High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate (HFHC) Diet induced Hyperlipidemia Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers various advanced animal models to evaluate the efficacy of hyperlipidemia treatments, providing tailored solutions based on your research needs. We help optimize drug development for hyperlipidemia and related cardiovascular conditions.
Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a medical condition characterized by elevated levels of lipids (fats) in the bloodstream, which is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke. There are two primary types of hyperlipidemia: primary and secondary. Primary hyperlipidemia is caused by genetic factors, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, where individuals have abnormally high cholesterol levels due to inherited mutations. Secondary hyperlipidemia is induced by lifestyle factors like poor diet, obesity, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease, leading to abnormal lipid profiles. Common lipid abnormalities include high levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides, which can accumulate in the arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. Symptoms are often not immediately noticeable, but over time, untreated hyperlipidemia can lead to serious health complications, including coronary artery disease and peripheral vascular disease. Management typically involves lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications, physical activity, and pharmacological therapies, including statins and fibrates.
Disease Models and Applications
The High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced Hyperlipidemia Model is commonly used to replicate the metabolic abnormalities seen in human hyperlipidemia. This model involves feeding rodents a diet rich in fats and carbohydrates to induce an imbalance in lipid metabolism. The resulting hyperlipidemia is characterized by elevated blood cholesterol, triglyceride levels, and insulin resistance. This model is valuable for studying the mechanisms underlying lipid accumulation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular diseases. Its advantages include cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation, but it may not perfectly mimic genetic forms of hyperlipidemia, which limits its application for studying hereditary causes of the disease.
- Simulates: The High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced Hyperlipidemia Model simulates hyperlipidemia and its associated complications, such as atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate various therapeutic interventions, including statins, fibrates, PCSK9 inhibitors, and natural compounds, for their efficacy in reducing cholesterol levels, improving lipid profiles, and mitigating cardiovascular risks.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced Hyperlipidemia Model, utilizing advanced technologies such as:
- General observations: Body weight, mortality rate, food intake, and stool consistency.
- Blood lipid profile: Measurement of total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels.
- Liver function tests: Serum levels of liver enzymes such as ALT, AST, and ALP.
- Inflammatory markers: Cytokine profiling (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) using ELISA.
- Histopathology: Liver and arterial tissue analysis for signs of fatty infiltration and atherosclerotic lesions.
- Gene/protein expression: RT qPCR and Western blot for analyzing the expression of genes related to lipid metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
In addition, our team is skilled in customizing models and providing tailored solutions for specific research needs, ensuring accurate data analysis at every stage.
Related Services
We also offer models induced by other methods, such as chemical agents or genetic modifications, to study hyperlipidemia. These approaches allow for more in-depth investigation of different pathways involved in lipid metabolism and cardiovascular disease progression.
Advantages
- Customization: We specialize in tailoring animal models and experimental designs to meet your specific research objectives, ensuring relevant and precise data.
- State-of-the-art Technology: We employ cutting-edge techniques, including advanced imaging, gene expression analysis, and bioinformatics, to enhance the quality of your studies.
- Comprehensive Support: From model development to post-study data analysis, our team provides end-to-end assistance, making the process smooth and efficient.
- Scientific Collaboration: We work closely with clients, offering expert consultation and guidance throughout the entire project lifecycle to ensure success.
- Reliable Results: Our rigorous quality control and data validation processes guarantee reliable and reproducible results, giving you confidence in your findings.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: How does the High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced Hyperlipidemia Model work?
A: The model involves feeding rodents a high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet to induce lipid imbalances and simulate human hyperlipidemia.
-
Q: What types of measurements can be taken in this model?
A: Measurements include blood lipid profiles, liver function tests, inflammatory markers, histopathology, and gene/protein expression.
-
Q: What diseases can be studied using this model?
A: This model simulates a range of conditions, including hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular complications.
-
Q: Can the model be used to evaluate natural compounds?
A: Yes, the model can be used to evaluate various drugs, including natural compounds, for their effects on lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health.
Published Data
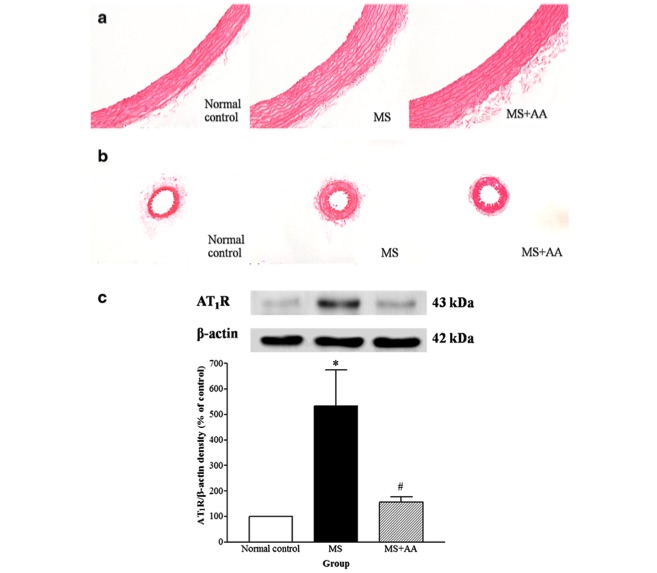 Fig. 1 Effects of asiatic acid on vascular remodeling and AT1 receptor protein expression in thoracic aorta.1
Fig. 1 Effects of asiatic acid on vascular remodeling and AT1 receptor protein expression in thoracic aorta.1
In a rat model of high high-carbohydrate, high-fat (HCHF) diet induced metabolic syndrome (MS), previous studies have suggested that asiatic acid may possess antihypertensive properties. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of asiatic acid on vascular structure, function, and the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in MS rats. Vascular wall hypertrophy was observed in both the aorta (Fig. 1a) and the mesenteric artery (Fig. 1b) of MS rats, with significant increases in vascular wall thickness, cross-sectional area (CSA), and lumen diameters compared to control rats. However, asiatic acid treatment did not reverse these vascular abnormalities in either the aorta or mesenteric artery. Additionally, there was an upregulation of AT1 receptor protein expression in the thoracic aorta of MS rats when compared to controls. In rats treated with asiatic acid, the overexpression of the AT1 receptor was normalized (p < 0.01; Fig. 1c).
Reference
- Maneesai, Putcharawipa et al. "Asiatic acid attenuates renin-angiotensin system activation and improves vascular function in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet fed rats." BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine vol. 16 123. 27 Apr. 2016, DOI:10.1186/s12906-016-1100-6. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
