Fear Conditioning Test
The contextual and cued fear conditioning test is one of the most widely used behavioral paradigms used to assess associative fear learning and memory in rodents. Creative Biolabs utilizes this test for evaluating drug compounds' ability to reverse drug-induced deficits in memory. Moreover, it can also be used to characterize mutant mice and the effects of genetic alterations.
Introduction of the Fear Conditioning Test
Typically, the fear conditioning test employs electrical footshock as an unconditioned fear stimulus (US) in conjunction with a neutral conditioned stimulus (CS), such as an experimental context or a discrete cue such as a light or a tone stimulus.
In a conditioning context, administration of a footshock (US) is paired with a tone (CS) in a certain test situation. Animals are placed in a box enclosure and receive multiple exposures of CS-US pairing (usually 1-5 times). Following an interval that is an independent variable for memory retention (usually >24 h for assessment of long-term memory), test animals are placed back in the original context where they received the CS-US exposures during the training session, as a conditioned context. If the test animals acquire an association of the US with a context (the box enclosure), they will demonstrate freezing responses to the context in the absence of CS co-exposure. Freezing is a species-specific response to fear, which has been defined as complete immobility with the exception of breathing.
In the cued fear conditioning, the test animals are placed in a chamber with a different context from the previously exposed US for several minutes (non-CS phase), and subsequently, only a CS is presented (CS phase) in the test enclosure. A successful cue-association with the US (fear) is defined by reduced freezing in the non-CS phase and a robust freezing response in the CS phase.
Features of the Fear Conditioning Test
- It is a widely used test to understand the neurobiological mechanisms of fear learning and memory in transgenic and knockout mice, even when more pronounced motor deficits are problematic in other learning assays.
- An advantage of footshock as an aversive stimulus and tone as an artificial neutral stimulus is that their intensity and duration can be easily controlled and precisely adjusted.
- Contextual and cue fear conditioning depend on different neural processes, whereas contextual conditioning is hippocampally driven and cued fear conditioning is not.
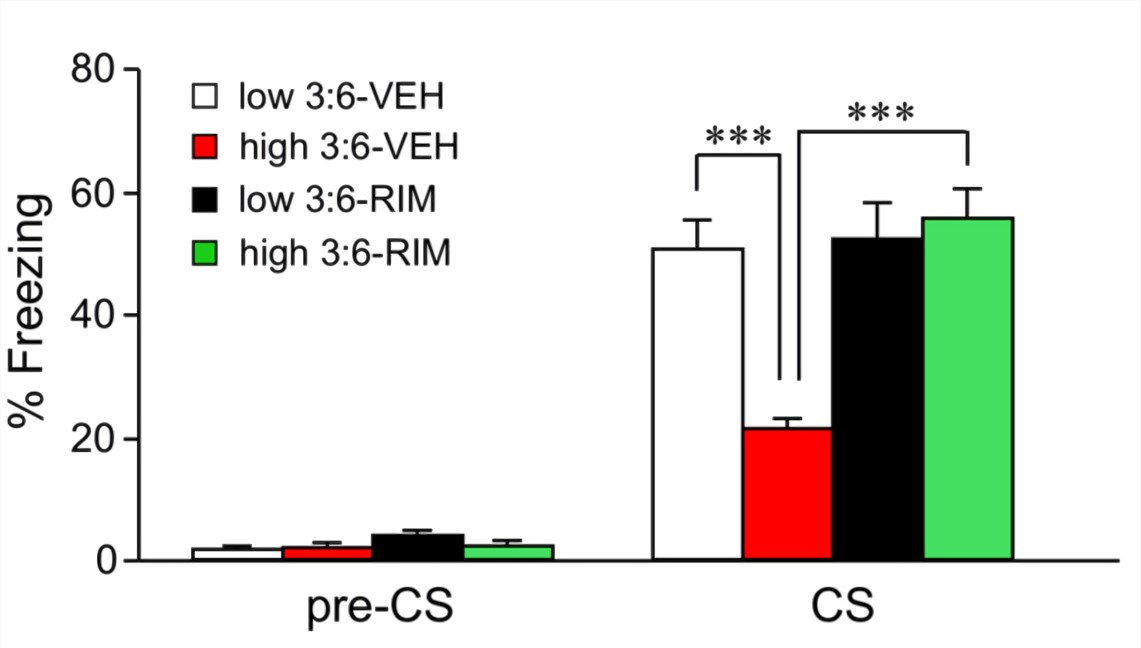 Fig.1 In the auditory fear conditioning test, the freezing rate was reduced in mice fed with a high 3:6 ratio diet compared with that in mice fed with a low 3:6 ratio diet. Vehicle (VEH) was injected as the control for rimonabant (RIM) treatment. (Daisuke et al. 2016)1, 2
Fig.1 In the auditory fear conditioning test, the freezing rate was reduced in mice fed with a high 3:6 ratio diet compared with that in mice fed with a low 3:6 ratio diet. Vehicle (VEH) was injected as the control for rimonabant (RIM) treatment. (Daisuke et al. 2016)1, 2
Creative Biolabs has a large battery of well-designed and validated test to assess memory and cognitive functions in rodents. Besides the fear conditioning test described here, we also provide the following tests:
Creative Biolabs provides highly customized behavioral tests to suit specific scientific needs of our clients. Moreover, new behavioral tests of cognition are constantly developed and validated. Moreover, these behavioral tests are widely used in combination with different neurological disease models to test the efficacy of drug candidates. Our comprehensive list of neurological disease models is summarized in the following chart:
For more information, please contact us or send us an inquiry.
References
- Daisuke, Y.; et al. Modulation of long-term potentiation of cortico-amygdala synaptic responses and auditory fear memory by dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid: [J]. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2016, 10.
- under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
