hERG Screening
As a recognized pioneer in the field of pharmaceutical innovation, Creative Biolabs offers professional lead optimization service using state-of-the-art hERG screening system.
Cardiotoxicity is one of the major safety concerns in drug discovery, which is the leading reason for development termination and market withdraw or restriction. Particularly, hERG ion channel inhibition or blockade is responsible for 25-40% of all preclinical lead compound discontinuance. Human ether-a-go-go (hERG), a potassium channel that is abundant in the cardiomyocytes, represents one pivotal component for IKr currents and cardiac repolarization. Drug-induced interference of hERG causes QT interval prolongation, which is associated with fatal ventricular tachyarrhythmia called Torsade de Pointes (TdP). Given the unacceptable adverse effects of hERG inhibition and the fact that many drug-like molecules exhibit hERG affinity, hERG assessment has become one priority requirement by regulatory agencies before IND submission.
Equipped with extensive expertise and impeccable technologies, Creative Biolabs offers multiple powerful approaches for rapidly and efficiently screening candidate compounds for hERG toxicity during early preclinical stage thus benefit the speed and safety of drug developing progress.
Manual/Automatic Patch Clamp Assay
Since manual patch clamping has long been regarded as the gold standard for evaluating hERG safety by FDA and other regulatory institutions, Creative Biolabs provides first-class manual patch clamp electrophysiology measurement of hERG inhibition with high accuracy. hERG currents are recorded before and after exposure to test compounds in different concentrations, and IC50 values (concentrations at which half the maximum inhibition is observed) will be determined by dose formulation analysis. Additionally, we also conduct automatic electrophysiology test to detect hERG risks with higher throughput and sensitivity. This automatic system can revolutionarily facilitate ion channel-focused library screening as well as pharmacology safety assessment. Both assays can be performed in the presence or absence of serum, in the case of protein-bounding disturbance.
hERG-Radioligand Binding Assay
With unique membrane preparation technology, potential hERG hazard can be detected by radioligand-binding assays. This assay enables higher throughput and specificity with 3 different types of radioligands, thus providing more reliable feedbacks. It has become a time-saving and cost-effective approach suitable for large-scale screening.
Fluorescence Polarization Assay
Using specific fluorescence tracer and membrane preparation, this highly reproducible assay is able to detect certain substance with binding affinity to hERG channel quickly. Precise protocols, highly automatic control, and stringent validation process can ensure comprehensive and reliable outcomes on hERG risks.
Microelectrode Array
Creative Biolabs has established a highly predictively tissue model composed of iPSC-induced human cardiomyocyte (SC-hCMs), cardiac endothelial and fibroblast cells, mimicking the spontaneously beating heart with electrophysiological and biochemical responses. Based on this so-called “microtissue”, microelectrode array can analyze changes in all major ion channels, including hERG, by ECG-like recordings. This novel in vitro system has revealed a promising method for efficient phenotypic screening in drug discovery.
In addition to hERG screening, Creative Biolabs provides a full range of assays identifying other ion channel and biomarkers related to cardiotoxicity. Together, integrated data based on multiple ion channel effects (MICE) can be generated for better understanding the cardiotoxicity potential of investigated compounds. Our experienced scientists are also pleased to provide further help with the interpretation of the results and useful advice for your drug development program.
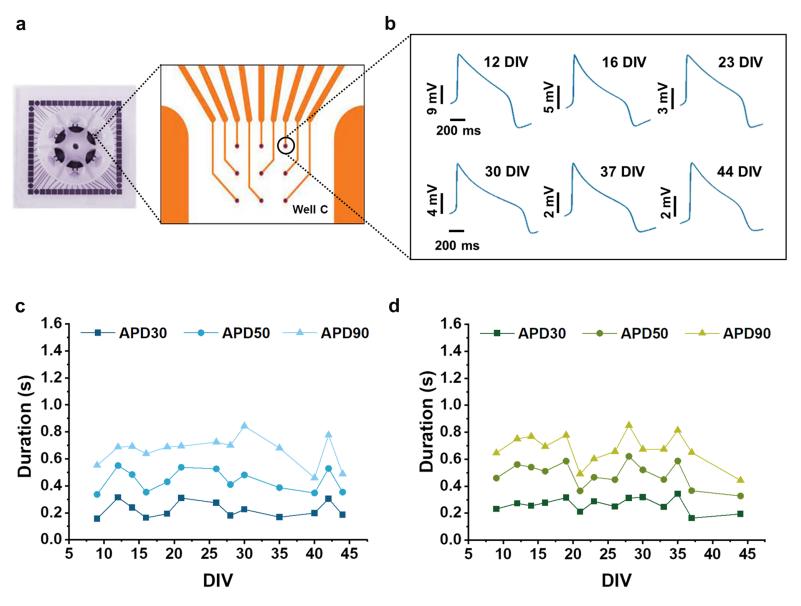 Fig.1 Long-term intracellular AP recordings from single cardiac cells.1
Fig.1 Long-term intracellular AP recordings from single cardiac cells.1
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry .
Reference
- Giuseppina Iachetta, et al. "Longterm in vitro recording of cardiac action potentials on microelectrode arrays for chronic cardiotoxicity assessment." Archives of Toxicology 97 (2023): 509-522. under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
