High-Fat Diet (HFD) & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs provides a variety of well-established models to evaluate the efficacy of drugs targeting Type II Diabetic Nephropathy. These models are designed to simulate the disease's progression and enable reliable preclinical testing of potential therapeutic agents for kidney protection and metabolic control.
Introduction
Type II Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is a major complication of diabetes, characterized by progressive kidney damage that can lead to end-stage renal failure. It primarily occurs in patients with long-standing type II diabetes, where chronic hyperglycemia induces structural changes in the kidneys, such as glomerular hypertrophy, basement membrane thickening, and mesangial expansion. These changes contribute to impaired renal filtration and proteinuria, a hallmark of diabetic nephropathy. Over time, these alterations lead to kidney fibrosis, which further exacerbates renal dysfunction and can eventually result in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and genetic factors are also known to play key roles in the development and progression of DN. Early detection and intervention are critical to managing the disease and preventing the progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which may require dialysis or kidney transplantation. The pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy is complex, involving a combination of metabolic, inflammatory, and hemodynamic changes that affect the kidneys.
Disease Models and Applications
The High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy model is a widely used method for simulating diabetic nephropathy in rodents. In this model, mice or rats are first fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for several weeks to induce obesity and insulin resistance. Following this, streptozotocin (STZ) is administered to induce hyperglycemia, mimicking the pathophysiological features of Type II diabetes. This model develops key characteristics of diabetic nephropathy, including renal dysfunction, albuminuria, glomerular hypertrophy, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. It has the advantage of mimicking both the metabolic and renal changes seen in human Type II diabetic nephropathy. However, a limitation of this model is that it does not fully replicate the complexity of human kidney disease, especially in terms of the immune response and renal injury progression over time. Despite this, it is a reliable and cost-effective tool for drug testing and pathophysiological studies.
- Simulates: High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model simulates Type II diabetic nephropathy in rodents.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate drugs targeting diabetic nephropathy, particularly those aimed at improving insulin sensitivity, reducing blood glucose levels, decreasing inflammation, and preventing kidney fibrosis. Common drug classes assessed include antihypertensive agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and renal protective agents.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model, utilizing advanced techniques such as:
- General observations: body weight, renal function (serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen), albuminuria, and survival rate.
- Histopathological analysis: Renal tissue examination for glomerular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and tubular damage.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in kidney tissues.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot techniques for markers such as TGF-β, fibronectin, and collagen I, which are involved in fibrosis and inflammation.
- Renal biomarkers: Levels of kidney injury markers such as KIM-1, NGAL, and cystatin C.
Additionally, we provide expertise in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis to customize your project for maximum efficacy.
Related Services
In addition to the High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model, we offer a wide range of other diabetes complications models. These include diabetic retinopathy, cardiovascular complications, and neuropathy models, each designed to meet specific research requirements. We aim to provide comprehensive solutions for studying the multifaceted impacts of diabetes on the body.
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Cataract Model
- db/db Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
Advantages
- Expertise in Drug Evaluation: We specialize in providing high-quality, reliable preclinical models tailored to your specific research needs. Our team of experienced scientists ensures that every model is designed to offer valuable insights into drug efficacy and safety.
- Customizable Models: We offer a wide range of customizable disease models, including Type II Diabetic Nephropathy, to meet the unique requirements of your project. Whether it's adjusting experimental parameters or developing new models, we ensure your research is fully supported.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Our advanced technologies, including histopathology, cytokine profiling, and gene expression analysis, allow for accurate and comprehensive evaluations of therapeutic candidates.
- Comprehensive Support: From model selection to data analysis, we provide end-to-end scientific support, ensuring that your research project is optimized for success at every stage.
- Validated Models: Our models are based on the latest scientific literature and have been rigorously validated to ensure their relevance and reliability in simulating human diseases.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the purpose of using the High-Fat Diet & STZ induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model?
A: This model mimics the pathophysiological features of Type II diabetic nephropathy in rodents and is useful for evaluating potential therapeutic agents for treating diabetes-related kidney damage.
