Acute Liver Injury Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established animal models to evaluate the pharmacological efficacy of treatments for acute liver injury. These models are induced by chemical, pharmacological, or surgical means, allowing for detailed assessments of liver function, tissue damage, and repair mechanisms. Our team provides expert support throughout the study, from experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring accurate and reliable results in your preclinical research.
Introduction
Acute liver injury (ALI) is a rapid and often severe liver damage caused by various insults, including drug toxicity, viral infections, ischemia, and exposure to environmental toxins. Common causes of ALI include acetaminophen overdose, alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and exposure to hepatotoxic drugs or chemicals. The condition can manifest with symptoms such as jaundice, coagulopathy, and liver dysfunction, and if left untreated, it may progress to acute liver failure, requiring transplantation. ALI is typically classified based on its underlying cause and severity. It can lead to inflammation, hepatocyte apoptosis, and necrosis, and may disrupt the liver's ability to detoxify the body and produce essential proteins. In some cases, recovery is possible if the liver can regenerate, while in others, it may result in permanent liver damage or failure.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of well-established rodent and non-rodent models for acute liver injury (ALI), including models induced by chemical toxins, viral infections, and ischemic injury. These models are meticulously developed to replicate the key aspects of human liver damage, providing a reliable platform for evaluating therapeutic candidates during the preclinical phase. Our models are equipped with detailed assessments of liver function, enzyme levels, histopathology, and molecular markers, enabling accurate evaluation of drug efficacy and mechanisms of action. Our team of experienced scientists will collaborate closely with you throughout the project, from experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring high-quality and consistent results. To learn more about the acute liver injury models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Model | Simulated Disease | Drug Evaluation Focus | Animal species |
| CCl4 induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Acute liver injury, liver fibrosis | Hepatoprotective drugs, anti-fibrotic agents, antioxidants | Mouse, Rat, NHPs |
| Concanavalin A (Con A) induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Acute autoimmune hepatitis | Immunomodulatory drugs, anti-inflammatory agents | Mouse |
| Polyinosinic:Polycytidylic Acid induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Viral hepatitis (mimics viral infection induced liver injury) | Antiviral agents, immune modulators, anti-inflammatory drugs | Mouse |
| Acetaminophen (APAP) induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Acetaminophen induced liver toxicity | Hepatoprotective agents, anti-apoptotic drugs, detoxifiers | Mouse |
| Alcohol induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) | Antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, hepatoprotective drugs | Mouse |
| Ischemia-Reperfusion induced Liver Injury Model | Liver ischemia-reperfusion injury (e.g., after liver transplantation) | Hepatoprotective agents, anti-inflammatory agents, cell survival drugs | Mouse |
| Alpha-Naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Cholestasis, bile duct injury | Anti-cholestatic agents, liver regeneration drugs, anti-inflammatory agents | Mouse |
| DDC (3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine) induced Acute Liver Injury Model | Cholestasis, bile duct obstruction | Anti-cholestatic drugs, hepatoprotective agents, fibrosis inhibitors | Mouse |
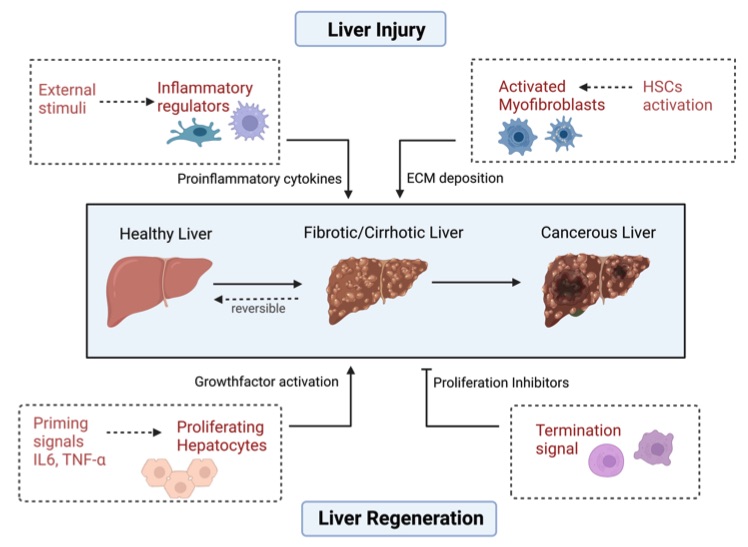 Fig. 1 Various factors influence liver homeostasis.1
Fig. 1 Various factors influence liver homeostasis.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in acute liver injury models, utilizing a range of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
General observations: Body weight, mortality rate, signs of jaundice, liver enlargement, and general health status.
