LDLR KO Mouse Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established preclinical models for evaluating NASH therapies, enabling comprehensive drug testing and a deeper understanding of the disease's pathophysiology.
Introduction
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a progressively concerning liver disease that primarily affects individuals who do not consume excessive alcohol. It is characterized by fat accumulation, inflammation, and cell damage in the liver, and can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver failure. NASH is closely associated with the global epidemics of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Due to its insidious course and the current lack of effective treatments, early detection and intervention are crucial. Given the complex pathophysiology of NASH, research into novel therapies and the use of animal models to explore its pathogenesis and screen potential drugs are of paramount importance.
Disease Models and Applications
The LDLR knockout (LDLR KO) mouse model is commonly used to study lipid metabolism disorders, particularly those associated with atherosclerosis and NASH. This model is generated by knocking out the LDL receptor gene, which leads to impaired clearance of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) from the bloodstream. As a result, LDL levels in the serum increase, mimicking hyperlipidemia and other lipid disorders observed in humans. LDLR KO mice exhibit a high susceptibility to developing atherosclerosis and NASH, especially when fed a high-fat or high-cholesterol diet. This model is advantageous for studying lipid metabolism and the role of LDL in the progression of cardiovascular diseases and liver dysfunction. However, the model's primary limitation is its reliance on a high-fat diet to induce disease, which may not fully replicate all the pathological features of human NASH. Despite this, it remains an essential tool for drug testing and understanding lipid-related diseases.
- Simulates: The LDLR KO mouse model simulates human lipid metabolism disorders, particularly hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It is used to explore the effects of high-fat and high-cholesterol diets on liver function and cardiovascular health, making it an excellent model for studying NASH progression.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is widely used to evaluate lipid-lowering therapies, anti-inflammatory drugs, and agents targeting liver fibrosis in the context of NASH. It allows for the testing of novel pharmaceutical compounds aimed at reducing lipid accumulation in the liver and reversing atherosclerotic lesions, providing critical data on drug efficacy.
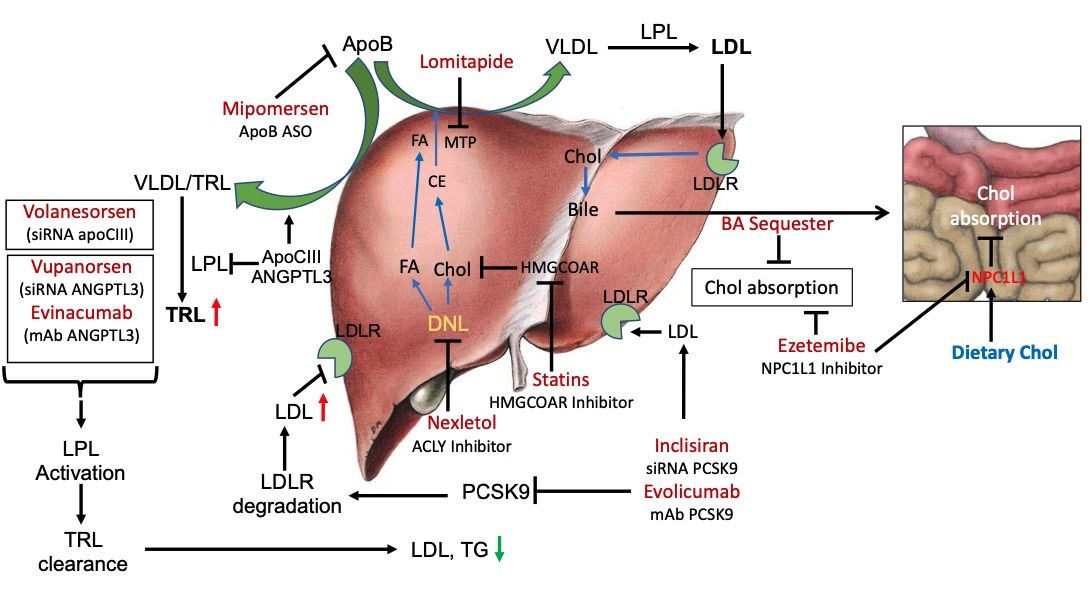 Fig. 1 LDLR-dependent and -independent pathways to manage circulating LDL levels.1
Fig. 1 LDLR-dependent and -independent pathways to manage circulating LDL levels.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the LDLR KO Mouse Model, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: body weight, serum lipid levels, liver size, and tissue morphology.
- Histological analysis: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to assess liver architecture, fat deposition, and inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of macrophage infiltration, oxidative stress markers, and fibrosis in liver tissues.
- Lipid profiling: Serum lipid analysis (LDL, HDL, triglycerides) to measure the impact of treatment on lipid metabolism.
- Gene/protein expression: Quantitative PCR and Western blotting to assess the expression of key genes involved in lipid metabolism, fibrosis, and inflammation (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, COL1A1).
In addition to the established lipid metabolism models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, guided by literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
We provide comprehensive services to support your research, including preclinical model development, pharmacokinetic studies, in vivo imaging, and tailored drug evaluation protocols. Our expert team ensures that your study is designed to address your specific scientific questions.