-
Q: How long does it take to develop diabetic nephropathy in this model?
A: It typically takes 8-12 weeks for the rodents to develop significant kidney damage after high-fat diet feeding and STZ administration.
-
Q: Can the model be used for testing drugs that target insulin resistance?
A: Yes, this model is widely used to evaluate drugs that target insulin resistance, kidney fibrosis, and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy.
-
Q: Do you offer customized models?
A: Yes, we offer customized models tailored to your specific research needs, including modifications to diet, drug dosing, and other experimental parameters.
Published Data
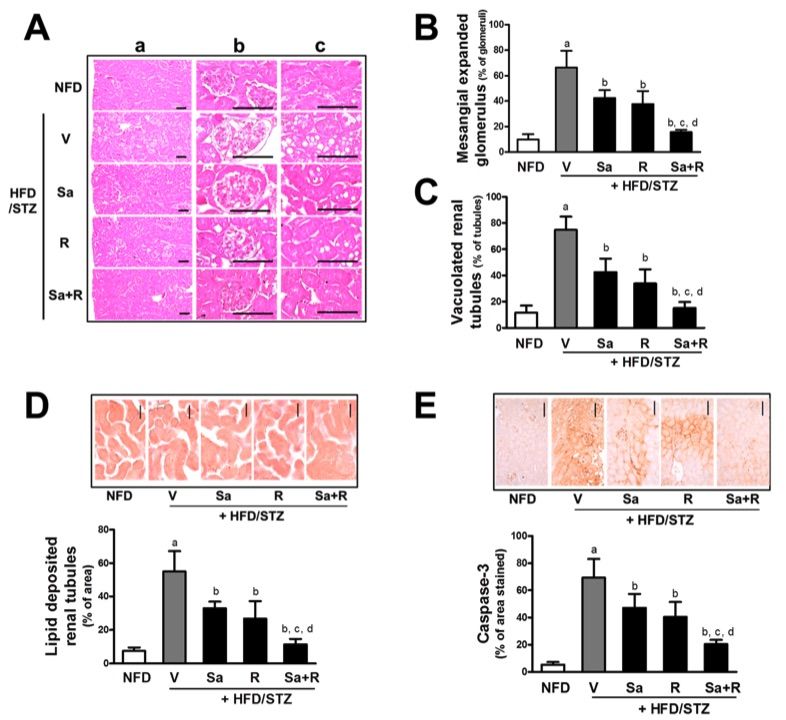 Fig. 1 Effects of sarpogrelate and rosuvastatin on histomorphological changes in HFD/STZ mice.1
Fig. 1 Effects of sarpogrelate and rosuvastatin on histomorphological changes in HFD/STZ mice.1
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by various renal structural alterations, such as glomerular and mesangial expansion, endothelial proliferation in the glomerulus, accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM), and tubular injury. Histopathological examination of renal tissues revealed significant glomerular structural changes, including enhanced glomerular vasodilation and mesangial expansion in the HFD/STZ group compared to the NFD group (Fig. 1A and 1B). Additionally, HFD/STZ mice exhibited a marked increase in vacuole or lipid droplet deposition within renal tubules (Fig. 1A, 1C, and 1D). These morphologic alterations were accompanied by elevated levels of caspase-3-reactive regions, a marker of tubular damage, in the HFD/STZ mice (Fig. 1E). Treatment with sarpogrelate or rosuvastatin significantly attenuated these histomorphometric and immunohistochemical changes. Notably, the combination of sarpogrelate and rosuvastatin exhibited an additive effect, improving all three parameters. These findings suggest that sarpogrelate and rosuvastatin effectively ameliorate nephropathy induced by HFD/STZ.
Reference
- Kim, Dong-Hyun et al. "Beneficial Effects of Sarpogrelate and Rosuvastatin in High Fat Diet/Streptozotocin induced Nephropathy in Mice." PloS one vol. 11,4 e0153965. 20 Apr. 2016, DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0153965. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
