Anti-CD40 Antibody induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) encompasses a group of chronic inflammatory disorders primarily affecting the gastrointestinal tract, with the two main types being Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Crohn’s disease is characterized by transmural inflammation that can occur anywhere along the digestive tract, commonly affecting the terminal ileum and colon. Ulcerative colitis, in contrast, is limited to the colon and rectum, with inflammation typically restricted to the mucosal layer. IBD is driven by a complex interplay between genetic predisposition, environmental factors, intestinal microbiota imbalance, and dysregulated immune responses. Diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, endoscopy, histology, and laboratory testing. Despite significant progress in understanding IBD pathogenesis, the exact etiology remains elusive, and there is currently no definitive cure. Treatments aim to control inflammation and maintain remission and include agents such as aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics targeting TNF-α, integrins, or interleukins, more recently, small molecule inhibitors. Due to the heterogeneity and complexity of IBD, reliable preclinical models are essential for exploring disease mechanisms and evaluating new therapies. Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive portfolio of well-characterized rodent models for IBD research, including DSS-, TNBS-, DNBS-, oxazolone-, and acetic acid-induced colitis models. These models replicate various immunopathological aspects of human IBD. Our services include model development, drug administration, disease scoring, histopathological examination, cytokine and biomarker analysis, and molecular profiling. Backed by advanced platforms and experienced scientists, we deliver high-quality, reproducible data to accelerate your IBD drug discovery and development programs.
Disease Models and Applications
The Anti-CD40 antibody-induced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) model is an immune-mediated colitis model primarily established in immunodeficient mice, such as Rag1- or Rag2-knockout strains, which lack functional T and B cells. In this model, a single intraperitoneal injection of an agonistic anti-CD40 antibody activates antigen-presenting cells and triggers a robust innate immune response, leading to acute colitis within a few days. The model mimics key features of human IBD, including weight loss, colonic inflammation, epithelial damage, and increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ. This model is particularly useful for studying innate immune pathways and macrophage- or dendritic cell-driven inflammation independent of adaptive immunity. Advantages include rapid disease onset, reproducibility, and well-characterized innate immune activation. However, the absence of adaptive immune components limits its utility for studying T cell- or B cell-mediated mechanisms and chronic disease progression. Overall, this model serves as a valuable tool for evaluating innate immune-targeted therapies and dissecting early inflammatory events in IBD pathogenesis.
- Simulates: The Anti-CD40 Antibody-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Model simulates acute innate immune-mediated colitis, resembling early-stage Crohn’s disease characterized by epithelial disruption, colonic inflammation, and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines. It is particularly suitable for studying inflammation driven by macrophages and dendritic cells in the absence of adaptive immunity.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is ideal for evaluating therapeutic candidates targeting innate immune pathways, including anti-inflammatory agents, cytokine inhibitors (e.g., anti-TNF-α, anti-IL-6), JAK inhibitors, and compounds modulating macrophage or dendritic cell activity.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Anti-CD40 Antibody-Induced IBD model, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight loss, diarrhea severity, colon length, and clinical disease activity index (DAI).
- Histopathology: colon tissue assessment for epithelial erosion, crypt loss, and immune cell infiltration.
- Immunohistochemistry: analysis of macrophage and dendritic cell infiltration (e.g., F4/80+, CD11c+ cells) and mucosal damage.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA or multiplex): measurement of innate immune-related cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, and IFN-γ in serum or colon homogenates.
- Flow cytometry: characterization of innate immune populations (e.g., monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells) in the colon and spleen.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: detection of inflammatory mediators and signaling pathway markers using RT-qPCR and Western blot.
This model enables the investigation of innate immune mechanisms in colitis. In addition to this and other IBD models, we specialize in developing customized models based on specific research objectives. Our expert team offers full support from study design to data interpretation, ensuring a robust and tailored solution for your project.
Related Services
In addition to the Anti-CD40 Antibody-Induced IBD model, we also offer other well-established methods for inducing IBD. These models allow for the exploration of different inflammatory pathways.
- TNBS/DNBS induced Colitis Model
- DSS induced Colitis Model
- Indomethacin induced Small Intestinal Inflammatory Model
- OXA induced Colitis Model
- Acetic Acid induced IBD Model
- IL-10 KO Mouse Spontaneous IBD Model
- CD4+CD45RBhi T Cells induced IBD Model
Advantages
- Comprehensive and Diverse Models: We offer a wide range of well-established and customizable animal models, including those for IBD, gastric ulcers, cancer, and other diseases, tailored to meet your specific research needs.
- Expertise in Drug Evaluation: Our team has extensive experience in preclinical drug evaluation, offering advanced techniques for measuring efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action across a range of disease models.
- Advanced Analytical Tools: We use cutting-edge technologies such as ELISA, Western blotting, RT-qPCR, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and histopathological analysis to provide in-depth insights into drug effects.
- Customization and Flexibility: We work closely with clients to design bespoke studies, including custom model development and protocol adjustments based on research goals.
