- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
Peripheral Vascular Disease Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) represents a significant global health challenge, characterized by the narrowing of arteries that supply blood to the limbs, most commonly the legs. This condition, often driven by atherosclerosis, leads to reduced blood flow, causing debilitating pain, impaired mobility, and a heightened risk of non-healing wounds, gangrene, and limb amputation. The escalating prevalence of PVD, fueled by an aging population and increasing rates of diabetes and obesity, underscores the urgent need for advanced therapeutic solutions.
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive suite of well-established PVD models, enabling precise evaluation of disease progression and the efficacy of novel interventions.
Available Peripheral Vascular Disease Models at Creative Biolabs
PVD models are indispensable for unraveling PVD's complex pathophysiology and rigorously testing new therapeutic strategies. These models simulate various human disease aspects, from acute ischemia to chronic inflammation, in controlled, reproducible environments. Our construction emphasizes translational relevance, ensuring findings translate clinically and provide reliable data for drug discovery, target validation, and mechanism elucidation.
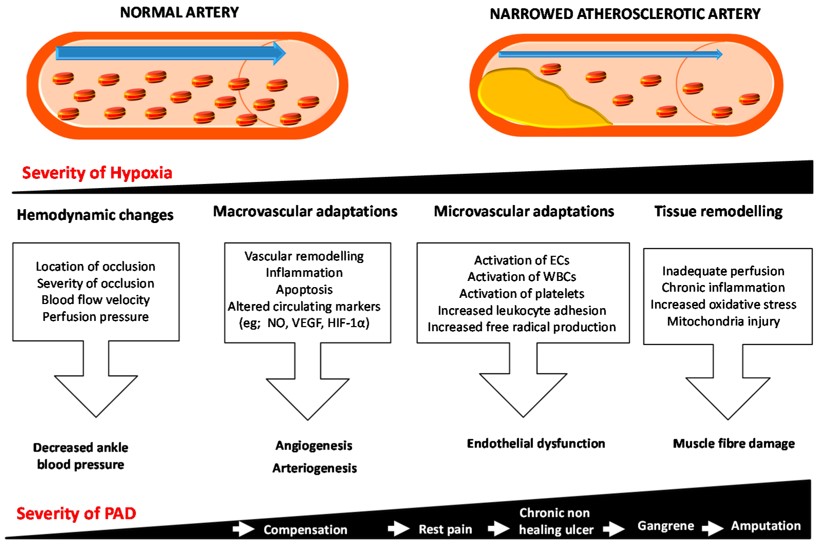 Fig.1 The response to ischemia in PAD.1
Fig.1 The response to ischemia in PAD.1
At Creative Biolabs, our team provides the following PVD models for studying disease mechanisms and testing drugs:
-
Femoral Artery Ligation induced PVD Model in Lower Limbs
- Modeling: This widely used model surgically ligates or excises the femoral artery in rodents, inducing acute hindlimb ischemia. It mimics reduced blood flow, allowing a comprehensive study of collateral formation, muscle regeneration, and functional recovery, crucial for evaluating pro-angiogenic and regenerative therapies.
- Animal species: Rat, Rabbit
-
Sodium Laurate induced Vasculitis Mode
- Modeling: This specialized rat model induces peripheral arterial vasculitis, serving as an excellent platform for inflammatory vascular conditions like thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO). Researchers assess inflammatory response, vascular damage, blood rheology, and coagulation, gaining critical insights into inflammatory PVD drivers and potential treatments.
- Animal species: Rat, Rabbit
-
Sodium Laurate induced Lower Limb Gangrene Model
- Modeling: Building on the vasculitis model, this severe manifestation uses specific sodium laurate protocols to induce extensive vascular inflammation and tissue necrosis, culminating in gangrene. It is invaluable for studying severe inflammatory PVD, evaluating interventions to prevent tissue loss, and understanding disease progression.
- Animal species: Rabbit
Evaluation Platform
To thoroughly assess the efficacy of new therapeutic agents in treating PVD, Creative Biolabs provides an extensive range of evaluation capabilities. We offer measurements of various parameters, including but not limited to:
- Biochemical Markers: Inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress indicators.
- Molecular Analyses: Gene expression, protein levels.
- Cellular Assessments: Cell viability, proliferation, migration.
- Histopathological Examinations: Vessel morphology, fibrosis, inflammation.
- Behavioral Tests: Limb function, pain assessment.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Laser Doppler perfusion imaging, micro-CT for vascular density.
Applications
Disease Simulation: Our models precisely simulate a spectrum of peripheral vascular conditions, including chronic limb ischemia, inflammatory vasculitis, and severe forms leading to gangrene, providing accurate representations of human disease states.
Drug Evaluation: We facilitate the rigorous evaluation of novel pharmacological agents, including pro-angiogenic compounds, anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-thrombotic agents, and compounds targeting oxidative stress or metabolic dysfunction.
Therapy Assessment: Our platforms are ideal for assessing the efficacy and safety of diverse therapeutic modalities, encompassing small molecule drugs, cell-based therapies (e.g., stem cells), gene therapies, and innovative medical devices designed for vascular repair and regeneration.
Related Cardiovascular Models
Our Advantages
- Extensive Animal Species: We offer a wide selection of animal models, including various rodent strains and larger animal options, to best suit your specific research requirements.
