Fe₂O₃ induced Arterial Thrombosis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Arterial thrombosis, the formation of blood clots within arteries, is a critical pathological event underlying severe cardiovascular conditions such as myocardial infarction (heart attack), ischemic stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. These conditions represent a major global health burden, necessitating the development of highly effective and safe antithrombotic therapies.
At Creative Biolabs, we understand the complexities of thrombus formation and are dedicated to providing a variety of well-established, physiologically relevant rodent models to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of novel antithrombotic compounds.
Fe2O3-Induced Arterial Thrombosis Model
The Fe2O3-induced arterial thrombosis model stands as a sophisticated and highly controlled in vivo platform for investigating the intricate mechanisms of arterial thrombus formation and for evaluating the therapeutic potential of new antithrombotic agents. This model leverages the unique procoagulant properties of iron oxide nanoparticles to precisely initiate and control thrombotic events.
Model Construction Steps
The construction of the Fe2O3-induced arterial thrombosis model is designed for precision and reproducibility, allowing for fine-tuned control over the thrombotic stimulus. The core strategy involves the localized application of iron oxide nanoparticles to an arterial wall, followed by a controlled activation process.
01Arterial Exposure
A target artery in a rodent model (e.g., carotid artery, femoral artery) is surgically exposed while maintaining physiological blood flow.
02Localized Delivery
Fe2O3 nanoparticles are precisely delivered to a defined arterial wall area, typically via direct topical application or controlled intravenous injection coupled with a localized stimulus (e.g., photochemical reaction) to induce endothelial damage and nanoparticle adhesion.
03Thrombus Induction
This localized presence initiates a controlled cascade of platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation, forming a platelet-rich thrombus. Parameters like Fe2O3 concentration or exposure duration can be precisely modulated to control thrombus size, stability, and formation rate.
04Monitoring and Evaluation
Thrombus formation and stability are monitored in real-time using various techniques, and the efficacy of test compounds is assessed.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- Targeted and Localized Control: Enables precise induction of thrombosis at a specific arterial site, mimicking physiological conditions more closely than generalized injury models.
- Reproducibility and Consistency: Offers high experimental reproducibility due to controlled stimulus, leading to statistically robust data and reduced animal usage.
- Physiological Relevance: Induces platelet-rich thrombi, which are characteristic of arterial thrombosis, making it highly relevant for evaluating antithrombotic drugs.
- Mechanistic Insights: Facilitates the study of specific molecular and cellular events, including platelet aggregation, contact system activation, and the release of pro-angiogenic factors.
Limitations:
- Biocompatibility: The potential for pristine iron oxide nanoparticles to induce systemic effects, such as contact system activation leading to hypotension or long-term angiogenesis, requires careful consideration and biocompatibility assessment.
- Technical Expertise: Requires specialized surgical and imaging expertise for precise nanoparticle delivery and accurate data acquisition.
- Cost: Advanced imaging and nanoparticle synthesis can contribute to higher experimental costs compared to simpler models.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs' state-of-the-art evaluation platform provides comprehensive analytical capabilities to support your thrombosis research. Our laboratories are equipped with advanced instrumentation for biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and cutting-edge imaging analyses.
Key Test Parameters:
- Thrombus Formation & Stability: Time to occlusion, thrombus size, stability (e.g., re-perfusion time), and embolization events.
- Platelet Function: Platelet count, aggregation assays, activation markers (e.g., P-selectin expression, GP IIb/IIIa activation).
- Coagulation & Fibrinolysis Markers: Plasma levels of thrombin-antithrombin (TAT) complexes, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), D-dimer.
- Inflammation Markers: Expression of endothelial adhesion molecules (VCAM-1, P-selectin), cytokine/chemokine profiles (e.g., IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α), myeloperoxidase (MPO).
- Vascular Histopathology: Endothelial integrity, thrombus composition (platelet-rich vs. fibrin-rich), inflammatory cell infiltration, plaque morphology.
- Molecular Imaging: MRI and Near-Infrared Fluorescence (NIRF) for non-invasive visualization and quantification of thrombus, inflammation, and plaque characteristics.
- Growth Factors: Levels of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Applications
- Simulated Diseases: Simulates acute arterial thrombosis (myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke), atherosclerosis, plaque vulnerability, vascular inflammation, and ischemia-reperfusion injury.
- Drug Evaluation: Evaluates novel antithrombotic (antiplatelet, anticoagulant, fibrinolytic), anti-inflammatory, and plaque-stabilizing therapies.
- Treatment Modalities: Supports pharmacological (oral, IV, local) and combination therapies, alongside biomarker discovery and validation for diagnostic/prognostic purposes.
