Myosin induced Immune Myocarditis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Myocarditis, an inflammatory condition of the heart muscle, poses a significant threat, often leading to severe cardiac dysfunction. Understanding its complex immune-mediated pathology is crucial for therapeutic advancement.
As a leading preclinical research organization, Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of developing robust models to address critical cardiovascular diseases. Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established models to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of novel myocarditis treatments.
Myosin-Induced Immune Myocarditis Model
The myosin-induced immune myocarditis (MIM) model, also known as experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM), is a cornerstone for investigating autoimmune-driven heart inflammation. This model faithfully recapitulates key immunological and pathological features observed in human autoimmune myocarditis, making it an invaluable tool for deciphering disease mechanisms, identifying novel biomarkers, and assessing the efficacy of immunomodulatory or cardioprotective therapies. It is particularly relevant for studying T-cell-mediated autoimmunity and the role of cardiac autoantigens in disease progression.
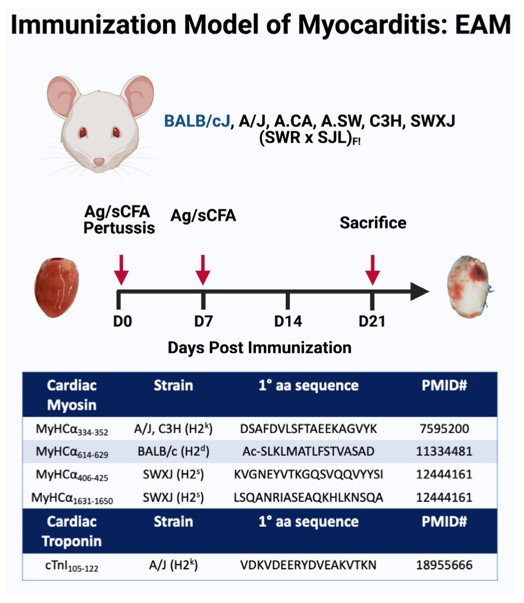 Fig.1 Experimental autoimmune myocarditis murine model.1,3
Fig.1 Experimental autoimmune myocarditis murine model.1,3
Model Construction Steps
The EAM model is typically induced by immunizing susceptible rodents with cardiac myosin (CM), a primary autoantigen in autoimmune myocarditis. This immunization triggers a robust autoimmune response directed against the heart muscle.
01Antigen Preparation
CM is isolated and purified, often from murine heart tissue.
02Adjuvant Emulsification
The purified cardiac myosin is emulsified with a strong adjuvant, commonly Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA), to enhance the immune response.
03Immunization
Susceptible mouse strains, such as A/J or BALB/c, are immunized subcutaneously with the CM/CFA emulsion. Booster immunizations may be administered depending on the experimental design.
04Disease Progression
Following immunization, the animals develop an acute inflammatory response in the heart, with peak inflammation typically observed around day 21. This phase is characterized by significant immune cell infiltration and myocardial damage.
05Monitoring
Animals are monitored for clinical signs, and cardiac function can be assessed non-invasively throughout the study.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths:
- High Reproducibility: Provides a consistent and predictable model of autoimmune myocarditis.
- Immunological Relevance: Directly models T-cell-mediated autoimmunity against a cardiac autoantigen.
- Translational Value: Recapitulates key pathological features seen in human autoimmune myocarditis.
- Versatility: Can be adapted to study various aspects of immune responses, including cytokine networks and T-cell subsets.
Limitations:
- Acute Phase Focus: Primarily models the acute inflammatory phase; chronic progression can be more variable.
- Species Differences: Murine model findings require careful translation to human physiology.
- Induction Method: Immunization does not fully mimic spontaneous onset in humans.
Evaluation Platform
Our state-of-the-art evaluation platform integrates comprehensive biochemical, molecular, cellular, histopathological, and imaging techniques to provide a holistic assessment of disease progression and therapeutic impact. We utilize advanced instruments for precise measurements and detailed analyses.
Test Indicators:
- Cardiac Function: Echocardiography (ejection fraction, fractional shortening, wall thickness), ECG analysis.
- Histopathology: H&E staining (inflammation scoring, necrosis), Masson's trichrome (fibrosis), immunohistochemistry (immune cell phenotyping, cytokine expression).