Histopathological analysis: Liver tissue examination through H&E staining to assess the extent of necrosis, inflammation, and hepatocyte damage.
Biochemical assays: Measurement of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), bilirubin levels, and other serum biomarkers to assess liver function and injury severity.
Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Quantification of pro-inflammatory mediators like TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, which are indicative of the inflammatory response in liver injury.
Oxidative stress markers: Detection of malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione levels, reflecting oxidative damage and cellular stress in liver tissue.
Gene/protein expression profiling via RT-qPCR and Western blot: Analysis of key genes and proteins involved in liver injury, inflammation, and regeneration, such as caspases, NF-κB, and hepatic markers.
In addition to the established acute liver injury models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, informed by the latest literature and previous studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
Advantages
- Expertise and Experience: With years of experience in the field of preclinical research, our team of scientists brings a wealth of knowledge to ensure the highest quality of service. We are committed to delivering precise, reliable, and reproducible results that help accelerate your research.
- Tailored Solutions: We understand that every research project is unique. Our models are customizable to suit your specific therapeutic goals, enabling you to study a wide range of diseases and conditions with precision. We work closely with you to ensure your research needs are met at every stage.
- Comprehensive Model Portfolio: We offer a diverse array of well-established models, including disease-specific rodent models for a variety of conditions like liver injury, metabolic disorders, cancer, and more. Each model is rigorously validated to replicate key aspects of human disease, providing you with robust data for preclinical development.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We integrate the latest technologies, such as RT-qPCR, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and high-resolution imaging, to provide comprehensive, multi-dimensional data that enhances your ability to evaluate therapeutic efficacy accurately.
- High-Quality Data and Support: We offer not only state-of-the-art models but also expert assistance in experimental design, data analysis, and interpretation. Our scientists are dedicated to supporting you throughout the process, ensuring the success of your research project.
- Commitment to Innovation: We continuously invest in the development of novel models and techniques to stay at the forefront of scientific research, providing you with the most advanced tools for your studies.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of models do you offer for preclinical research?
We offer a wide range of well-established rodent and non-rodent models for diseases such as metabolic disorders, liver injury, cancer, neurological diseases, and more. Our models are designed to closely mimic human disease, enabling reliable evaluations of therapeutic candidates.
-
2. Can you customize the models based on our specific research needs?
Yes, we specialize in tailoring animal models to meet your unique research objectives. Whether you need specific disease progression, drug delivery systems, or evaluation parameters, we will customize the models to fit your requirements.
-
3. What types of measurements and analyses do you provide in your studies?
We offer comprehensive measurements, including general observations (e.g., body weight, survival rates), histopathology, biochemical assays (e.g., liver enzymes, cytokine profiling), gene/protein expression analysis (via RT-qPCR, Western blot), and more.
-
4. How do you ensure the quality and reliability of your results?
Our team follows strict protocols and industry best practices to ensure high-quality, reproducible results. We also use advanced technologies for data collection and analysis, ensuring accuracy and reliability throughout the study.
-
5. Do you provide assistance with experimental design?
Yes, our team of experienced scientists is available to collaborate with you in the planning and design of your experiments. We offer expert guidance to ensure that your research objectives are met and your experiments are conducted efficiently.
-
6. How long does it take to get results from your models?
The timeline depends on the complexity of the study and the specific model used. Typically, you will receive preliminary data within a few weeks, with final reports delivered after thorough data analysis and interpretation.
