Hepatitis B Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established rodent models to study hepatitis B, including models that replicate acute and chronic HBV infections, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Our models are ideal for evaluating therapeutic candidates targeting HBV replication, immune modulation, and liver protection. Our team provides comprehensive support throughout the research process, from study design to data interpretation.
Introduction
Hepatitis B (HBV) is a viral infection that attacks the liver, leading to both acute and chronic conditions. The disease is caused by the hepatitis B virus, which is primarily transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids. While many people clear the virus naturally, others may develop chronic infection, which can result in serious complications such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B is categorized into two main types: acute and chronic hepatitis B. Acute HBV is a short-term infection that often resolves without treatment, whereas chronic HBV lasts for more than six months and may require long-term management. Hepatitis B can be diagnosed through blood tests that detect the presence of HBV DNA and antibodies. The disease can also lead to various extrahepatic manifestations such as kidney disease and vasculitis. Vaccination is available and effective for preventing HBV infection, but there is currently no universal cure for chronic hepatitis B.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established rodent models for studying Hepatitis B (HBV), including models for acute and chronic HBV infection, liver fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These models are carefully designed to closely mimic human HBV progression, allowing for the in-depth study of viral dynamics, immune response, liver damage, and tumorigenesis. Our comprehensive evaluation techniques include monitoring HBV replication, assessing liver histopathology, and measuring inflammatory cytokines and serum biomarkers. These models are ideal for preclinical testing of antiviral therapies, immune modulators, and liver protection strategies. Our team of skilled scientists will assist you throughout your project, from model selection and experimental design to data analysis and interpretation, ensuring high-quality, reproducible results. To learn more about our Hepatitis B models and their application in preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Model | Simulated Disease | Drug Evaluation Focus | Animal species |
| AAV/HBV induced Chronic HBV Infection Model | Chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection, liver damage | Antiviral agents, immune modulators, liver protective agents, HBV surface antigen inhibitors | Mouse |
| HBV Transgenic Mouse Model | Chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection, liver fibrosis | Antiviral drugs, liver fibrosis inhibitors, immune response modulators | Mouse |
| Hydrodynamic Injection HBV Model | Chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection, viral replication | HBV DNA replication inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, liver regeneration therapies | Mouse |
| Hepatitis B Humanized Mouse Model | Human-like HBV infection and liver injury | Antiviral drugs, liver regeneration agents, immune modulators, HBV cure therapies | Mouse |
| Chronic Hepatitis B Woodchuck Model | Chronic Hepatitis B (Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus, WHV, similar to HBV) | Antiviral agents, immune response modulators, liver regeneration therapies, WHV vaccine candidates | Woodchuck |
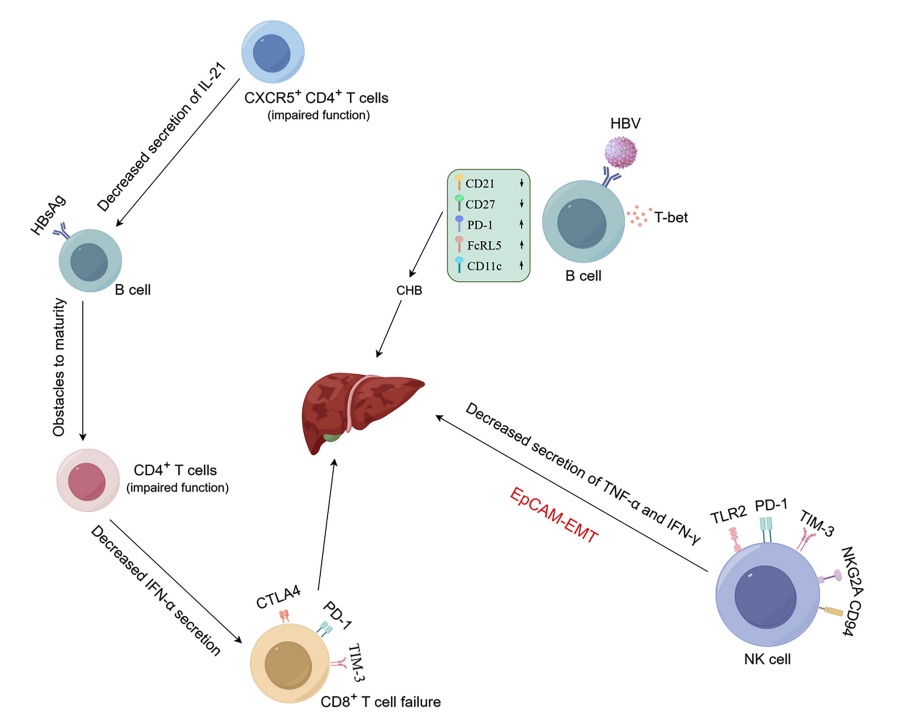 Fig. 1 Mechanisms of hepatitis B virus (HBV) involvement in liver disease.1
Fig. 1 Mechanisms of hepatitis B virus (HBV) involvement in liver disease.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent Hepatitis B models, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, mortality rate, liver enlargement, jaundice, and general health assessment.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of viral antigens (e.g., HBsAg, HBcAg) and infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in liver tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) in serum and liver samples.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Measurement of liver enzymes (e.g., AST, ALT), bilirubin levels, and viral load (HBV DNA) in serum.
