Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide (STZ-NA) induced Type II Diabetes (T2D) Rat Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established and reliable animal models to evaluate the efficacy of Type II Diabetes treatments. Our models are designed to assist researchers in testing the effectiveness of new drugs and therapies in a controlled and reproducible environment, helping to advance the search for better treatments for this widespread disease.
Introduction
Type II Diabetes (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. It is the most common form of diabetes and is closely associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. Over time, the inability to regulate blood sugar can result in severe complications, including cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, kidney failure, and vision impairment. Unlike Type I Diabetes, where the body fails to produce insulin, Type II Diabetes is primarily due to the body's inability to respond to insulin effectively. The disease progresses gradually and is often diagnosed after significant damage to organs. While genetic factors contribute to its onset, environmental factors such as diet and physical activity play a critical role. Management of T2D typically involves lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the quality of life for patients.
Disease Models and Applications
The Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model is commonly used for studying Type II Diabetes. In this model, rats are first administered Nicotinamide to induce insulin resistance, followed by a single dose of Streptozotocin, which impairs pancreatic β-cell function. This combination leads to elevated blood glucose levels, mimicking human Type II Diabetes. This model is particularly useful in evaluating drugs that target insulin resistance, glucose metabolism, and β-cell regeneration. Its advantages include the reproducibility of diabetes induction and the ability to evaluate long-term effects of treatments. However, its limitations include the fact that the model does not fully replicate the complex etiology of human Type II Diabetes, such as the role of obesity.
Simulates: The Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model simulates insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism, which are key features of human Type II Diabetes. It is used to study the pathophysiology of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of diabetes treatments.
Evaluates Drugs: This model is commonly employed to evaluate anti-diabetic drugs, including those that improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and protect pancreatic β-cells. It is also used to assess the impact of lifestyle interventions and novel therapies that target the mechanisms of Type II Diabetes.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, blood glucose levels, food and water intake.
- Glucose tolerance test (GTT): Assessment of glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
- Hematology analysis: Measurement of blood parameters such as red blood cell count, white blood cell count, and platelets.
- Serum biomarkers: Levels of insulin, HbA1c, and other metabolic markers.
- Histological analysis: Examination of pancreatic tissues for β-cell mass, liver, and kidney histopathology.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Quantification of key molecules involved in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism via RT-qPCR and Western blot.
Additionally, our scientific team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized approach to your research project.
Related Services
In addition to the Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model, we also offer other methods to induce diabetes. Our services encompass a wide range of approaches to help you choose the most suitable model for your research needs.
- Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes Model
- Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model
- db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model
- Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model
- Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Combined Spleen & Partial Pancreas Resection & Glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model
Advantages
- Expertise in Diabetes Models: We offer a wide range of well-established, reliable models to study Type II Diabetes, ensuring the most accurate evaluation of your drug candidates.
- Tailored Solutions: Our models can be customized to fit the specific requirements of your research, whether you're studying insulin resistance, glucose metabolism, or related comorbidities.
- Advanced Technology: We utilize state-of-the-art equipment and technologies for precise and high-quality measurements, including glucose tolerance tests, histology, and gene expression profiling.
- Comprehensive Support: From experimental design to data analysis, our experienced team is here to support you at every step of your project, ensuring seamless execution and reliable results.
- Reproducibility and Consistency: Our models have been rigorously validated, offering reproducible results to enhance the reliability and validity of your research outcomes.
- Fast Turnaround: We provide timely and efficient services, helping you meet your research deadlines without compromising quality.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the primary benefit of using your Type II Diabetes models?
A: Our models are specifically designed to closely mimic the pathophysiology of Type II Diabetes, offering reliable and reproducible results for drug efficacy testing.
-
Q: Can I customize the diabetes models to fit my research needs?
A: Yes, we offer customizable solutions for Type II Diabetes models, allowing you to adjust factors like diet, treatment protocols, and disease progression to meet your research objectives.
-
Q: How do you ensure the accuracy of the results in your diabetes models?
A: We use cutting-edge technology for precise monitoring and measurements, such as glucose tolerance tests, histological analysis, and gene expression profiling, ensuring high-quality and accurate data.
-
Q: What kind of support do you offer throughout the research process?
A: Our team provides comprehensive support, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring that your project is executed smoothly and effectively.
-
Q: How long does it take to develop Type II Diabetes in the models?
A: Type II Diabetes typically develops within 1-2 weeks after the administration of Streptozotocin and Nicotinamide in our rat models.
Published Data
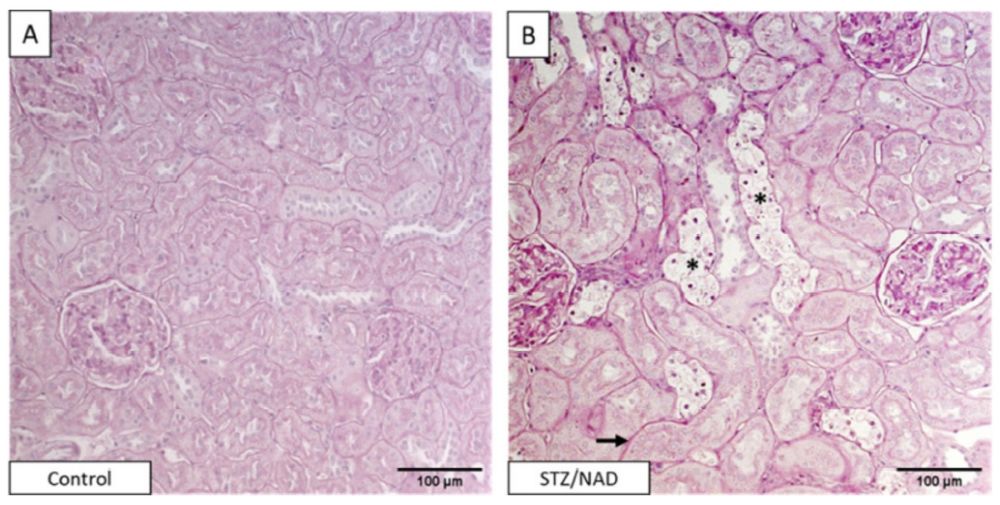 Fig. 1 Histopathology staining of diabetic nephropathy.1
Fig. 1 Histopathology staining of diabetic nephropathy.1
This experiment utilized a rodent model of non-obese Type 2 diabetes, induced by a combination of nicotinamide (NA) and streptozotocin (STZ). The underlying mechanism of diabetes induction with these two agents involves NA mitigating the toxic effects of STZ, resulting in partial destruction of pancreatic β cells. This allows the remaining viable β cells to retain their ability to respond to glucose stimulation. Figure 1 presents typical histological staining of kidney tissues using periodic acid-Schiff (PAS). As shown in these PAS-stained sections, significant pathophysiological changes are evident in the kidneys of NA-STZ-induced diabetic rats. Panels (A) and (B) display renal sections from a nondiabetic control rat and a diabetic rat at week 12, respectively. Notable changes include tubular epithelial cell necrosis (asterisk) and thickening of the tubular basement membrane (arrow), highlighting the renal complications associated with diabetes in this model.
Reference
- Yan, Liang-Jun. "The Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin Rodent Model of Type 2 Diabetes: Renal Pathophysiology and Redox Imbalance Features." Biomolecules vol. 12,9 1225. 2 Sep. 2022, DOI:10.3390/biom12091225. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