- Diet induced Obesity (DIO) Mouse NASH Model
- High-Fat Diet induced NASH Model
- Methionine Choline-Deficient (MCD) Diet induced NASH Model
- Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid-Defined (CDAA) Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & High-Cholesterol Diet & Fructose induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & Fructose induced NASH Model
- Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) & High-Fat & High-Carbohydrate Diet induced NASH Model
- High-Fat & CCL4 induced NASH Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat induced NASH Model
- MC4R KO Mouse Model
Advantages
- Expertise: We have a team of experts with extensive experience in preclinical model development and drug evaluation, ensuring high-quality results.
- Customized Solutions: We offer tailored experimental designs and models to meet the unique needs of each research project.
- Comprehensive Service: From model selection to final data analysis, we provide end-to-end support throughout your study.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Our cutting-edge technologies ensure accurate, reproducible, and reliable results in drug testing and disease modeling.
- Global Reach: Trusted by researchers and pharmaceutical companies worldwide for advancing drug discovery and development.
- Regulatory Compliance: Our models and testing methods meet international standards, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements for preclinical studies.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the LDLR KO mouse model?
A: The LDLR KO mouse model is genetically modified to lack the LDL receptor, leading to hyperlipidemia and lipid-related disorders, including atherosclerosis and NASH.
-
Q: How does the LDLR KO model simulate NASH?
A: By inducing lipid accumulation and liver inflammation through high-fat diets, the LDLR KO mouse model closely mimics the pathophysiology of human NASH, making it ideal for drug testing.
-
Q: What types of drugs can be evaluated in the LDLR KO model?
A: This model is suitable for evaluating lipid-lowering agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and compounds targeting liver fibrosis, among others.
Published Data
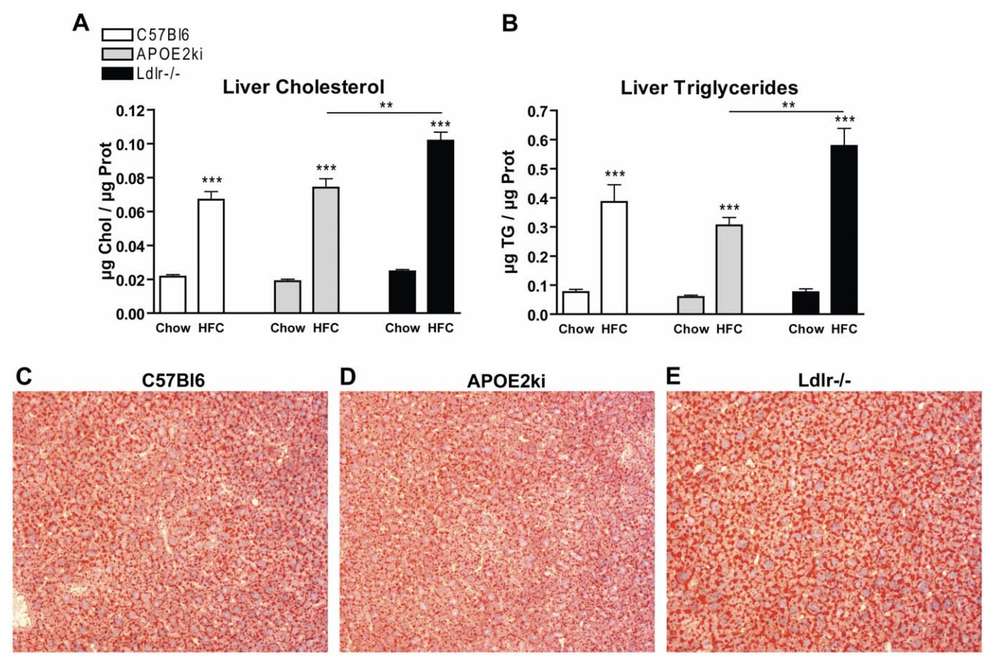 Fig. 2 Parameters of hepatic steatotis.2
Fig. 2 Parameters of hepatic steatotis.2
Following HFC feeding, liver cholesterol and triglyceride levels were elevated in all C57BL/6, APOE2ki, and Ldlr−/− mice compared to those on a chow diet. Notably, Ldlr−/− mice exhibited significantly higher levels of cholesterol and triglycerides than C57BL/6 and APOE2ki mice under the same HFC diet conditions (Fig. 2A-B). These results were further validated by Oil Red O staining, which confirmed the lipid accumulation in the liver (Fig. 2C-E).
References
- Srivastava, Rai Ajit K. "A Review of Progress on Targeting LDL Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Pathways for the Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia, a Major Risk Factor of ASCVD." Cells vol. 12,12 1648. 16 Jun. 2023, DOI:10.3390/cells12121648. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Bieghs, Veerle et al. "LDL receptor knock-out mice are a physiological model particularly vulnerable to study the onset of inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease." PloS one vol. 7,1 (2012): e30668. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0030668. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
