TNBS/DNBS induced Colitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Colitis refers to inflammation of the colon, which can result from various causes, including infections, ischemia, autoimmune responses, or exposure to irritants. The most well-known forms are inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which include ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD). Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the mucosal lining of the colon and rectum, presenting with continuous inflammation and symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, urgency, and fatigue. Crohn's disease, on the other hand, can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and involves transmural inflammation, often leading to complications like strictures and fistulas. Colitis may also arise from infectious agents (e.g., Clostridioides difficile), ischemic events (ischemic colitis), radiation exposure (radiation colitis), or as a side effect of certain medications (drug-induced colitis). The pathogenesis of colitis involves a complex interplay between genetic predisposition, immune system dysregulation, gut microbiota, and environmental factors. Diagnosis typically relies on clinical presentation, endoscopy, histological examination, and laboratory tests. Creative Biolabs offers a diverse range of well-established rodent models for evaluating the efficacy of anti-colitis drugs. Our models simulate various forms of inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, induced by agents such as TNBS, DNBS, and DSS. These models provide a reliable preclinical platform for assessing therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of action, supporting the development of novel treatments for colitis.
Disease Models and Applications
The TNBS/DNBS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model is widely used to study the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and evaluate potential therapeutic agents. This model is established by intrarectal administration of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) or dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS) dissolved in ethanol, which disrupts the mucosal barrier and allows the haptenating agent to bind colonic proteins, triggering a T-cell-mediated immune response. The resulting inflammation resembles human Crohn's disease, characterized by transmural inflammation, ulceration, and infiltration of immune cells. One of the major advantages of this model is its reproducibility, rapid onset, and ability to mimic key immunopathological features of IBD. It is also dose-dependent, allowing the severity of colitis to be modulated. However, the model has some limitations, including variability due to differences in animal strains, sensitivity to administration technique, and the fact that it does not fully replicate the chronic and relapsing nature of human IBD. Despite these limitations, the TNBS/DNBS-induced colitis model remains a valuable tool in preclinical IBD research, particularly for testing immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Simulates: The TNBS/DNBS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model simulates key features of human Crohn's disease, including transmural inflammation, mucosal ulceration, immune cell infiltration, and a Th1/Th17-skewed immune response. It mimics the immunopathological mechanisms underlying chronic intestinal inflammation, making it a relevant model for studying inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is commonly used to evaluate anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs such as corticosteroids, TNF-α inhibitors, IL-12/23 blockers, JAK inhibitors, and novel biologics or small molecules targeting T-cell responses, oxidative stress, or cytokine pathways involved in IBD.
Measurements
We offer a comprehensive set of evaluations for the TNBS/DNBS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model to assess drug efficacy, employing a range of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight changes, diarrhea severity, stool consistency, fecal occult blood, rectal bleeding, and survival rate.
- Disease activity index (DAI): Composite scoring based on weight loss, stool consistency, and presence of blood in feces.
- Colon length measurement: Shortening of the colon as an indicator of inflammation severity.
- Histopathological analysis: Evaluation of epithelial damage, ulceration, inflammatory cell infiltration, and crypt architecture using H&E staining.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Quantification of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ in colon tissues or serum.
- Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity assay: Measurement of neutrophil infiltration as a marker of inflammation.
- Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry: Detection of immune cell subsets (e.g., CD4⁺ T cells, macrophages) and activation markers in colonic tissues.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Analysis of pro-inflammatory genes and signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, COX-2, iNOS) by RT-qPCR and Western blot.
In addition to standard protocols, we offer the flexibility to develop customized colitis models tailored to specific research objectives. Our experienced team provides end-to-end support from study design to data interpretation, ensuring scientifically robust and project-specific solutions.
Related Services
In addition to the TNBS/DNBS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model, we also offer other colitis models to explore different underlying mechanisms of inflammation.
- DSS induced Colitis Model
- Indomethacin induced Small Intestinal Inflammatory Model
- OXA induced Colitis Model
- Acetic Acid induced IBD Model
- Anti-CD40 Ab induced IBD Model
- IL-10 KO Mouse Spontaneous IBD Model
- CD4+CD45RBhi T Cells induced IBD Model
Advantages
1. Expertise and Experience: With years of experience in preclinical models, we offer reliable, scientifically sound models for colitis research.
2. Comprehensive Services: From experimental design to data analysis, we provide full support throughout your study, ensuring a tailored approach that aligns with your research objectives.
3. Advanced Technologies: Our cutting-edge techniques, including cytokine profiling, histopathological analysis, and gene/protein expression profiling, enable accurate and reproducible results.
