Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established animal models to evaluate acute kidney injury (AKI) drug efficacy, such as the gentamicin Induced model, cisplatin Induced model, and renal ischemia-reperfusion model. These models represent different forms of AKI and are ideal for testing potential therapeutic agents.
Introduction
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is a rapid decline in kidney function, characterized by a sudden decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the accumulation of waste products such as creatinine and urea in the blood. AKI can be caused by a variety of factors, including ischemia, toxins, infections, and medications. There are three main types of AKI: prerenal, intrinsic, and postrenal, each involving different underlying mechanisms of kidney damage. Prerenal AKI is due to decreased blood flow to the kidneys, intrinsic AKI results from damage to the kidney tissue itself, and postrenal AKI is caused by obstruction of the urinary tract.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Models
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established animal models for Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), including models for gentamicin Induced renal failure, cisplatin Induced kidney injury, glycerol induced acute renal failure, contrast agent Induced AKI, and more. These models are carefully designed to mimic human AKI and allow for accurate preclinical assessment of therapeutic candidates. Our comprehensive evaluations cover multiple parameters, enabling the precise evaluation of potential nephroprotective and therapeutic drugs. Our team of experienced scientists will collaborate with you throughout your project, from model selection to data interpretation, ensuring high-quality results. To learn more about the available rodent AKI models for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Acute Kidney Injury Model | Simulated Diseases | Evaluated Drugs | Animal species |
| Gentamicin Induced Acute Renal Failure Model | Nephrotoxicity, Acute Kidney Injury | Nephroprotective agents (e.g., ACE inhibitors, angiotensin blockers), Anti-inflammatory agents | Mouse, Rat |
| Cisplatin Induced Acute Renal Injury Model | Cisplatin Induced nephropathy, AKI | Nephroprotective drugs (e.g., N-acetylcysteine, antioxidants), Anti-inflammatory agents, Renal recovery drugs | Mouse, Rat |
| Glycerol Induced Acute Renal Failure Model | Rhabdomyolysis, Acute Kidney Injury | Anti-inflammatory agents, Antioxidants, Nephroprotective drugs | Rat |
| Contrast Agent Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Contrast Induced nephropathy (CIN) | Contrast agents, Nephroprotective drugs (e.g., fluids, antioxidants) | Mouse, Rat |
| Folic Acid Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Folic acid Induced nephropathy, AKI | Immunosuppressive drugs, Nephroprotective agents, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Mouse, Rat |
| Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Sepsis Induced kidney injury, AKI | Anti-inflammatory agents, Sepsis-modifying drugs, Immune-modulating agents | Mouse, Rat |
| Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Sepsis, Septic AKI | Anti-inflammatory drugs, Antibiotics, Sepsis-modulating agents | Mouse, Rat |
| Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Lipid Induced nephropathy, AKI | Anti-inflammatory agents, Lipid-lowering drugs | Mouse, Rat |
| Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Growth hormone Induced AKI | Growth hormone antagonists, Nephroprotective agents | Mouse, Rat |
| Anti-TSHR Antibody Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Autoimmune thyroid disease Induced AKI | Immunosuppressive drugs, Antibody therapies | Mouse, Rat |
| Aristolochic Acid A Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model | Aristolochic acid nephropathy, AKI | Renal protective agents, Anti-inflammatory agents, Antioxidants | Mouse, Rat |
| Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR) Model | Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury, AKI | Nephroprotective agents, Ischemia-recovery drugs, Anti-inflammatory agents | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, NHPs |
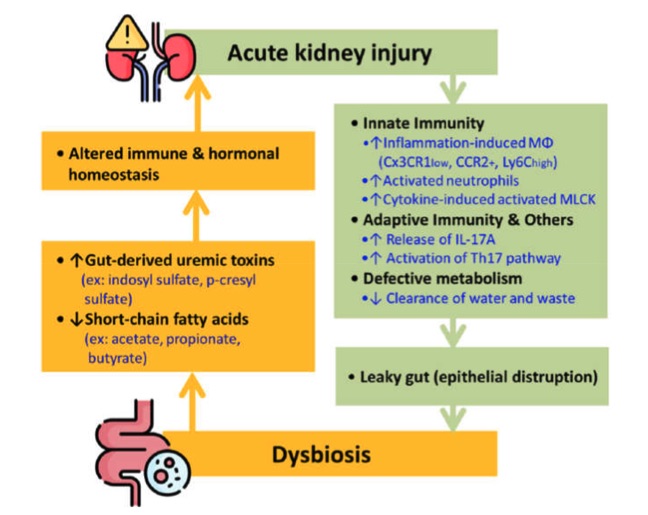 Fig. 1 The bidirectional interplay between AKI and gut dysbiosis.1,3
Fig. 1 The bidirectional interplay between AKI and gut dysbiosis.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Rabbit, Dog, NHPs.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in AKI models, utilizing advanced techniques such as:- General observations: Body weight, survival rate, renal function markers (e.g., serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen)
- Histopathology: Assessment of tubular damage, glomerular injury, and immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in kidney tissues
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory mediators like TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and kidney injury markers (e.g., NGAL, KIM-1)
- Hematology analysis: Blood counts, serum biomarkers (e.g., renal function indicators)
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot for markers of renal injury, inflammation, and repair (e.g., TGF-β, fibronectin)
In addition to the established AKI models, our team can develop tailored models based on your specific research needs, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to autoimmune nephropathy models, we also offer a wide range of other disease models for comprehensive drug evaluation and therapeutic development. These models are designed to address various therapeutic areas.
