Photochemically induced Ischemic Stroke Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Ischemic stroke represents a critical global health challenge, leading to significant disability and mortality. Its intricate pathophysiology demands precise preclinical models to effectively decipher disease mechanisms and accelerate the development of innovative therapeutic strategies.
Creative Biolabs, with its extensive expertise, offers a diverse portfolio of well-established stroke models designed to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of novel interventions.
Photochemically Induced Ischemic Stroke Model
The photochemically induced ischemic stroke model is a highly controlled, reproducible, and relatively non-invasive method for inducing focal cerebral ischemia. It serves as an invaluable tool for translational studies, facilitating a deeper understanding of stroke pathology and the development of new therapies. This model is particularly adept at mimicking thrombotic stroke, the most common form of human ischemic stroke, by precisely inducing a localized vascular occlusion.
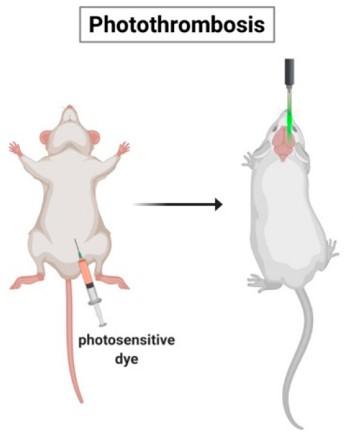 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the photothrombotic stroke model.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the photothrombotic stroke model.1
Model Construction Steps
The development of this sophisticated model hinges on a targeted photochemical reaction, enabling selective occlusion within the cerebral microvasculature. This innovative approach facilitates the creation of highly localized and precisely controllable lesions, circumventing the need for extensive or invasive surgical procedures.
01Animal Preparation and Anesthesia
Rodents are anesthetized, with core body temperature rigorously maintained at 37°C for physiological stability.
02Vascular Access Establishment
The left femoral vein is surgically exposed and cannulated with a polyethylene catheter, providing a secure route for photosensitive dye administration.
03Precise Stereotactic Positioning
Animals are secured in a stereotactic frame. The scalp is incised to expose the skull, identifying anatomical landmarks. For enhanced spatial control and reduced light scattering, a small cranial window (e.g., 3mm×6mm) may be created over the target cortical area (e.g., somatosensory cortex).
04Targeted Laser Illumination and Dye Infusion
A focused cold light laser (e.g., 532nm wavelength, 1.5mm diameter) is stereotactically directed onto the skull or cranial window for 20minutes. During the initial 2minutes, the photosensitive dye, Rose Bengal (10mg/mL saline, 2mL/kg body weight), is slowly injected intravenously, with the dose adjusted for desired lesion characteristics.
05Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After laser illumination and dye injection, the femoral catheter is withdrawn, and the skin incision is sutured. Animals recover in a controlled environment with ad libitum food and water. Sham controls undergo the same procedure, omitting laser illumination.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Reproducibility: Delivers consistent infarct size and location, minimizing variability.
- Focal and Targeted Lesions: Creates small, well-delimited infarcts in specific cortical regions.
- Minimally Invasive: Avoids craniotomy and mechanical vessel manipulation (though a small window can be used for precision), reducing animal stress.
- Low Mortality: Exhibits a procedure-associated mortality rate typically below 10%.
- Versatile Lesion Size: Allows for precise modulation of infarct volume by adjusting laser parameters and dye concentration.
- Platelet Aggregation: Directly involves platelet aggregation, a key aspect of clinical ischemic events.
Limitations:
- Atypical Edema Dynamics: Can induce early vasogenic edema and severe vessel wall effects, which may not fully reflect the typical cytotoxic-to-vasogenic edema progression seen in human stroke.
- Mild to Moderate Deficits: Due to cortical location and smaller lesion size, sensorimotor deficits are often less severe than in larger stroke models, potentially requiring more sensitive behavioral tests.
Evaluation Platform
Creative Biolabs provides a robust evaluation platform to comprehensively assess the effects of interventions in the photochemically induced ischemic stroke model. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team enable precise biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, behavioral, and advanced imaging analyses.
Key Test Indicators:
- Infarct Volume Quantification: TTC staining, MRI (T2WI, DWI).
- Neurological Deficit Scoring: Comprehensive neurological assessments.
- Behavioral Assessments: Rotarod, grip strength, cylinder test, adhesive tape removal test, beam balance test, Morris Water Maze (for cognitive deficits).
- Histological & Immunohistochemical Analysis: Neuronal viability (NeuN), glial activation (GFAP, CD68), angiogenesis (vWF, SMA), apoptosis, neurogenesis, dendritic/axonal plasticity, inflammatory response.
- Molecular Biology Techniques: Western blot, qPCR, ELISA.
- Advanced Imaging: MRI (T2WI, DWI, PWI for CBF), PET (18F-FDG for glucose metabolism), laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI for cerebral vasculature and CBF).
- Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Integrity: Evans Blue (EB) dye staining.
Applications
- Modeling Thrombotic Stroke: This model precisely simulates focal ischemic stroke, particularly common thrombotic events. It is crucial for understanding clot formation, microvascular occlusion, and immediate pathological cascades, providing a highly relevant platform for studying disease initiation and progression.