- Gene/protein expression profiling via RT qPCR and Western blot techniques: Quantification of key genes involved in HBV replication, immune responses, and liver injury (e.g., HBV polymerase, MxA, STAT1, HLA-DR).
In addition to the established HBV models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, including studies on HBV induced fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to the hepatitis B model, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Advantages
- Specialized Expertise: We specialize in providing high-quality rodent models for Hepatitis B research. With extensive experience in viral pathogenesis, immune responses, liver damage, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), our team can offer unparalleled insights and guidance for your studies.
- Comprehensive Model Solutions: We offer a wide range of well-established and custom Hepatitis B models to suit your research needs, from acute and chronic infection models to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis models. Our models are designed to replicate human disease progression accurately.
- Advanced Research Capabilities: We employ cutting-edge technologies, including advanced molecular profiling (e.g., RT qPCR, Western blot), histological analysis, cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA), and serum biomarkers, enabling a thorough evaluation of therapeutic candidates. Our models allow for precise assessment of viral load, liver damage, immune response, and inflammation.
- Tailored Approach: Every research project is unique. We work closely with you to customize models based on your specific research questions and objectives. Whether you're testing antiviral drugs, immune modulators, or investigating liver regeneration, we ensure that your study is designed for success.
- Reliable and Reproducible Results: Our models are rigorously validated for accuracy and reproducibility, ensuring that your research is built on a solid foundation. We prioritize the consistency of results to make your studies robust and scientifically sound.
- Full Support from Start to Finish: Our team provides comprehensive support at every stage of your research, from model selection and experimental design to data interpretation and analysis. We are committed to ensuring your project progresses smoothly and efficiently.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. How do you assess the severity of Hepatitis B infection in these models?
The severity is assessed through various measures, including serum viral load (HBV DNA), liver histopathology, cytokine levels, liver function markers (e.g., ALT, AST), and tissue fibrosis or necrosis scores.
-
2. What therapeutic interventions can be tested in these models?
Our Hepatitis B models are ideal for testing antiviral therapies, immune modulators, anti-inflammatory agents, liver protection drugs, and treatments aimed at preventing HBV-related liver fibrosis and HCC.
-
3. How long does it take to obtain results from your Hepatitis B models?
The timeline varies depending on the model and the specific research focus. Preliminary results can be obtained within a few weeks, while more comprehensive data (e.g., histology, gene expression) may take several weeks to months.
-
4. Do you provide support with experimental design and data interpretation?
Yes, we offer full support throughout your project, from the selection of the appropriate model and experimental design to data analysis and interpretation. Our experienced scientists work closely with you to ensure the study aligns with your research goals.
-
5. Are your Hepatitis B models suitable for preclinical drug testing?
Yes, our models are specifically designed for preclinical drug testing, allowing for the evaluation of antiviral agents, immune modulators, and liver-protective therapies. These models are validated for assessing both viral replication and liver damage.
