High-Fat & Carbon Tetrachloride (CCL₄) induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established, customizable models to assess the efficacy of potential NASH therapies, ensuring reliable and reproducible results for preclinical drug testing and research.
Introduction
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver disease characterized by inflammation and fat accumulation in the liver, without significant alcohol consumption. It is a more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is becoming increasingly common due to rising rates of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. NASH is associated with the progression of liver damage, leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. The disease develops when excessive fat accumulates in the liver, triggering inflammatory responses and liver cell injury. As a result, oxidative stress, cytokine production, and altered lipid metabolism contribute to the fibrosis and liver damage observed in NASH patients. The disease often remains asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to diagnose until significant liver damage has occurred. Currently, there are no approved drugs for treating NASH, and early intervention is critical to prevent its progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Disease Models and Applications
The High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model is a widely used experimental tool to study the progression of NASH and to test potential therapeutic agents. This model is established by feeding rodents a high-fat diet (HFD) combined with carbon tetrachloride (CCL₄), a well-known hepatotoxic compound. The HFD induces liver steatosis, while CCL₄ induces hepatocyte damage and inflammation, mimicking the pathological features of NASH, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis. The model is advantageous in simulating the progression of NASH through multiple stages, including fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis. However, the CCL₄ induced liver damage may also cause acute toxicity, making it difficult to distinguish between NASH-related fibrosis and direct liver injury. This model is especially useful for evaluating the efficacy of drugs targeting inflammation, fibrosis, and steatosis.
- Simulates: The High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model simulates human NASH, with characteristics including hepatic steatosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, closely resembling the disease's progression in humans.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to assess drugs that target various stages of NASH, such as anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid-lowering therapies. It provides insight into the efficacy of therapeutic agents in reducing liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis, making it ideal for preclinical drug testing.
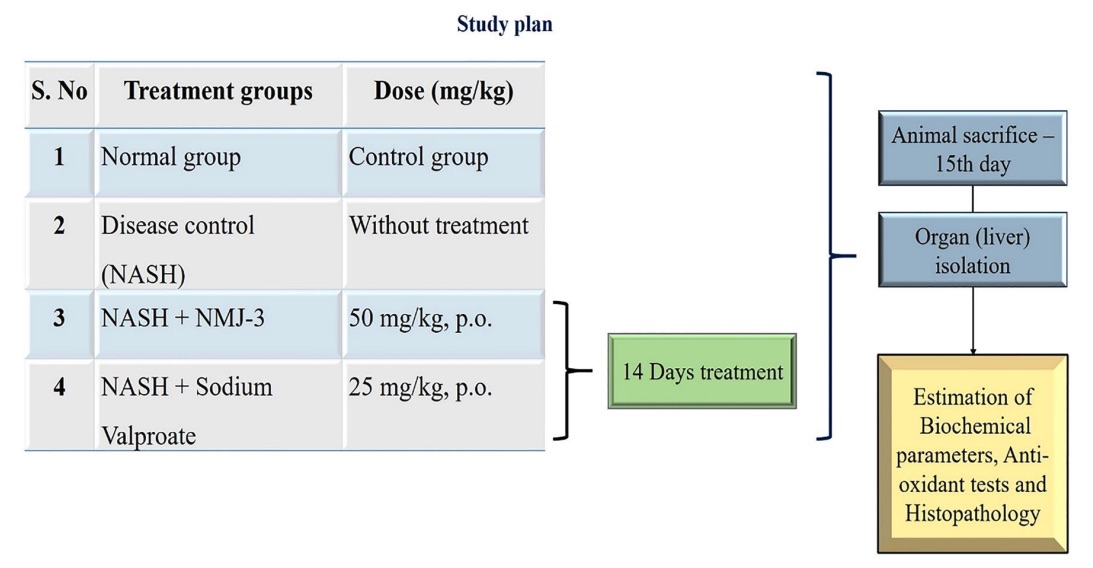 Fig. 1 Treatment groups and study plan.1
Fig. 1 Treatment groups and study plan.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, liver weight, food intake, and mortality rate.
- Histological analysis: Liver tissue staining (H&E, Masson's Trichrome) for fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis assessment.
- Cytokine profiling: Measurement of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) via ELISA.
- Liver biomarkers: Serum liver enzymes (ALT, AST) and bilirubin levels for assessing liver injury.
- Gene/protein expression: RT qPCR and Western blot analysis to evaluate fibrosis markers (e.g., collagen, α-SMA) and inflammatory mediators.
Additionally, we provide expertise in the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, and our scientific team assists with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis.
Related Services
In addition to the High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model, our company offers several other preclinical models of NASH, each designed to address specific research needs. Whether you are investigating the molecular mechanisms of NASH or testing novel therapeutics, our models are adaptable to a variety of experimental designs.