Published Data
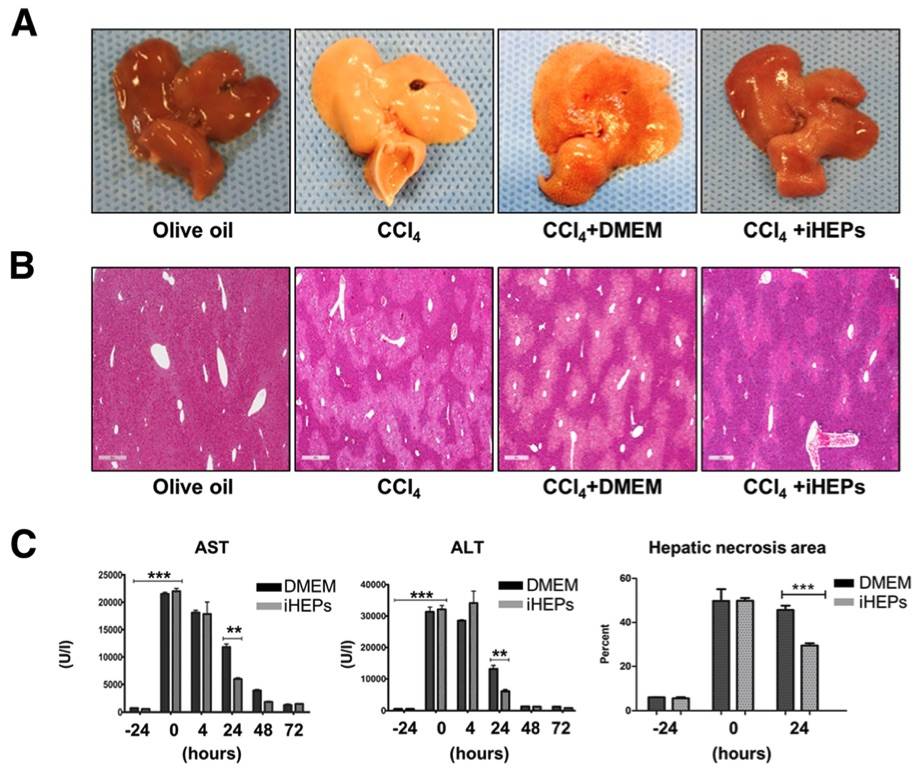 Fig. 2 CCl4 induced liver acute injury was significantly attenuated by iHEPs transplantation in BALB/c nude mouse.2
Fig. 2 CCl4 induced liver acute injury was significantly attenuated by iHEPs transplantation in BALB/c nude mouse.2
This article investigated the effects of intra-splenic transplantation of iHEPs on CCl4 induced acute liver injury. Gross findings revealed significant liver alterations following CCl4 injection, including a yellowish color, swelling, hard texture, and rough surface, compared to the control group, which exhibited a soft texture and smooth surface (Fig. 2a). Histological analysis via H&E staining of liver sections showed moderate necrosis localized to the centrilobular regions in the iHEPs-transplanted mice, with relatively preserved acinar structure, in contrast to the extensive damage observed in the CCl4 and CCl4 + DMEM groups (Fig. 2b). To quantify the degree of liver injury, we measured serum levels of AST and ALT, along with the extent of hepatic necrosis (Fig. 2c). CCl4 injection resulted in elevated AST and ALT levels, which were significantly reduced in the iHEPs transplantation group. Additionally, the necrotic area in the liver was smaller in the iHEPs group compared to the control (DMEM-only transplantation) group 24 hours post-transplantation. These findings suggest that intra-splenic transplantation of iHEPs effectively mitigates CCl4 induced acute liver injury, as evidenced by both histological and serum markers.
References
- Hora, Shainan, and Torsten Wuestefeld. "Liver Injury and Regeneration: Current Understanding, New Approaches, and Future Perspectives." Cells vol. 12,17 2129. 22 Aug. 2023, DOI:10.3390/cells12172129. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Park, Suhyun et al. "The therapeutic potential of induced hepatocyte-like cells generated by direct reprogramming on hepatic fibrosis." Stem cell research & therapy vol. 10,1 21. 11 Jan. 2019, DOI:10.1186/s13287-018-1127-3. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