4. Customized Models: In addition to established protocols, we offer the flexibility to develop novel models based on your specific requirements and research needs.
5. Collaborative Approach: Our scientific team works closely with you at every stage of your study, ensuring that the results meet your expectations and are suited for publication.
6. Reliable Results: Rigorous quality control and standardized procedures guarantee consistent, reproducible outcomes, providing reliable data for drug evaluation and mechanistic studies.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: How long does it take to conduct a study using your colitis models?
A1: The duration of the study can vary depending on the severity and type of colitis induced, as well as the treatment protocol. Preclinical studies typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, including data collection and analysis.
-
Q2: What support do you provide during the study?
A2: Our scientific team provides complete support, including experimental design, model selection, data analysis, and interpretation, ensuring that your study progresses smoothly from start to finish.
-
Q3: Do you offer other disease models beyond colitis?
A3: Yes, we offer a range of rodent disease models, including those for gastric ulcers, liver diseases, cancer, atherosclerosis, kidney fibrosis, and more.
-
Q4: How do I get started with your services?
A4: Simply reach out to discuss your research goals. Our team will guide you through model selection, study design, and the appropriate timelines to begin your project.
-
Q5: Are your models validated for publication?
A5: Yes, our TNBS/DNBS-induced colitis models are validated through well-established protocols, making them suitable for publication in peer-reviewed journals.
Published Data
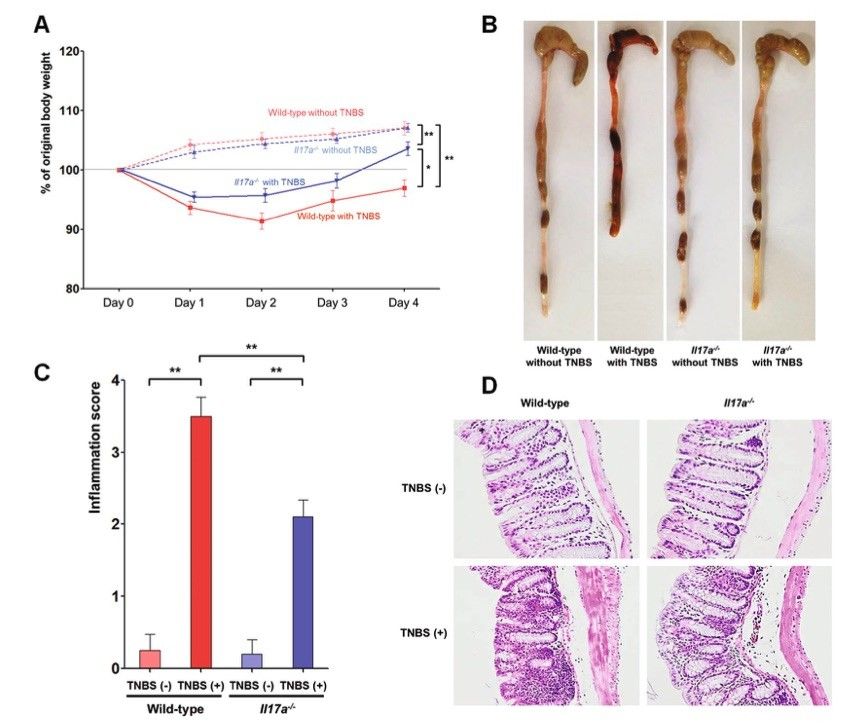 Fig. 1 TNBS-induced colitis model.1
Fig. 1 TNBS-induced colitis model.1
The objective of this study was to assess the impact of IL-17A inhibition in both acute and chronic colitis mouse models. To achieve this, Il17a−/− knockout mice were utilized. In the acute colitis model, 3.7 mg of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS) was administered intrarectally to both wild-type (WT) and Il17a−/− mice (Figure 1A). Following TNBS treatment, a decrease in body weight was observed on the first and second days in both groups. However, the body weight of the TNBS-treated Il17a−/− mice remained slightly higher compared to their WT counterparts. Additionally, the mean total colon length in Il17a−/− mice was greater than that in WT mice (Figure 1B). Although both groups exhibited an increase in macroscopic inflammation scores after TNBS treatment, the inflammation severity in the Il17a−/− mice was lower than in the WT mice, as indicated by reduced post-TNBS intestinal inflammation scores (Figure 1C). These findings suggest a potential protective role of IL-17A in acute intestinal inflammation.
Reference
- Park, Chan Hyuk et al. "Role of innate lymphoid cells in chronic colitis during anti-IL-17A therapy." Scientific Reports vol. 10,1 297. 15 Jan. 2020, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-57233-w. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
