Oxazolone (OXA) induced Colitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Colitis refers to inflammation of the colon and encompasses a range of conditions that affect the large intestine. It can be classified into several types based on etiology, including inflammatory, infectious, ischemic, and microscopic colitis. Among these, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)—which includes ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD)—is the most widely studied form. UC is typically limited to the colon and rectum, presenting with continuous inflammation of the mucosal layer, while CD can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and often involves transmural inflammation. Common clinical symptoms of colitis include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, urgency, and weight loss. The pathogenesis of colitis involves complex interactions between genetic predisposition, dysregulated immune responses, intestinal microbiota, and environmental triggers. While UC tends to be confined to the colon's inner lining, CD is more heterogeneous in presentation and severity. Diagnosis often involves a combination of endoscopic, histological, and imaging assessments. Although current therapies—including corticosteroids, aminosalicylates, immunomodulators, biologics (e.g., anti-TNF agents), and small-molecule inhibitors—help manage inflammation and induce remission, many patients experience relapses or treatment resistance. As such, there remains a significant need for novel therapeutic strategies that can effectively control inflammation and promote long-term mucosal healing. Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established rodent models to evaluate the efficacy of candidate drugs for colitis, including DSS-induced colitis, TNBS/DNBS-induced colitis, and adoptive T-cell transfer models. These models simulate different aspects of human colitis and allow for comprehensive assessment of disease severity, histopathological changes, immune responses, and therapeutic outcomes. Our experienced team provides full support from model selection to endpoint analysis, ensuring reliable and customized preclinical research solutions.
Disease Models and Applications
The OXA-Induced rodent colitis model is commonly used to study T cell-mediated immune responses and evaluate potential therapies for ulcerative colitis. This model is established by sensitizing rodents, typically BALB/c mice, with a topical application of oxazolone (OXA) dissolved in ethanol to the skin, followed by intrarectal administration of OXA a few days later. This induces a Th2-skewed immune response, resulting in acute colonic inflammation that mimics key features of human ulcerative colitis, including mucosal edema, epithelial damage, and infiltration of eosinophils and CD4+ T cells. The model is highly reproducible and allows for rapid induction of colitis with clear clinical symptoms such as weight loss, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. Its advantages include a well-defined mechanism of Th2-mediated inflammation and strong histopathological correlation with human disease. However, it represents an acute model and may not fully capture the chronic or relapsing-remitting nature of ulcerative colitis. Additionally, disease severity can vary based on dosing and mouse strain sensitivity. Despite these limitations, the OXA model remains a valuable tool for studying mucosal immunology and testing anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agents.
- Simulates: The OXA-Induced Rodent Colitis Model simulates human ulcerative colitis, particularly the acute phase of the disease. It is characterized by Th2-dominant immune responses, mucosal inflammation, epithelial damage, and infiltration of eosinophils and CD4+ T cells—closely resembling the immunopathology and histological features of ulcerative colitis.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is commonly used to evaluate the efficacy of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapies, including corticosteroids, aminosalicylates (e.g., mesalamine), anti-IL-4/IL-13 antibodies, JAK inhibitors, and novel agents targeting Th2-related cytokines or epithelial repair mechanisms.
Measurements
We offer a comprehensive evaluation system for the OXA-Induced rodent colitis model, utilizing a variety of advanced technologies and scientific methods, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Monitoring of body weight changes, stool consistency, presence of fecal blood, and rectal inflammation scores.
- Disease activity index (DAI): Combined assessment of body weight loss, diarrhea severity, and rectal bleeding to quantify colitis progression.
- Colon macroscopic evaluation: Assessment of rectal swelling, edema, and ulceration following oxazolone (OXA) challenge.
- Histopathological analysis: H&E staining to evaluate epithelial disruption, mucosal thickening, goblet cell depletion, and inflammatory cell infiltration in rectal tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of Th2-related cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, as well as pro-inflammatory markers including TNF-α and IL-1β.
- Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity assay: Quantification of neutrophil accumulation in rectal tissue as an indicator of acute inflammation.
- Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry: Characterization of immune cell infiltration, particularly CD4+ T cells, eosinophils, and mast cells, in affected regions.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses for Th2-associated genes, tight junction proteins, and signaling molecules like STAT6 or GATA3.
In addition to standardized protocols, we support custom modifications of the OXA model to suit specific therapeutic targets or mechanistic studies. Our team offers full assistance from experimental planning to data interpretation, ensuring scientifically robust and tailored research outcomes.
Related Services
In addition to the OXA-induced rodent colitis model, we also offer a range of other colitis models for investigating diverse immunological mechanisms and pathologies associated with intestinal inflammation, including:
- TNBS/DNBS induced Colitis Model
- DSS induced Colitis Model
- Indomethacin induced Small Intestinal Inflammatory Model
- Acetic Acid induced IBD Model
- Anti-CD40 Ab induced IBD Model
- IL-10 KO Mouse Spontaneous IBD Model
- CD4+CD45RBhi T Cells induced IBD Model
Advantages
- Comprehensive Model Portfolio: We offer a wide range of well-characterized rodent models for digestive system diseases, including various types of colitis, tailored to mimic human pathophysiology.
- Customization & Flexibility: Models can be adapted or newly developed according to specific research needs, supported by thorough literature and technical validation.
- End-to-End Support: From study design to data analysis, our experienced scientific team provides full-cycle support to ensure high-quality, reliable, and interpretable results.
- Advanced Analytical Capabilities: We utilize cutting-edge technologies such as ELISA, qPCR, Western blotting, flow cytometry, and histopathology for comprehensive pharmacological evaluations.
