Autoimmune Nephropathy Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established animal models for autoimmune nephropathy, including the Thy-1 nephritis model, anti-GBM nephritis model, and spontaneous SLE models, to evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic candidates such as immunosuppressive agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and novel biologics.
Introduction
Autoimmune nephropathy refers to kidney diseases where the immune system attacks the kidneys, leading to inflammation and damage. This condition includes diseases like lupus nephritis, IgA nephropathy, and anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) nephritis. The autoimmune response targets various parts of the kidney, often resulting in glomerular damage and kidney dysfunction. These diseases can lead to proteinuria, hypertension, and eventually kidney failure if untreated.
Autoimmune Nephropathy Models
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of well-established animal models for autoimmune nephropathy research. These models are meticulously designed to simulate human autoimmune nephropathy conditions, allowing for an accurate preclinical assessment of therapeutic candidates. We offer detailed evaluations of kidney function and immune response, as well as a full range of histological, biochemical, and molecular analyses. Our team of experts will guide you throughout your project, from experimental design to final data interpretation, ensuring high-quality and reliable results for your autoimmune nephropathy drug development. To learn more about the autoimmune nephropathy models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Autoimmune Nephropathy Model | Simulated Diseases | Evaluated Drugs | Animal species |
| Thy-1 Nephritis Model | Lupus Nephritis, Glomerulonephritis | Immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus), Anti-inflammatory agents | Mouse |
| Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane (GBM) Nephritis Model | Anti-GBM Nephritis, Glomerulonephritis | Biologics targeting specific immune responses (e.g., TNF-α inhibitors, B-cell depletion therapies) | Mouse, Rat |
| Fx1A Nephritis Model | Lupus Nephritis, Glomerulonephritis | Immunosuppressive drugs, Anti-inflammatory agents, Biologics | Rat |
| IgA Nephropathy Model | IgA Nephropathy | Immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., corticosteroids, mycophenolate), Anti-inflammatory drugs, Biologics | Mouse, Rat |
| Spontaneous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Model | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | Immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil), Anti-inflammatory drugs | Mouse |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induced Model | Induced SLE | Immunosuppressive agents (e.g., methotrexate, corticosteroids), Antibodies targeting immune cells | Mouse |
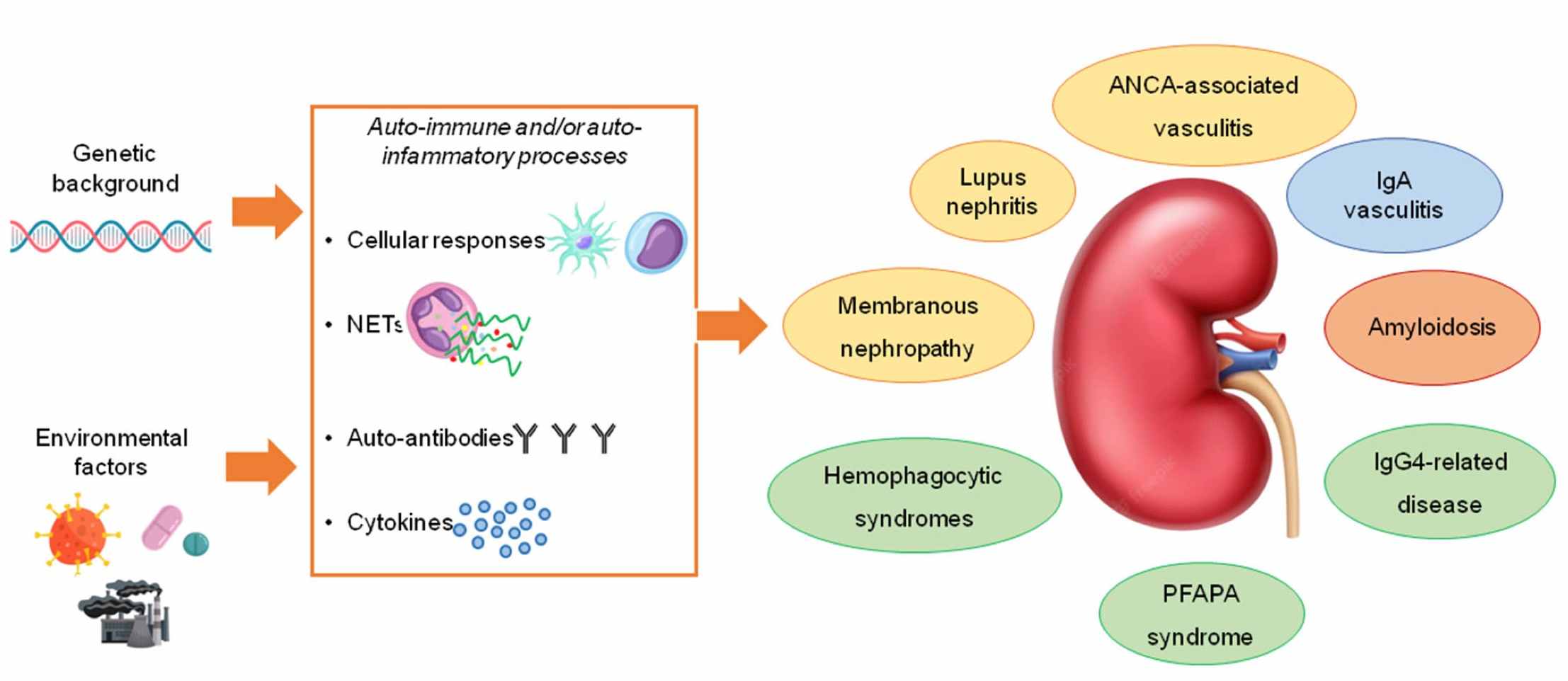 Fig. 1 The kidney in auto-immune and auto-inflammatory processes: definitions, mechanisms, and biomarkers.1,3
Fig. 1 The kidney in auto-immune and auto-inflammatory processes: definitions, mechanisms, and biomarkers.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat
-
Measurements
