation.
- Cell Biology: Various cell models (e.g., epithelial, dendritic, and mast cells) are used for high-throughput screening, in vitro mechanistic studies, and evaluating compound effects on specific cellular functions.
- Imaging: Confocal microscopy and Micro-CT are used for high-resolution observation of subcellular structure and 3D quantitative analysis of sinus structure, providing morphological and structural evidence.
Applications
- Disease Mechanism Research: These models provide a controlled in vivo platform for cellular and molecular analysis of AR pathogenesis. They mainly investigate allergen-driven TH2 differentiation, the release and nerve activation by inflammatory mediators, and the basis of nasal barrier dysfunction.
- Drug Screening and Efficacy Testing: AR models serve as the core platform for evaluating the efficacy of all novel and existing anti-allergic drugs, including antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and leukotriene antagonists.
- Development of Novel Therapies: AR models are crucial for validating innovative immunotherapies. They also serve as in vivo platforms for optimizing allergy vaccines, adjuvants, and gene/cell-based immune modulation.
Our advantages
- Extensive Model Library: We offer a wide range of AR animal models to meet diverse research needs. For example, classic models can simulate AR pathologies triggered by various allergens, and genetic engineering models are used to investigate the role of specific genes in AR pathogenesis.
- High Model Stability: We rigorously control the sensitization and challenge procedures to ensure consistency across different experimental batches and the stability of the models.
- Innovative Capabilities: We continuously update and improve model and experimental methods, integrate the latest innovative achievements, scientific progress, and technologies.
- Customized Services: We provide flexible solutions to meet specific client requirements.
- Rapid Project Delivery: We are committed to completing projects within a reasonable timeframe and providing timely research reports to meet our clients' deadlines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: How do you assess the successful establishment of an allergic rhinitis model?
A: We evaluate success through several methods, including symptom scoring (e.g., sneezing frequency, nasal rubbing counts), IgE level determination, cytokine analysis, and histopathological analysis.
-
Q: What additional services does your company offer alongside these model studies?
A: In addition to providing the models and experimental services, we also offer customized experimental design, data analysis, pharmacodynamic evaluation, and research report writing.
-
Q: What are the advantages of genetically engineered models compared to wild-type models, and for which research scenarios are they suitable?
A: The primary advantage of genetically engineered models is their ability to precisely elucidate the function of specific genes. These models are particularly well-suited for target validation studies.
-
Q: During the model construction process, how do you prevent systemic allergic reactions caused by allergens?
A: Through protocol optimization, we effectively control the risk of systemic allergic reactions. This involves allergen dose gradient testing to prevent overdose and utilizing the classic intraperitoneal sensitization followed by intranasal challenge to limit systemic exposure. Continuous monitoring of animal status (e.g., body weight and activity) allows for prompt removal of severely affected individuals. Currently, under our standardized protocols, the incidence of systemic reactions is controlled to below 5%.
-
Q: Can you detect neurogenic inflammation indicators in AR models?
A: Yes, we can. We can detect neurogenic inflammation-related molecules in the nasal mucosa, such as the expression of Substance P (SP) and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP). We also assess the activity of ion channels like TRPV1 in the trigeminal ganglia. This helps in researching the mechanisms of neuro-immune interactions in AR sneezing symptoms.
Published Data
Luteolin inhibits inflammatory response in HDM-induced AR mice: In the AR model group, eosinophil infiltration in the nasal mucosa and mucus secretion were significantly increased. High-dose luteolin reduced both by approximately 60% and 50%, respectively.
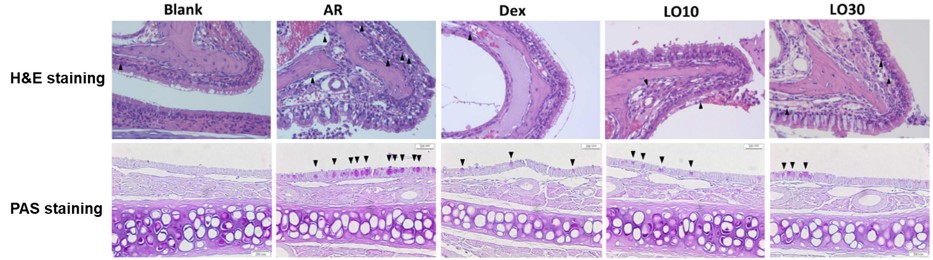 Fig.2 Hematoxylin and eosin staining (400×) of tissue sections and Periodic acid-Schiff staining of the nasal mucosa (400×).2
Fig.2 Hematoxylin and eosin staining (400×) of tissue sections and Periodic acid-Schiff staining of the nasal mucosa (400×).2
References
- Hao, Yan et al. "Multi-omics in Allergic Rhinitis: Mechanism Dissection and Precision Medicine." Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology vol. 68,1 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-025-09028-3. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Liang, Kai-Li et al. "Luteolin Attenuates Allergic Nasal Inflammation via Inhibition of Interleukin-4 in an Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model and Peripheral Blood From Human Subjects With Allergic Rhinitis." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 11 291. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00291. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, with modification.
For Research Use Only.
