Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) induced Colitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Dextran Sodium Sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis is a widely used preclinical model to study ulcerative colitis (UC), a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the mucosal layer of the colon. UC is characterized by chronic inflammation, mucosal ulceration, and immune cell infiltration, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. DSS-induced colitis mimics the acute phase of UC, making it a valuable model for investigating disease mechanisms and testing new therapies. In this model, rodents are administered DSS through drinking water, which disrupts the intestinal epithelial barrier, triggering an immune response that leads to inflammation and ulceration. The model closely resembles the immunopathological features of human UC, including the activation of T cells, macrophages, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. While DSS-induced colitis primarily mimics acute inflammation, it is widely used for studying therapeutic agents that target inflammatory pathways involved in IBD. Creative Biolabs offers well-established and customizable DSS-Induced Rodent Colitis Models for evaluating the efficacy of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs. Our models provide a reliable platform for assessing drug candidates targeting inflammatory pathways in UC and IBD, supporting the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Disease Models and Applications
The DSS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model is commonly employed to investigate the mechanisms underlying ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the mucosal lining of the colon. In this model, rodents are administered DSS via their drinking water, leading to dose-dependent epithelial damage, inflammation, and colonic ulceration. This model is characterized by acute inflammation and epithelial shedding, with an inflammatory response involving the activation of immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells. One of the major advantages of this model is its reproducibility, ease of administration, and its relevance to human UC, particularly in terms of mucosal damage and immune response activation. However, it should be noted that the model primarily mimics the acute phase of UC, and does not fully replicate the chronic, relapsing nature of the disease. Despite these limitations, DSS-induced colitis remains a reliable model for evaluating anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapies for IBD.
- Simulates: The DSS-Induced Rodent Colitis Model simulates key features of ulcerative colitis, including epithelial injury, immune cell infiltration, and acute mucosal inflammation. This model is particularly relevant for studying mucosal repair, epithelial regeneration, and the role of immune responses in UC.
- Evaluates Drugs: The DSS model is commonly used to evaluate the efficacy of anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, and biologics, including corticosteroids, TNF-α inhibitors, IL-12/23 blockers, JAK inhibitors, and other small molecules targeting cytokine signaling pathways and immune cell activation involved in UC.
Measurements
We offer a comprehensive set of evaluations for the DSS-Induced rodent colitis model to assess drug efficacy, utilizing a variety of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight changes, stool consistency, diarrhea severity, rectal bleeding, and survival rate.
- Disease activity index (DAI): Composite scoring system based on weight loss, stool consistency, and presence of blood in feces.
- Colon length measurement: Shortening of the colon as a marker of inflammation severity.
- Histopathological analysis: Assessment of mucosal damage, ulceration, inflammatory cell infiltration, and crypt architecture using H&E staining.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Quantification of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ in colon tissues or serum.
- Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity assay: Measurement of neutrophil infiltration as a marker of inflammation.
- Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry: Detection of immune cell subsets (e.g., CD4⁺ T cells, macrophages) and activation markers in colonic tissues.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Analysis of pro-inflammatory genes and signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, COX-2, iNOS) via RT-qPCR and Western blot.
In addition to the established protocols, we provide the flexibility to develop customized models tailored to specific research goals. Our team offers comprehensive support from study design to data interpretation, ensuring scientifically rigorous and project-specific solutions.
Related Services
In addition to the DSS-induced rodent colitis model, we also offer a range of other colitis models for investigating different mechanisms of intestinal inflammation, including:
- TNBS/DNBS induced Colitis Model
- Indomethacin induced Small Intestinal Inflammatory Model
- OXA induced Colitis Model
- Acetic Acid induced IBD Model
- Anti-CD40 Ab induced IBD Model
- IL-10 KO Mouse Spontaneous IBD Model
- CD4+CD45RBhi T Cells induced IBD Model
Advantages
- Expertise and Experience: Our team has years of expertise in preclinical models, ensuring reliable, scientifically sound models for colitis research.
- Comprehensive Services: From experimental design to data analysis, we provide full support to ensure that your study meets your research objectives.
