MDCK Permeability
Creative Biolabs is an expert in the field of drug discovery and development. We provide reliable MDCK and MDR1-MDCK permeability assay services to determine drug permeability.
The Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell is an epithelial cell line of canine kidney origin which has low expression of transporter proteins and low metabolic activity. Compared to Caco-2 cell, MDCK cell grows and differentiates more quickly. Therefore, it provides an attractive alternative to Caco-2 cells to assess the human intestine barrier.
MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay for P-glycoprotein Substrate Identification
In addition to predicting passive permeability, MDCK cells can be used to study drug efflux and active transport, usually efflux by P-gp (P-glycoprotein, a well-recognized efflux transporter in many tissues, i.e. brain, kidney and intestine). This can be achieved by MDR1-MDCK permeability assay.
MDR1 gene encodes for the human P-gp efflux protein and this gene can be transfected into MDCK cells to form MDR1-MDCK cell line. The MDR1-MDCK cell line is a valuable tool to identify P-gp substrates and investigate P-gp efflux as it avoids the complexities of multiple transporters by specifically focusing on P-gp. Besides, it can help characterize the mechanism of drug efflux and highlight drug permeability potential issues at an early stage.
MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay Experimental Protocol
To determine the role of human P-gp, it is recommended to analyze a test compound on both wild type MDCK and MDCK-MDR1 cell monolayer. The wild type MDCK uses as a negative control in confirming the role of human P-gp in the MDR1-MDCK permeability assay. The typical experimental procedures are described below:
- MDCK cells and MDR1-MDCK cells are seeded on Multiscreen 24- or 96-well plates for 4 days to form a confluent monolayer.
- Monolayer integrity is checked with TEER (Transepithelial Electrical Resistance) measurement.
- Dosing solution containing test compound is washed with HBSS transport buffer at pH 7.4.
- The test compound is added to the apical side of the membrane to measure the permeation from apical to basolateral (A-B). The assay was performed in the reverse basolateral to apical direction (B-A). The fluorescent integrity marker Lucifer yellow was also included in the dosing solution for both directions.
- Test compound permeability was assessed in duplicate at 37°C, 5% CO2, with a relative humidity of 95% for over 1 h incubation.
- Compounds were quantified by LC-MS/MS.
- A Leakage of monolayer (Lucifer Yellow) is determined by fluorescent reader.
Data Analysis
The permeability coefficient (Papp) is calculated from the following equation:
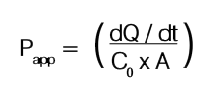 dQ/dt: The rate of permeation of the drug across the cells
dQ/dt: The rate of permeation of the drug across the cellsC0: The donor compartment concentration at time zero
A: The area of the cell monolayer.
An asymmetry index (AI) was calculated from the following equation:
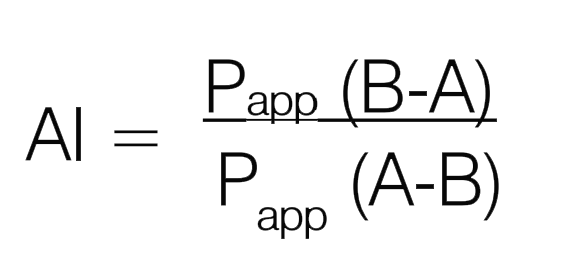 Papp(B-A): basolateral to apical Papp
Papp(B-A): basolateral to apical PappPapp(A-B): apical to basolateral Papp
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality MDR1-MDCK permeability assay to predict human intestinal permeability and to investigate drug efflux. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
For Research Use Only.
