Sarcopenia Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive services for evaluating the efficacy of sarcopenia therapies by providing various well-established preclinical models. These models simulate sarcopenia under different conditions, enabling the testing of drug candidates and therapeutic strategies. We use a range of techniques, including muscle strength and mass assessments, to offer precise evaluation tools. Our expert team ensures that these models are tailored to meet specific research and development needs, facilitating efficient drug discovery and development for sarcopenia.
Introduction
Sarcopenia is a syndrome characterized by the progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function, primarily seen in older adults. It is associated with aging, but it can also be exacerbated by factors such as malnutrition, physical inactivity, chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, cancer), and hormonal imbalances. Sarcopenia significantly impacts an individual's quality of life, increasing the risk of frailty, falls, fractures, and loss of independence. The condition typically develops gradually and is often underdiagnosed because its symptoms can be subtle and overlap with other aging-related conditions. There are two main types of sarcopenia: primary and secondary. Primary sarcopenia is related to the natural aging process, while secondary sarcopenia is caused by other factors, such as chronic disease, prolonged bed rest, or poor nutrition. Diagnosis is typically based on assessing muscle mass, strength, and physical performance. Tools such as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and handgrip strength measurement are commonly used in clinical settings. Interventions for sarcopenia include resistance training, physical activity, and nutritional interventions, particularly increasing protein intake and vitamin D supplementation. In some cases, pharmacological treatments may be considered, though no specific drug has yet been universally approved for sarcopenia.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a diverse range of well-established rodent models for sarcopenia, designed to simulate the loss of muscle mass and strength seen in aging and disease. Our sarcopenia models encompass both age-related and disease induced forms, including models for muscle atrophy, frailty, and physical dysfunction. These models are carefully crafted to mimic the pathophysiology of human sarcopenia, allowing for the accurate evaluation of therapeutic candidates in preclinical studies. Our team of skilled scientists is dedicated to supporting you throughout your project, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring high-quality and dependable results. To explore the sarcopenia models available for preclinical research, please visit the links below:
| Model | Simulated Disease | Drug Evaluation Focus | Animal species |
| Dexamethasone induced Sarcopenia Model | Sarcopenia due to glucocorticoid treatment | Muscle wasting, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle regeneration therapies, glucocorticoid antagonists | Mouse, Rat |
| Type I Diabetes induced Sarcopenia Model | Sarcopenia associated with Type 1 Diabetes | Muscle atrophy, insulin-like growth factor (IGF) modulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle regeneration agents | Rat |
| High-Fat Diet induced Sarcopenia Model | Sarcopenia induced by obesity/metabolic dysfunction | Muscle wasting, anti-inflammatory agents, muscle regeneration therapies, metabolic modulators | Mouse |
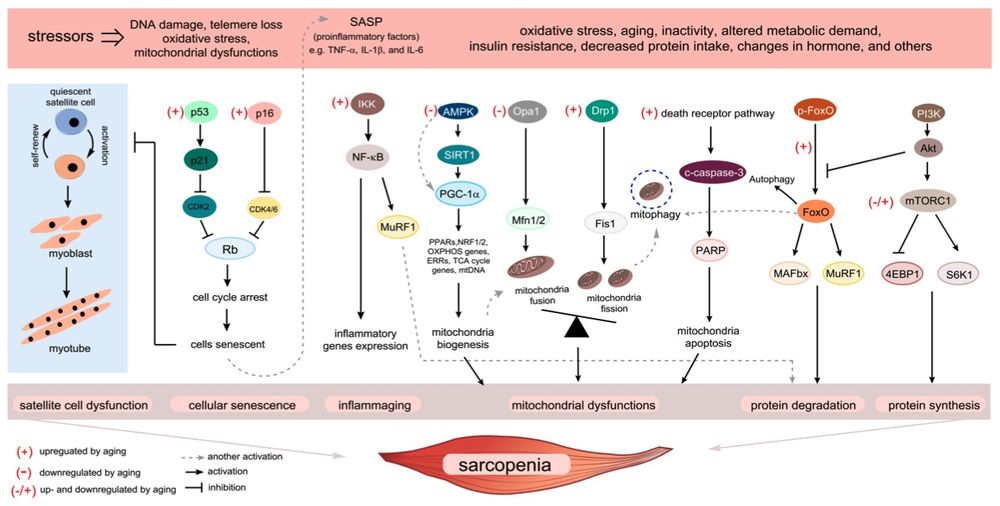 Fig. 1 Overview of the fundamental aging mechanisms that contribute to sarcopenia.1
Fig. 1 Overview of the fundamental aging mechanisms that contribute to sarcopenia.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent sarcopenia models, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, grip strength, muscle mass, and mobility assessment to evaluate muscle function and physical performance.
- Histological analysis: Muscle tissue staining (e.g., H&E, Masson’s trichrome) to assess muscle fiber size, fibrosis, and degeneration.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and myostatin, which are involved in muscle atrophy and inflammation.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Assessment of muscle-specific biomarkers such as creatine kinase (CK), myosin heavy chain, and other markers of muscle damage and regeneration.
- Gene/protein expression profiling via RT qPCR and Western blot: Analysis of key genes and proteins involved in muscle degradation and repair, such as MAFbx, MuRF1, and IGF-1.
In addition to the established sarcopenia models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, guided by literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to sarcopenia models, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Advantages
- Expertise in Sarcopenia Research: We specialize in the development and application of rodent models for sarcopenia, offering in-depth knowledge and experience in studying muscle wasting and related diseases. Our team is well-versed in the underlying mechanisms and biomarkers involved in sarcopenia, ensuring precise and reliable results.