- Evaluating Novel Therapeutics: This model can be used to rigorously assess diverse therapeutic agents, including neuroprotective, thrombolytic, anti-thrombotic, and anti-inflammatory compounds. Efficacy is measured by evaluating infarct volume reduction, neuronal function preservation, and modulation of key molecular pathways.
- Assessing Regenerative Therapies: The model excels in exploring cell-based, gene, and other neuroregenerative strategies. Researchers can investigate their potential to promote intrinsic repair mechanisms like neurogenesis, angiogenesis, axonal sprouting, and synaptic plasticity, ultimately aiming for enhanced chronic functional recovery.
- Advancing Fundamental Research: Beyond therapeutic evaluation, this model facilitates in-depth investigation into stroke pathophysiology. This includes understanding acute/chronic injury phases, cell roles in neuroinflammation, mechanisms of structural/functional plasticity (e.g., cortical reorganization), and discovery/validation of novel biomarkers for detection and prognosis.
Related Stroke Models
- tMCAO Model
- pMCAO Model
- Collagenase induced Hemorrhagic Stroke Model
- Sodium Laurate induced Cerebral Microvascular Injury Model
Our Advantages
- Customized Study Design: Protocols meticulously tailored to your unique research objectives.
- Standardized Procedures: Rigorous adherence to established, validated protocols ensuring consistent and reliable data.
- Comprehensive Endpoint Analysis: Access to a broad spectrum of advanced analytical techniques and readouts.
- Expert Data Interpretation: In-depth analysis and clear, actionable reporting to inform your research decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: All studies conducted in strict accordance with ethical guidelines and industry best practices.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to accelerating your stroke research endeavors. By providing precise and reliable preclinical services utilizing the photochemically induced ischemic stroke model, we aim to support your journey from discovery to clinical impact. Please contact us to discuss how our expertise can benefit your next project.
FAQs
-
Q1: How does the photochemically induced stroke model compare to other common stroke models, like MCAO, in terms of translational relevance?
A: This model offers distinct advantages for translational relevance by directly inducing thrombotic occlusion, closely mirroring the primary cause of human ischemic stroke. Unlike MCAO models, which often involve mechanical occlusion, the photochemical approach replicates the crucial process of platelet aggregation, making it highly relevant for evaluating thrombosis-targeting therapies.
-
Q2: Given the absence of a salvageable penumbra in this model, how can it still be useful for evaluating neuroprotective agents?
A: While this model typically lacks a large, salvageable penumbra, limiting acute neuroprotective assessment, it uniquely differentiates neuroprotective from neuroregenerative effects. Its stable, well-defined infarct allows researchers to focus on interventions promoting long-term recovery, plasticity, and tissue repair beyond acute salvage.
-
Q3: What specific behavioral deficits can be reliably assessed in animals subjected to photochemically induced stroke, considering the typically mild to moderate lesion size?
A: Despite smaller lesion sizes, this model consistently produces mild to moderate sensorimotor deficits. These are reliably captured using sensitive behavioral tests like the cylinder test (forelimb asymmetry), adhesive tape removal test (sensory/motor function), and beam balance test (motor coordination). Cognitive deficits can also be assessed via the Morris Water Maze.
-
Q4: Can this model be adapted for long-term studies, and what are the typical survival rates?
A: Absolutely. A key strength of this model is its suitability for longitudinal and chronic studies. Its minimally invasive nature results in remarkably low mortality rates, typically under 10%. This enables extended observation periods to track long-term behavioral recovery, assess chronic interventions, and study neuroplasticity over weeks or months.
-
Q5: Is it possible to control the size and location of the infarct in this model, and if so, how?
A: Yes, precise infarct control is a key advantage. Researchers modulate size and location by adjusting laser light intensity, illumination duration, stereotactic coordinates of the laser beam on the skull or cranial window, and the photosensitive dye (Rose Bengal) concentration. This flexibility allows tailoring the model to specific experimental needs.
Published Data
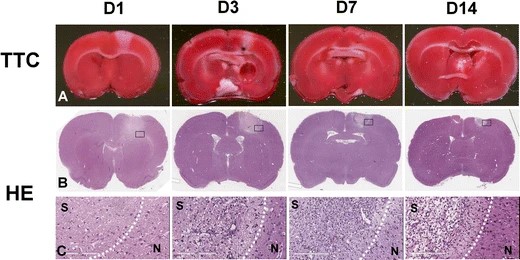 Fig.2 Longitudinal TTC and H&E staining after induction of photochemical thrombosis.2
Fig.2 Longitudinal TTC and H&E staining after induction of photochemical thrombosis.2
This research longitudinally characterized the evolution of photochemically induced stroke in rats over 14 days using a multimodality imaging and molecular biological approach. The study revealed the temporal progression of infarct volume reduction, brain edema, inflammation, astrogliosis, neovascularization, cerebral blood flow, glucose metabolism, and blood-brain barrier permeability. These detailed findings underscore the model's reliability for understanding cerebral ischemia and developing therapeutic strategies.
References
- Lunardi Baccetto, Sarah, and Christian Lehmann. "Microcirculatory Changes in Experimental Models of Stroke and CNS-Injury Induced Immunodepression." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 20,20 5184. 19 Oct. 2019. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205184
- Liu, Nai-Wei et al. "Evolutional Characterization of Photochemically Induced Stroke in Rats: a Multimodality Imaging and Molecular Biological Study." Translational stroke research vol. 8,3 (2017): 244-256. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0512-4
For Research Use Only.
