Dexamethasone induced Sarcopenia Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established models to assess the efficacy of therapeutic interventions in sarcopenia research. These models help in evaluating potential drugs and understanding their effects on muscle preservation and restoration.
Introduction
Sarcopenia is a condition characterized by the progressive loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, primarily affecting older adults. It is often associated with aging but can also be influenced by other factors such as chronic diseases, hormonal imbalances, malnutrition, and physical inactivity. The condition leads to reduced mobility, frailty, and an increased risk of falls and fractures, significantly impacting the quality of life. Sarcopenia is typically diagnosed based on criteria such as muscle mass measurement, strength assessment, and physical performance tests. As the global population ages, sarcopenia has become a growing concern due to its prevalence and associated health risks. The underlying mechanisms of sarcopenia are multifactorial, involving changes in muscle protein turnover, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and hormonal alterations, particularly involving growth hormone, testosterone, and insulin-like growth factor (IGF). Understanding these processes is crucial for developing effective treatments to prevent or reverse muscle wasting.
Disease Models and Applications
The Dexamethasone induced Sarcopenia Model involves the administration of Dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid, to induce muscle wasting and simulate sarcopenia in rodents. This model has been extensively utilized to study the effects of glucocorticoids on muscle metabolism, leading to muscle atrophy, weakness, and a decrease in muscle protein synthesis. The process typically includes the administration of Dexamethasone over a period of several days or weeks, leading to notable changes in muscle mass, muscle fiber size, and functionality. This model is particularly advantageous for investigating the molecular mechanisms behind muscle atrophy, as well as for evaluating potential drug candidates that could mitigate or reverse muscle wasting. However, its major limitation lies in the fact that it is drug-induced, and the model does not fully mimic the complexity of age-related sarcopenia.
- Simulates: This model simulates muscle wasting due to glucocorticoid treatment, resembling aspects of sarcopenia in humans. It is primarily used to study glucocorticoid induced muscle atrophy and understand the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms that lead to muscle dysfunction.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is highly effective for evaluating drugs that target muscle preservation, anabolic agents, and anti-inflammatory therapies. Drugs such as selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), myostatin inhibitors, and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly tested for their potential to prevent or reduce muscle atrophy in this model.
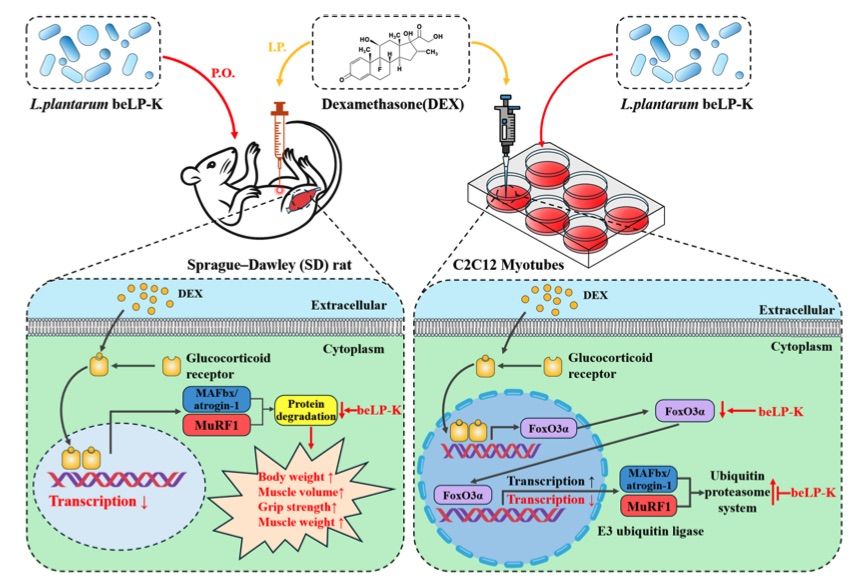 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the mechanisms of beLP-K in modulating sarcopenia in DEX- induced C2C12 myotubes and SD rats. 1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the mechanisms of beLP-K in modulating sarcopenia in DEX- induced C2C12 myotubes and SD rats. 1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in this model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General Observations: Muscle weight, body weight, grip strength, endurance, and overall activity levels.
- Histology: Muscle fiber morphology (e.g., cross-sectional area), muscle fiber types, and inflammatory cell infiltration in skeletal muscle.
- Biochemical Assays: Serum levels of muscle-related biomarkers, such as creatine kinase (CK), myostatin, and other myokines.
- Protein Expression Profiling: Western blot analysis to assess the expression of muscle-related proteins like myosin heavy chain, atrogin-1, and MuRF1.
- Gene Expression: qPCR to evaluate genes involved in muscle protein turnover, inflammation, and anabolic pathways.
- Functional Measurements: Grip strength, open field test for locomotor activity, and treadmill test to assess muscle endurance.
In addition to these standard assessments, we offer customization options based on specific research requirements, ensuring a tailored approach for each project.
Related Services
In addition to this model, other methods for inducing sarcopenia are available, including models based on fasting, denervation, or immobilization. These models provide various ways to simulate muscle wasting under different conditions. Our team will assist you in selecting the most appropriate model based on your specific research goals.