Related Thrombosis Models
- Transient Blood Flow Occlusion induced Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Model
- Thrombin induced Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Model
- Arteriovenous Fistula Thrombosis Model
- Foreign Matter induced Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Ferric Chloride induced Thrombosis Model
Our Advantages
- Customized Solutions: Flexible study designs tailored to your specific research objectives and drug development pipeline.
- Cutting-Edge Facilities: Access to advanced imaging, biochemical, and histopathological platforms for comprehensive data generation.
- Rigorous Quality Assurance: Adherence to the highest scientific and ethical standards, ensuring reliable and reproducible results.
- Accelerated Timelines: Our efficient processes and robust models help expedite your research, leading to faster decision-making and reduced costs.
- Safety-Conscious Protocols: Deep understanding and protocols for assessing nanoparticle biocompatibility and mitigating potential adverse effects.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs' unparalleled expertise and advanced Fe2O3-induced arterial thrombosis model to propel your cardiovascular research forward. We provide comprehensive services from study design to data interpretation. Contact us today to discuss your project needs.
FAQs
-
Q1: How do you ensure the reproducibility of results with this model?
A: Reproducibility is central to our methodology. We standardize nanoparticle synthesis, delivery, and thrombotic stimulus parameters like concentration, exposure, and light intensity. Our experienced technicians follow rigorous protocols, utilizing sensitive quantitative imaging and biochemical assays to minimize variability, ensuring robust and reliable data.
-
Q2: Can this model be used to evaluate both antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs?
A: Yes, the Fe2O3-induced model generates platelet-rich thrombi, ideal for antiplatelet agents. Concurrently, coagulation cascade activation makes it suitable for anticoagulants. We customize studies to comprehensively assess your therapeutic candidates' mechanisms and efficacy in preventing or resolving arterial clots.
-
Q3: What types of imaging techniques are compatible with the Fe2O3 nanoparticles in this model?
A: Iron oxide nanoparticles serve as excellent MRI contrast agents, offering superior sensitivity over gadolinium-based alternatives for detailed anatomical and functional imaging of thrombus and vasculature. Fluorescently labeled nanoparticles also enable Near-Infrared Fluorescence (NIRF) imaging for multimodal assessment of plaque vulnerability and inflammation. These non-invasive techniques provide invaluable real-time data.
-
Q4: How do you handle data analysis and reporting for studies using this model?
A: We offer comprehensive data analysis and reporting. Our expert team processes raw imaging, biochemical, and histological data via validated pipelines. Results are presented in clear, publication-ready reports, including statistical analyses and expert interpretations. We also provide consultative support to help you understand findings and guide next research steps.
-
Q5: Is it possible to integrate this model with other cardiovascular disease models offered by Creative Biolabs?
A: Our models are flexible. While powerful alone, the Fe2O3-induced arterial thrombosis model integrates well with other rodent cardiovascular disease models. For example, it can study thrombus formation on pre-existing atherosclerotic plaques, offering a more complex, clinically relevant scenario. We encourage discussing integrated approaches to maximize research insights.
Published Data
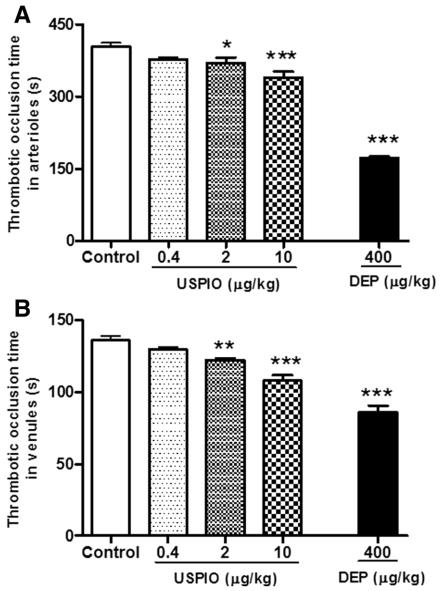 Fig.1 Effect of USPIO on thrombosis in pial arterioles and venules.1
Fig.1 Effect of USPIO on thrombosis in pial arterioles and venules.1
In a typical study, the intravenous administration of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO) in mice induced a prothrombotic effect in pial arterioles and venules in vivo, alongside an increase in plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). The project results also indicated that USPIO caused a shortening of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and prothrombin time (PT), and led to increased cardiac levels of oxidative stress markers and DNA damage in the heart.
Reference
- Nemmar, Abderrahim et al. "Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles acutely promote thrombosis and cardiac oxidative stress and DNA damage in mice." Particle and fibre toxicology vol. 13,1 22. 30 Apr. 2016. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-016-0132-x
For Research Use Only.