- Autoimmune Nephropathy Models
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Models
- Metabolic Nephropathy Models
- Hyperuricemia Models
- Kidney Transplantation Models
- Cystitis Models
Our advantages
- Expertise: Our team is experienced in providing high-quality AKI models for preclinical research, with extensive knowledge in renal biology and drug development.
- Comprehensive Services: We assist in every phase of your research, from model selection and experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring reliable results.
- Validated Models: Our AKI models are thoroughly validated, ensuring their relevance and accuracy for evaluating nephroprotective therapies.
- Customized Solutions: We offer tailored model development to fit your specific research goals, maximizing the relevance of our services to your project.
- Reliable Results: Our advanced technology platforms and quality assurance protocols ensure reproducible and accurate findings for your drug efficacy evaluation.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of AKI models do you offer?
We offer a variety of AKI models, including gentamicin Induced, cisplatin Induced, glycerol Induced, and ischemic models, among others.
-
2. Can the AKI models be customized?
Yes, we can tailor the AKI models to your specific research needs and therapeutic evaluations.
-
3. What measurements are used to assess drug efficacy in AKI models?
We offer a comprehensive range of measurements, including renal function markers, histopathology, cytokine profiling, and gene expression analysis.
-
4. How can I get started with your AKI models?
Simply contact us with your research requirements, and our team will assist you in model selection, experimental design, and data analysis to ensure the success of your study.
Published Data
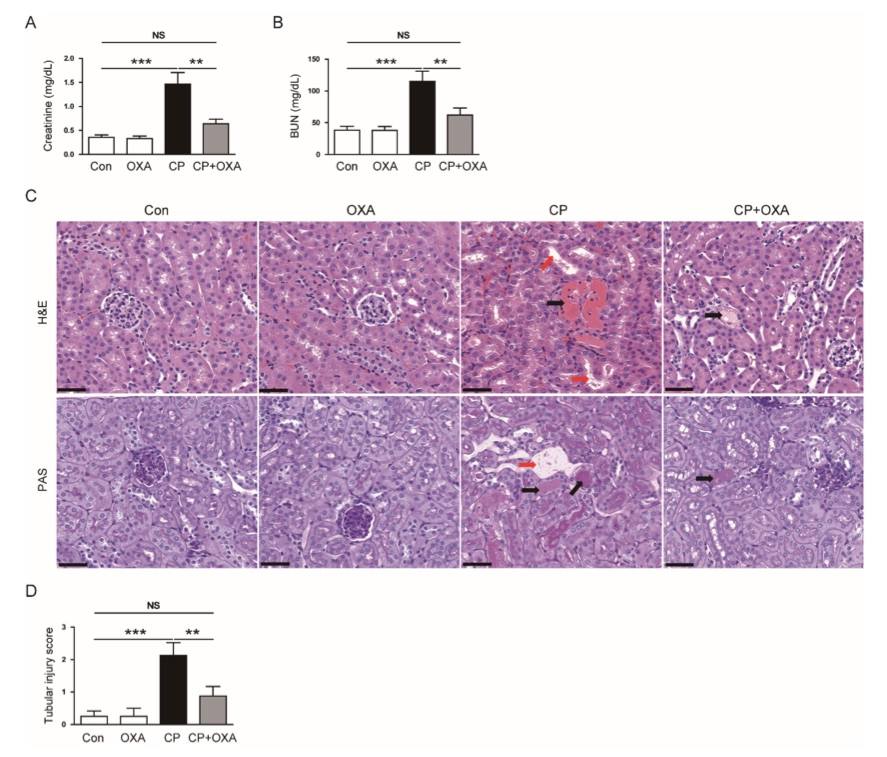 Fig. 2 Effects of orexin A (OXA) on renal dysfunction and histological changes in mice injected with cisplatin.2,3
Fig. 2 Effects of orexin A (OXA) on renal dysfunction and histological changes in mice injected with cisplatin.2,3
Mice injected with cisplatin showed elevated serum creatinine and BUN concentrations. Treatment with OXA significantly reduced the elevated levels of both kidney function markers (Figure 2A, B). To assess the histopathological changes induced by cisplatin, a histological examination was conducted. Mice treated with cisplatin displayed notable abnormalities, including tubular dilation and cast formation. These histological changes were markedly alleviated following OXA treatment (Figure 2C, D).
References
- Chou, Yu-Ting et al. "Acute Kidney Injury and Gut Dysbiosis: A Narrative Review Focus on Pathophysiology and Treatment." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 23,7 3658. 26 Mar. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073658
- Jo, Jungmin et al. "Protective Effects of Orexin A in a Murine Model of Cisplatin Induced Acute Kidney Injury." Journal of Clinical Medicine vol. 11,23 7196. 3 Dec. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237196
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