We provide a variety of measurements to evaluate drug efficacy in autoimmune nephropathy models, utilizing advanced techniques such as:- General observations: Body weight, kidney function (e.g., serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen), proteinuria.
- Histopathology: Glomerular and tubular injury assessments, immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages).
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, interferon-γ.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of immune cell infiltration in kidney tissues, assessment of complement activation.
- Hematology analysis: Blood counts, renal function markers, and serum biomarkers such as creatinine, albumin, and uric acid levels.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis for markers of inflammation and fibrosis in kidney tissues (e.g., TGF-β, collagen type I).
Additionally, we can develop novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, ensuring a personalized approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to autoimmune nephropathy models, we also offer a wide range of other disease models for comprehensive drug evaluation and therapeutic development. These models are designed to address various therapeutic areas.
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Models
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Models
- Metabolic Nephropathy Models
- Hyperuricemia Models
- Kidney Transplantation Models
- Cystitis Models
Our advantages
- Expertise: We have a dedicated team of scientists with extensive experience in developing and working with autoimmune nephropathy models.
- Comprehensive Services: From experimental design to data interpretation, we provide a full range of services to ensure the success of your research.
- High-Quality Models: Our autoimmune nephropathy models are meticulously validated and designed to closely mimic human diseases, ensuring the highest level of accuracy in preclinical evaluations.
- Tailored Approaches: We offer customized solutions, developing models and methods that best suit your specific research goals and therapeutic evaluations.
- Reliable Results: Our advanced technology platforms ensure accurate, reproducible results, which are critical for your drug development process.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of autoimmune nephropathy models do you offer?
We offer a variety of models, including Thy-1 nephritis, anti-GBM nephritis, lupus nephritis, IgA nephropathy, and more, each designed to simulate different autoimmune kidney diseases.
-
2. Can you customize models to suit my specific research needs?
Yes, we offer tailored model development based on your specific therapeutic area or disease focus, ensuring the most relevant and accurate model for your research.
-
3. What types of analyses are available for autoimmune nephropathy models?
We provide a wide range of analyses, including histopathology, cytokine profiling, immunohistochemistry, and gene expression studies, among others, to evaluate drug efficacy in preclinical studies.
-
4. How do I get started with your services?
Simply contact us with your research requirements, and our team will assist you with model selection, experimental design, and data analysis to ensure the success of your study.