- Proven Track Record: With years of experience in preclinical research, we have successfully supported numerous drug development projects for academic and industry clients globally.
- Quality & Compliance: All studies are conducted under rigorous quality standards to ensure reproducibility, reliability, and compliance with ethical research practices.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: What types of colitis models do you offer?
A1: We provide a variety of rodent colitis models, including TNBS-, DNBS-, DSS-, OXA-, and adoptive T cell transfer-induced models, each tailored to mimic different pathological and immunological features of human inflammatory bowel diseases.
-
Q2: Can you customize a colitis model based on our research needs?
A2: Yes. Our team can adjust parameters such as induction method, dosage, duration, and evaluation endpoints, or even develop new models based on literature and client-specific objectives.
-
Q3: What kinds of readouts and analyses do you provide?
A3: We offer a full suite of evaluations, including clinical scoring (DAI), colon length measurement, histopathology, cytokine profiling (ELISA), gene/protein expression (qPCR, Western blot), MPO activity, and immune cell analysis (IHC, flow cytometry).
-
Q4: How are animal welfare and ethical standards maintained?
A4: All studies are conducted in compliance with international guidelines for the ethical use of animals in research. Our animal care practices follow strict protocols to ensure humane treatment.
-
Q5: What species and strains are used in your colitis models?
A5: We commonly use C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice, as well as Sprague Dawley and Wistar rats, depending on the model type and experimental requirements.
-
Q6: Can you assist with study design and data interpretation?
A6: Absolutely. Our experienced scientists provide support at every stage, from experimental planning and model selection to data analysis and reporting.
Published Data
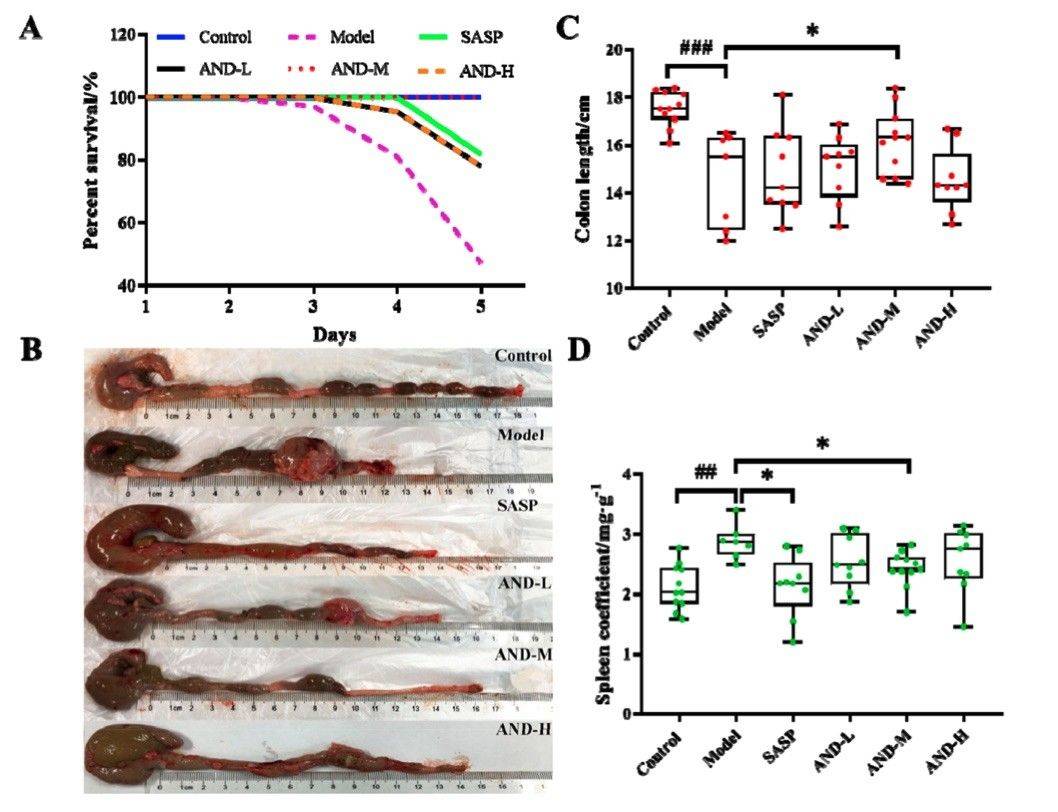 Fig. 1 Effect of andrographolide (AND) on oxazolone (OXZ)-induced colitis.1
Fig. 1 Effect of andrographolide (AND) on oxazolone (OXZ)-induced colitis.1
Andrographis paniculata extract, primarily composed of andrographolide (AND), has been reported to alleviate ulcerative colitis (UC) symptoms. This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of AND using the oxazolone (OXZ)-induced UC rat model. Oral administration of 80 mg/kg AND significantly prolonged survival in treated animals, as shown by statistical analysis of mortality across groups (Figure 1A). Notably, the 120 mg/kg AND group showed higher mortality than the 80 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg groups, warranting further investigation. Colon shortening and splenomegaly, typical indicators of UC, were evident in the model group. Treatment with 80 mg/kg AND markedly improved colon length (Figure 1B, C). Additionally, splenomegaly was significantly increased in the model group, reflecting immune dysfunction (Figure 1D), while treatment with 80 mg/kg AND and SASP significantly reduced spleen enlargement. However, no significant improvements in colon length or spleen size were observed in the 40 mg/kg and 120 mg/kg AND groups.
Reference
- Zhang, Liuhong et al. "Improvement of Oxazolone-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats Using Andrographolide." Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 25,1 76. 24 Dec. 2019, DOI:10.3390/molecules25010076. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