- Comprehensive Model Solutions: We offer a variety of sarcopenia models tailored to different stages and causes of muscle loss, including age-related sarcopenia, disuse atrophy, and disease induced muscle wasting. Whether you are researching the effects of exercise, nutritional interventions, or drug therapies, we have the right models to suit your research needs.
- Advanced Measurement Techniques: Our models come equipped with state-of-the-art measurement tools, including histological analysis, muscle strength testing, cytokine profiling, and gene/protein expression analysis. This allows for a thorough evaluation of therapeutic candidates at both the tissue and molecular levels.
- Customized Research Solutions: We work closely with our clients to design studies that meet their specific research objectives. From model selection and experimental design to data analysis, we ensure a tailored approach for optimal outcomes.
- Validated and Reproducible Models: Our sarcopenia models are validated for accuracy and reproducibility, ensuring that your research is built on reliable foundations. These models mimic the progression of muscle wasting and provide meaningful results for drug efficacy testing and therapeutic development.
- End-to-End Support: We offer full support throughout your project, from initial consultation and study design to final data interpretation. Our experienced team provides clear communication and expert guidance at every step.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of sarcopenia models do you offer?
We offer various rodent models for sarcopenia, including age-related sarcopenia, disuse induced muscle atrophy, and models of disease induced muscle wasting (e.g., cancer cachexia, diabetes induced sarcopenia). These models help simulate different causes and stages of muscle degeneration.
-
2. Can the models be customized for specific research needs?
Yes, our sarcopenia models are fully customizable. Whether you are interested in evaluating drug efficacy, testing nutritional interventions, or studying muscle regeneration, we can adapt the models to meet your specific research objectives.
-
3. What measurements and assays are included in the evaluation of sarcopenia models?
We offer comprehensive evaluations, including general observations (e.g., body weight, muscle strength), histopathological analysis (e.g., muscle fiber size, fibrosis), serum biomarker assessments (e.g., creatine kinase, myostatin), and gene/protein expression analysis (e.g., MAFbx, MuRF1, IGF-1).
-
4. How do you assess the severity of sarcopenia in these models?
The severity of sarcopenia is assessed through a combination of muscle mass measurements, histological scoring of muscle degeneration, and functional tests such as grip strength and mobility. Additionally, we analyze biomarkers of muscle damage and regeneration to track disease progression.
-
5. What drugs or therapies can be tested in these models?
Our sarcopenia models are ideal for evaluating a range of therapeutic interventions, including anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle-promoting agents, myostatin inhibitors, anabolic steroids, and exercise-based therapies. We also support studies focusing on nutritional interventions.
Published Data
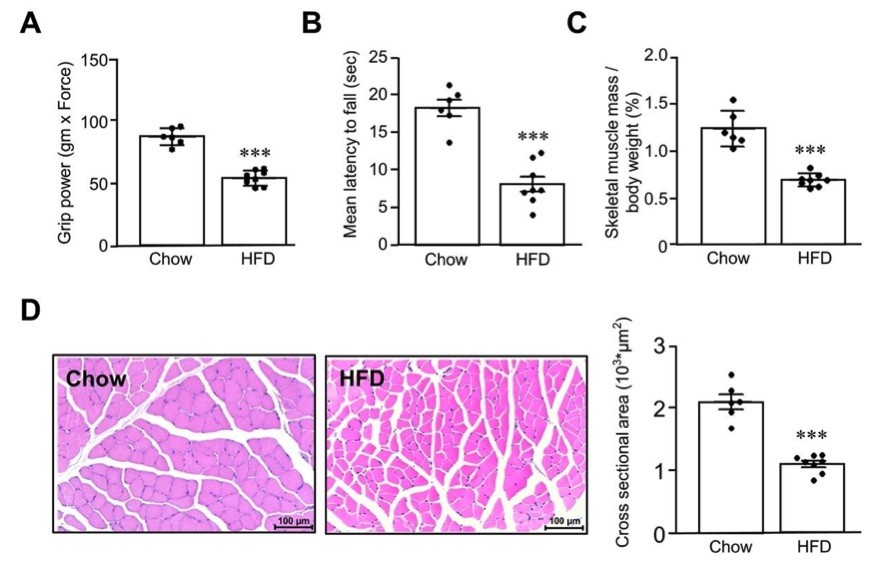 Fig. 2 High-fat-diet induced sarcopenia mouse model.1
Fig. 2 High-fat-diet induced sarcopenia mouse model.1
To investigate the factors contributing to the development of sarcopenia, a high-fat diet (HFD) induced sarcopenia mouse model was first established following a protocol described in a previous study. After 24 weeks of HFD feeding, the body weight of the mice was significantly increased compared to the chow-fed group. As shown in Figure 2, HFD-fed mice displayed impaired motor function, as evidenced by reduced grip strength (Figure 2A) and shorter latency to fall in the rotarod test (Figure 2B). Since gastrocnemius muscle thickness is closely associated with skeletal muscle mass, we further examined changes in this muscle. The skeletal muscle mass index of the HFD-fed mice was significantly lower than that of the chow group (Figure 2C), while the cross-sectional area of gastrocnemius muscle fibers was markedly reduced (Figure 2D). These findings suggest that long-term HFD feeding leads to significant muscle dysfunction and atrophy, providing an effective model for studying the mechanisms of sarcopenia.
References
- Mankhong, Sakulrat et al. "Experimental Models of Sarcopenia: Bridging Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategy." Cells vol. 9,6 1385. 2 Jun. 2020, DOI:10.3390/cells9061385. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Liang, Yu-Cheng et al. "Calsarcin-2 May Play a Compensatory Role in the Development of Obese Sarcopenia." Biomedicines vol. 11,10 2708. 5 Oct. 2023, DOI:10.3390/biomedicines11102708. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