-
6. How does your company differentiate from others in Hepatitis B research?
Our company offers specialized expertise in Hepatitis B research, validated and reproducible models, and a highly personalized approach. We combine cutting-edge technologies with comprehensive customer support to ensure that your research progresses efficiently and accurately.
-
7. How do I get started with a Hepatitis B study?
Simply contact us with your research goals, and our team will assist you in selecting the appropriate model, designing your experiment, and beginning your study. We are here to provide the expert support and resources needed to achieve meaningful results in your research.
Published Data
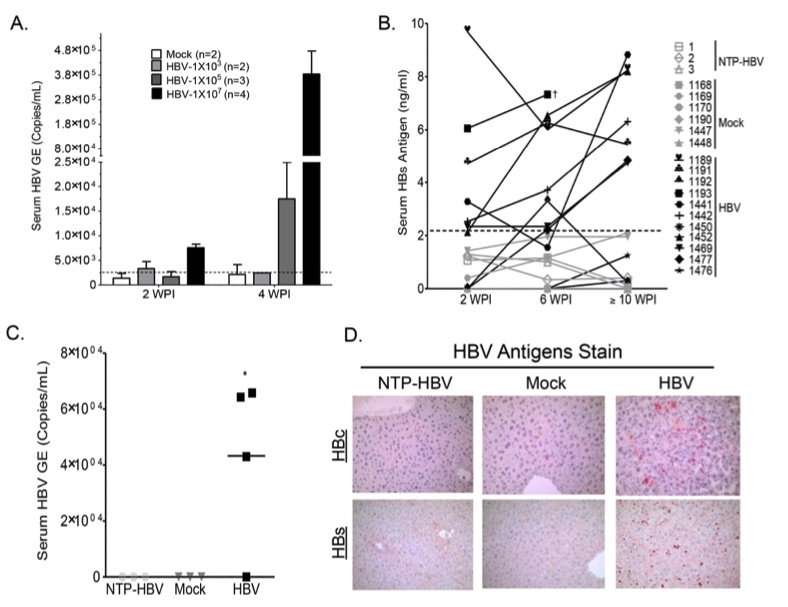 Fig. 2 Persistent HBV infection in A2/NSG/Fas-hu HSC/Hep mice.2
Fig. 2 Persistent HBV infection in A2/NSG/Fas-hu HSC/Hep mice.2
In this study, we investigated whether the A2/NSG-hu HSC/Hep mouse model could support HBV infection. To assess this, both humanized and non-humanized mice were inoculated with HBV patient isolates at varying doses: 1.61 × 103, 1 × 105, or 1 × 107 genome copies per mouse (Figure 2A). The progression of HBV infection was monitored by measuring serum levels of HBV genome and HBsAg. At a dose of 1 × 105 HBV genome copies per mouse, HBV replication was first detected at 4 weeks post-infection (wpi). In contrast, mice inoculated with 1 × 107 genome copies showed detectable HBV genomes as early as 2 wpi (104 copies/ml), which rose to higher levels by 4 wpi (4.61 × 105 copies/ml) (Figure 2A). Persistent serum HBs antigen was observed in approximately 75% of HBV-inoculated humanized mice (HBV), but not in non-transplant control mice inoculated with HBV (NTP-HBV) or mock-inoculated humanized mice (Mock) (Figure 2B). Similarly, serum HBV genome was detected in about 75% of HBV-inoculated humanized mice, but not in non-humanized or mock-inoculated humanized mice at the time of sacrifice (Figure 2C). To evaluate HBV infection in the liver, mice were sacrificed at approximately 12–16 weeks post-inoculation. HBV core and surface antigens were present in the livers of all humanized mice with detectable HBV viremia but absent in the livers of control animals (non-transplanted HBV-inoculated mice and mock-inoculated humanized mice) (Figure 2D).
References
- Li C, Wei C, Yang X. Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccines. Explor Dig Dis. 2024; 3:443–58. https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2024.00060. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Bility, Moses T et al. "Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages." PLoS Pathogens vol. 10,3 e1004032. 20 Mar. 2014, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004032. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