- Diet induced Obesity (DIO) Mouse NASH Model
- High-Fat Diet induced NASH Model
- Methionine Choline-Deficient (MCD) Diet induced NASH Model
- Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid-Defined (CDAA) Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet & Fructose induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & Fructose induced NASH Model
- Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) & High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat induced NASH Model
- MC4R KO Mouse Model
- LDLR KO Mouse Model
Advantages
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored NASH models to suit the specific needs of your research.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A full range of advanced measurements and techniques to assess drug efficacy in NASH models.
- Expert Support: Our scientific team offers guidance on experimental design, model selection, and data interpretation throughout the study.
- Reliable Results: Our models provide reproducible and accurate data, ensuring high-quality outcomes for your preclinical studies.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: We utilize cutting-edge technologies like cytokine profiling and gene expression analysis to evaluate therapeutic effects in NASH models.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the benefit of using the High-Fat & CCL₄ induced NASH Model?
A: This model closely mimics the metabolic and histopathological features of human NASH, making it highly valuable for preclinical drug testing and mechanistic studies.
-
Q: Can the model be customized for different research purposes?
A: Yes, our team can adapt the model and experimental design to meet the specific objectives of your research project.
-
Q: What measurements can be used to assess drug efficacy in this model?
A: We offer a comprehensive range of tests, including liver histology, cytokine profiling, serum biomarkers, and gene/protein expression analysis, to evaluate drug effects in the model.
Published Data
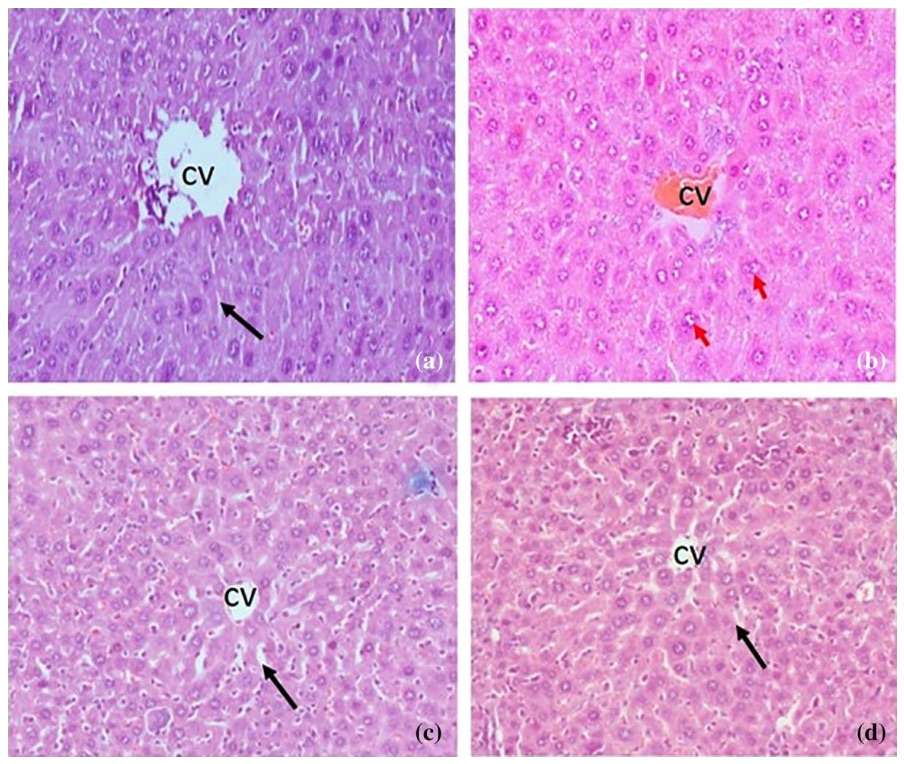 Fig. 2 Histology of liver samples.1
Fig. 2 Histology of liver samples.1
Histological analysis of HFD + CCL₄ induced NAFLD in mice is presented through photomicrographs of H&E-stained liver sections. The groups studied include: a) Normal control, b) Disease control (DC), c) Sodium valproate (SV), and d) Treatment drug (NMJ-3). In the normal control group (a), the liver architecture is intact with no visible abnormalities. In the disease control group (c), the liver shows well-maintained architecture but exhibits large cell changes in hepatocytes (red arrow), sinusoidal congestion, and mild microvesicular changes. Inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis are also observed. In the SV and NMJ-3 treated groups (b and d), the liver architecture is significantly restored with minimal large cell changes (red arrow) and no signs of inflammation, fibrosis, or necrosis. The central vein (CV) is marked, with sinusoids indicated by black arrows. These results suggest that both SV and NMJ-3 provide protection and promote recovery in liver architecture following HFD + CCL₄ induced damage.
Reference
- Sodum, Nalini et al. "Amelioration of high-fat diet (HFD) + CCL₄ induced NASH/NAFLD in CF-1 mice by activation of SIRT-1 using cinnamoyl sulfonamide hydroxamate derivatives: in-silico molecular modelling and in-vivo prediction." 3 Biotech vol. 12,7 (2022): 147. DOI:10.1007/s13205-022-03192-5. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