- Integrated Evaluation: Our capabilities span one-stop in vivo and in vitro evaluation, providing a holistic view of therapeutic effects from cellular mechanisms to systemic outcomes.
- Expert Team & Quality Systems: Our professional team comprises highly experienced biologists and researchers, supported by a robust and perfect management system ensuring scientific rigor, data integrity, and project efficiency.
Work with Us
Inquiry Stage
Project Start
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
Project Progress
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
Project Completion
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
After-Sales Support
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Leverage Creative Biolabs' extensive experience and advanced modeling capabilities to accelerate your PVD research. We are committed to providing the precise, high-quality preclinical data necessary to advance your therapeutic candidates. Contact us today for a confidential consultation to discuss how our services can best support your project objectives.
FAQs
-
Q1: What is the primary advantage of using rodent models for PVD research compared to larger animal models?
A: Rodent models, particularly mice and rats, offer significant benefits due to their genetic tractability, which allows for the creation of specific knockout or transgenic lines, and their cost-effectiveness. Their smaller size also makes them suitable for higher-throughput studies and easier handling within research facilities, accelerating initial screening and mechanistic investigations.
-
Q2: Can your PVD models be adapted to study diabetic complications in peripheral arteries?
A: Absolutely. We frequently combine our hindlimb ischemia models with established diabetic models, such as diet-induced obesity or streptozotocin-induced diabetes. This allows for the investigation of impaired angiogenesis, delayed wound healing, and other specific challenges associated with PVD in a diabetic context, closely mimicking the human condition.
-
Q3: What types of therapeutic agents can be tested using your peripheral vasculitis models?
A: Our peripheral vasculitis models are ideal for evaluating a wide range of therapeutic agents, including anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, antioxidants, and novel compounds designed to modulate immune responses or coagulation pathways. These models help in understanding how different interventions can mitigate vascular inflammation and its downstream effects.
-
Q4: Do you offer custom model development if our research requires a unique PVD model?
A: Yes, we specialize in custom model development. Our experienced scientific team works closely with clients to understand their specific research needs and design bespoke models that accurately reflect the desired disease pathology or therapeutic challenge, ensuring the most relevant and impactful preclinical data.
-
Q5: Can your evaluation platform differentiate between various mechanisms of action for therapeutic compounds?
A: Our comprehensive evaluation platform is designed to provide granular insights into mechanisms of action. By combining biochemical, molecular, cellular, and histopathological analyses, we can often elucidate how a compound influences specific pathways, such as angiogenesis, inflammation, or oxidative stress, helping to differentiate its primary therapeutic effects.
-
Q6: What kind of support do you offer beyond just providing the models?
A: We offer end-to-end support, acting as an extension of your research team. This includes expert consultation during study design, meticulous execution of experiments, comprehensive data analysis and interpretation, and detailed reporting. We are committed to collaborative partnerships that drive successful outcomes for your PVD research.
Published Data
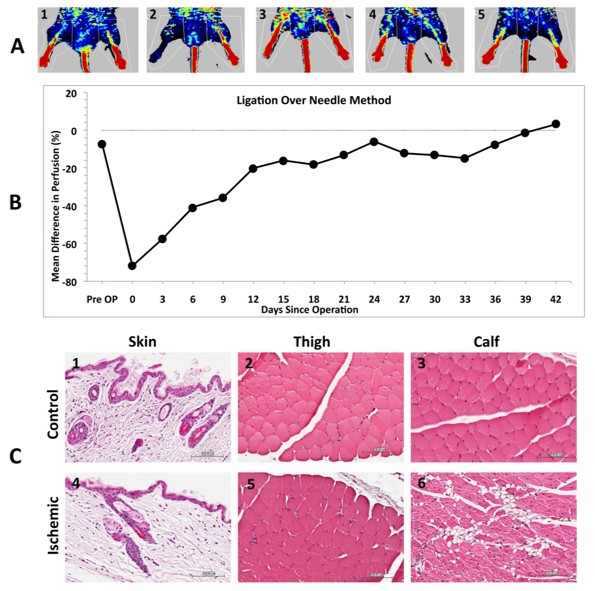 Fig.2 Ligation-induced PAD model.2
Fig.2 Ligation-induced PAD model.2
A notable example involves the use of the femoral artery ligation-induced PVD model in mice to investigate the duration of post-operative ischemia and patterns of blood flow recovery under different ligation conditions. Researchers compared "ligation over needle" and "transfixation" methods in male BALB/c mice, assessing perfusion using Laser Doppler Perfusion Imaging over 42 days. The project successfully characterized the distinct recovery patterns for each method, noting that perfusion remained below baseline for extended periods, and confirmed the calf muscle as the optimal sample site for representative histological results.
References
- Krishna, Smriti Murali et al. "A review of the pathophysiology and potential biomarkers for peripheral artery disease." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 16,5 11294-322. 18 May. 2015, DOI:10.3390/ijms160511294. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Al-Mubarak, Husain A et al. "Effects on duration of post-operative ischemia and patterns of blood flow recovery in different conditions of mouse hind limb ischemia." Vascular cell vol. 3,1 14. 14 Jun. 2011, DOI:10.1186/2045-824X-3-14. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