- Full Support Throughout the Process: From experimental design to data analysis and report generation, our dedicated scientific team ensures high-quality, reproducible results, supporting your research every step of the way.
- Quality and Reliability: We adhere to the highest standards of quality control, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of results across all studies and models.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: What types of disease models do you offer?
A1: We provide a comprehensive range of well-established and customizable rodent models, including models for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), gastric ulcers, liver injury, fibrosis, cancer, and more.
-
Q2: Can you customize an animal model based on our study needs?
A2: Yes. Our team can develop and optimize custom models based on your specific requirements, literature references, or prior experimental data.
-
Q3: What parameters can you evaluate in IBD or colitis models?
A3: We can assess body weight, disease activity index (DAI), colon length, histopathological changes, immune cell infiltration, cytokine profiles, gene/protein expression, and more.
-
Q4: Do you assist with study design and protocol development?
A4: Absolutely. Our experienced scientists collaborate with you to design the most suitable experimental plan, including model selection, dosing strategies, and endpoints.
-
Q5: What sample types do you provide for downstream analysis?
A5: We offer tissues (colon, spleen, liver, etc.), blood, serum, stool, and other sample types for histology, molecular, or biochemical analyses.
Published Data
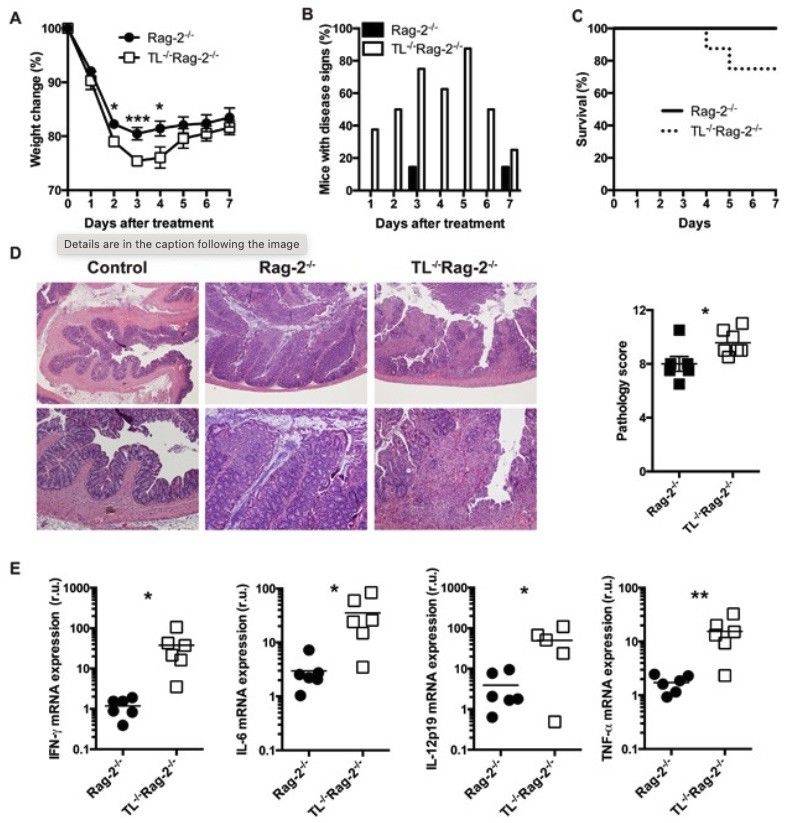 Fig. 1 Anti-CD40 antibody-mediated colitis in mice.1
Fig. 1 Anti-CD40 antibody-mediated colitis in mice.1
To investigate the role of iCD8α cells in intestinal inflammation, this article employed the anti-CD40-induced colitis model. Following treatment, Rag-2-/- mice exhibited rapid weight loss beginning on day 1, whereas TL-/-Rag-2-/- mice, which have reduced numbers of iCD8α cells, experienced even greater weight loss, particularly on days 3 and 4 (Fig. 1A). This exacerbated weight loss in TL-/-Rag-2-/- mice was accompanied by more severe clinical symptoms, including scruffiness, rectal bleeding, and diarrhea (Fig. 1B). Additionally, around 20% of the TL-/-Rag-2-/- mice succumbed to the inflammation by day 4, whereas all Rag-2-/- mice survived throughout the experiment (Fig. 1C). Histological analysis revealed that TL-/-Rag-2-/- mice also developed more pronounced colonic pathology compared to Rag-2-/- controls (Fig. 1D). To assess the early cytokine response, mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines were measured on day 2 post-treatment. TL-/-Rag-2-/- mice exhibited significantly higher expression of IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-12p19, and TNF-α mRNA, correlating with their more severe disease phenotype (Fig. 1E).
Reference
- Kumar, Aaram A et al. "Innate CD8αα+ lymphocytes enhance anti-CD40 antibody-mediated colitis in mice." Immunity, Inflammation and Disease vol. 5,2 (2017): 109-123. DOI:10.1002/iid3.146. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