Published Data
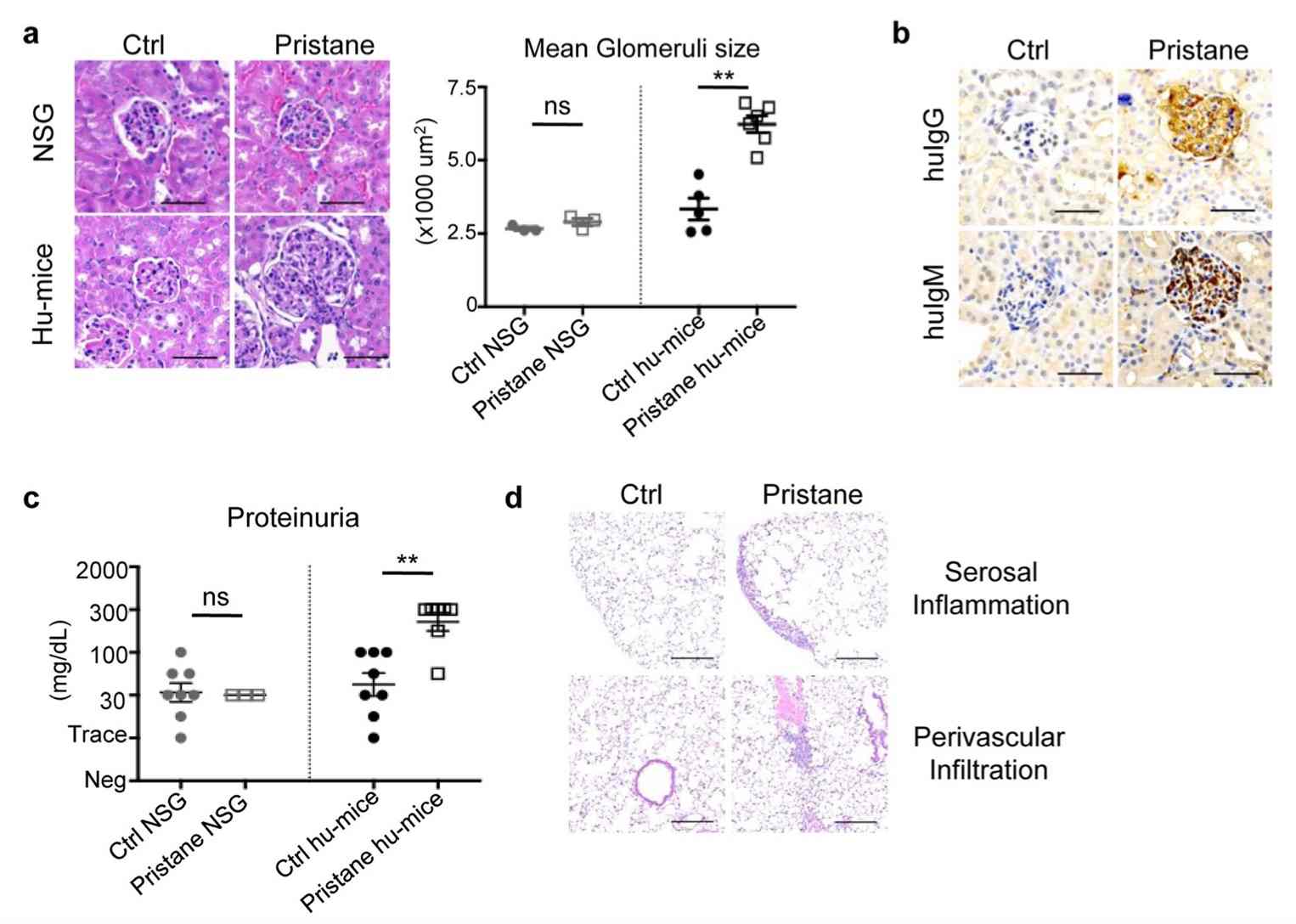 Fig. 2 Lupus nephritis and pulmonary inflammation.2,3
Fig. 2 Lupus nephritis and pulmonary inflammation.2,3
Histological analysis of kidneys from pristane-injected hu-mice revealed significant kidney inflammation and glomerular changes, characteristic of proliferative glomerulonephritis. Specifically, we observed focal to diffuse global glomerular enlargement due to mesangial/endocapillary proliferation and increased glomerular cellularity, which was absent in kidneys from pristane-injected NSG mice (Fig. 2A). In line with immune complex deposition seen in SLE patients, human IgG and IgM were deposited in the glomeruli of pristane-injected hu-mice (Fig. 2B). This was accompanied by significant proteinuria in pristane-injected hu-mice, a phenomenon not observed in pristane-injected NSG mice (Fig. 2C). These findings underscore the crucial role of the human immune system, with minimal contribution from residual mouse cells, in driving the pathogenesis of SLE following pristane injection. Additionally, lung pathology in pristane-injected hu-mice showed increased multifocal serosal and subpleural inflammation, fibrosis, and perivascular, interstitial, and intra-alveolar mononuclear cell infiltrates (Fig. 2D). Collectively, these findings demonstrate that pristane injection induces SLE pathogenesis in hu-mice, driven by the human immune system, and leads to the development of lupus nephritis, pulmonary serositis, and autoantibody production.
References
- Vaglio, Augusto et al. "Editorial: The kidney in auto-immune and auto-inflammatory processes: Definitions, mechanisms, and biomarkers." Frontiers in medicine vol. 9 1129021. 10 Jan. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.1129021
- Gunawan, Merry et al. "A Novel Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Model in Humanised Mice." Scientific Reports vol. 7,1 16642. 30 Nov. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16999-7
- Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