- Advanced Technologies: We employ cutting-edge technologies, including cytokine profiling, histopathological analysis, and gene/protein expression profiling, to ensure reproducible, high-quality results.
- Customized Models: We offer the flexibility to develop novel models based on your specific needs, ensuring that your research goals are met.
- Collaborative Approach: Our scientific team works closely with you to ensure that each phase of the study aligns with your expectations and is suited for publication.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q1: How long does it take to conduct a study using your DSS colitis model?
A1: The study duration depends on the severity and type of colitis induced, as well as the treatment protocol. Preclinical studies typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, including data collection and analysis.
-
Q2: What support do you provide during the study?
A2: Our scientific team offers complete support, including experimental design, model selection, data analysis, and interpretation, ensuring a smooth progression of your study.
-
Q3: Do you offer other disease models beyond colitis?
A3: Yes, we offer a variety of rodent disease models, including those for gastric ulcers, liver diseases, cancer, atherosclerosis, kidney fibrosis, and more.
-
Q4: How do I get started with your services?
A4: Contact us to discuss your research goals. Our team will guide you through the model selection, study design, and timeline to get your project started.
-
Q5: Are your models validated for publication?
A5: Yes, all our models are validated using well-established scientific protocols and are suitable for publication in peer-reviewed journals.
Published Data
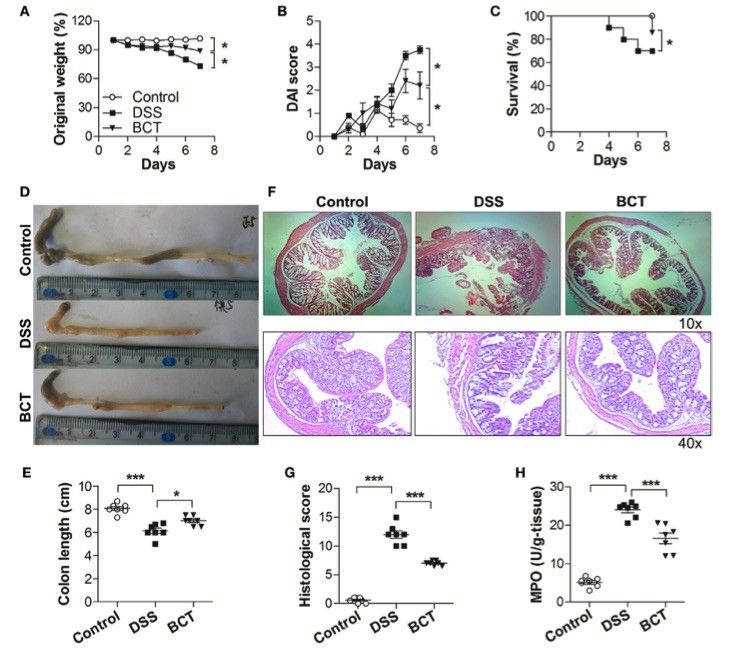 Fig. 1 BCT ameliorated DSS-induced colitis in mice.1
Fig. 1 BCT ameliorated DSS-induced colitis in mice.1
Bacterial consortium transplantation (BCT) has emerged as a promising alternative to fecal microbiota transplantation for treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Recent studies have demonstrated that a defined bacterial consortium derived from healthy mice can improve intestinal barrier function in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. The impact of BCT on DSS-treated mice was evaluated through several key parameters: (A) changes in body weight, (B) Disease Activity Index (DAI) score, (C) survival rate, (D, E) colon length measurement post-sacrifice, (F) histological examination of colon sections via H&E staining, (G) detailed histopathological analysis of the H&E-stained sections, and (H) quantification of myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels in colonic tissue using ELISA following the manufacturer's protocol. These comprehensive assessments help to determine the therapeutic potential of BCT in modulating the inflammatory response and enhancing gut barrier function in colitis.
Reference
- Li, Ming et al. "Upregulation of Intestinal Barrier Function in Mice with DSS-Induced Colitis by a Defined Bacterial Consortium Is Associated with Expansion of IL-17A Producing Gamma Delta T Cells." Frontiers in Immunology vol. 8 824. 12 Jul. 2017, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00824. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