Advantages
- Comprehensive Expertise: Our team brings extensive experience in developing and optimizing sarcopenia models for diverse research needs.
- Tailored Approach: We offer flexible model configurations and customized study designs to address your unique research questions.
- High-Quality Data: Advanced technologies and robust measurement techniques ensure reliable and reproducible results.
- Broad Drug Evaluation: Evaluate a wide range of therapeutics, including novel biologics, small molecules, and regenerative medicine products.
- Collaborative Support: From model selection to data analysis, our scientific team provides hands-on guidance at every stage of your project.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What are the advantages of using this model?
This model closely mimics the effects of glucocorticoid induced muscle wasting, making it ideal for studying muscle atrophy and testing therapeutic interventions.
-
2. How long does it take to induce sarcopenia in this model?
Sarcopenia can be induced in rodents within 2-4 weeks of Dexamethasone administration, depending on the specific dosing regimen.
-
3. Can this model be used for long-term drug efficacy studies?
Yes, this model is suitable for both short-term and long-term studies, allowing researchers to evaluate the chronic effects of potential treatments.
-
4. Is this model applicable to human sarcopenia?
While it does not fully replicate age-related sarcopenia, it provides valuable insights into muscle atrophy and treatment options, especially for drug induced muscle loss.
Published Data
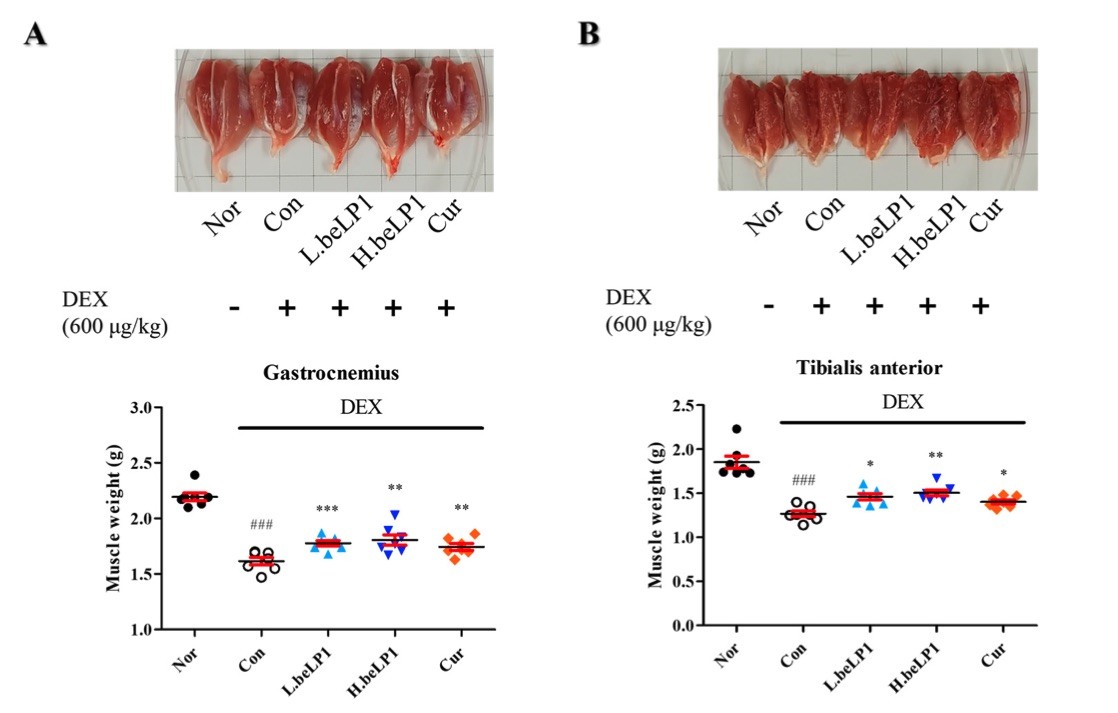 Fig. 2 Effects of the oral administration of beLP1 on the muscle weight of dexamethasone- induced sarcopenic rats.2
Fig. 2 Effects of the oral administration of beLP1 on the muscle weight of dexamethasone- induced sarcopenic rats.2
In this experiment, muscle mass was compared across different groups by isolating and weighing four major leg muscles: the gastrocnemius, tibialis anterior, soleus, and plantaris, following animal sacrifice. The results showed that the dexamethasone-only group (Con) exhibited a significant reduction in muscle weight compared to the normal control group (Nor). However, in the beLP1-treated groups, muscle weight loss was notably alleviated, suggesting that beLP1 has a protective effect against dexamethasone induced muscle atrophy (Figure 2).
References
- Moon, Juyeong et al. "Protective Efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum Postbiotic beLP-K in a Dexamethasone induced Sarcopenia Model." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 26,15 7504. 3 Aug. 2025, DOI:10.3390/ijms26157504. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Choi, Jinsu et al. "Heat-Killed Lactobacillus plantarum beLP1 Attenuates Dexamethasone induced Sarcopenia in Rats by Increasing AKT Phosphorylation." Biomedicines vol. 13,7 1668. 8 Jul. 2025, DOI:10.3390/biomedicines13071668. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