- Molecular Analysis: Gene expression (qPCR for inflammatory markers, fibrosis markers), protein expression (Western blot, ELISA for cytokines/chemokines).
- Cellular Analysis: Flow cytometry (immune cell populations in heart, spleen, lymph nodes), T-cell proliferation assays.
- Serum Biomarkers: Cardiac troponins, inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), autoantibodies
Applications
- Disease Simulation: This model effectively simulates autoimmune myocarditis, including forms like giant cell myocarditis and post-viral myocarditis, and is also highly relevant for understanding immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-associated myocarditis. It can further investigate dilated cardiomyopathy as a potential long-term consequence of myocarditis.
- Drug Efficacy Evaluation: It serves as an ideal platform for evaluating a diverse range of therapeutic agents. This includes immunosuppressants, biologics targeting specific inflammatory cytokines (e.g., anti-TNF, anti-IL-1), general anti-inflammatory compounds, cardioprotective agents, and novel immunomodulators.
- Therapeutic Modality Assessment: Beyond traditional pharmacology, the model is suitable for assessing the efficacy of various advanced therapeutic modalities. This encompasses pharmacological interventions, cell-based therapies, gene therapies, and even vaccine strategies aimed at preventing or mitigating autoimmune heart disease.
Related Myocarditis Models
Our Advantages
- Deep Expertise: Years of experience in preclinical cardiovascular disease models.
- Customized Study Design: Flexible protocols tailored to your specific research objectives.
- Comprehensive Capabilities: Integrated platform for multi-modal assessment from molecular to functional.
- High-Quality Data: Rigorous experimental execution and robust data analysis for reliable results.
- Accelerated Timelines: Efficient project management to expedite your drug development process.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs stands ready to empower your myocarditis research. Leveraging our scientific strengths and comprehensive services, we provide the critical data needed to advance your therapeutic candidates. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can guide your next breakthrough.
FAQs
-
Q1: What is the primary advantage of using the MIM model over other myocarditis models?
A: The MIM model excels by directly simulating autoimmune myocarditis, providing a highly relevant platform for studying immune-mediated cardiac damage. Unlike viral or toxin-induced models, MIM focuses on adaptive immune responses against cardiac autoantigens, crucial for understanding a significant subset of human myocarditis, enabling precise evaluation of immunomodulatory therapies.
-
Q2: How do you ensure the reproducibility and consistency of the MIM model?
A: We implement stringent protocols for model induction, including standardized CM preparation, precise adjuvant emulsification, and consistent immunization. Utilizing well-characterized, susceptible rodent strains and rigorous quality control at every stage ensures minimal variability and highly reproducible outcomes across studies.
-
Q3: Can the MIM model be adapted to study chronic phases of myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy?
A: While the classic MIM model primarily focuses on the acute inflammatory phase, it can be adapted to investigate chronic progression. This often involves extended study durations or specific genetic backgrounds. Our experts can customize protocols to explore the transition from acute inflammation to chronic heart remodeling, offering valuable insights into long-term disease outcomes.
-
Q4: Is the MIM model suitable for evaluating cell-based therapies?
A: Absolutely. The MIM model is an excellent platform for evaluating cell-based therapies, especially those aimed at modulating immune responses or promoting cardiac repair. We can assess engraftment, survival, and immunomodulatory effects of various cell types on cardiac inflammation and function within this autoimmune context.
-
Q5: Can you help in identifying novel biomarkers using the MIM model?
A: Yes, our platform is ideal for biomarker discovery. By combining comprehensive molecular profiling with detailed pathological and functional assessments, we can identify potential diagnostic, prognostic, or pharmacodynamic biomarkers. Our expertise in data analysis helps pinpoint significant changes that could serve as novel indicators of disease or treatment response.
-
Q6: Can the MIM model be used to study ICI-associated myocarditis?
A: Yes, the MIM model and its variants are highly relevant for studying ICI-associated myocarditis. Recent research demonstrates that CM-specific T cells play a crucial role in this severe adverse event. Our expertise allows us to design studies mimicking ICI-induced autoimmunity, offering a valuable platform for understanding pathogenesis and testing mitigation strategies.
Published Data
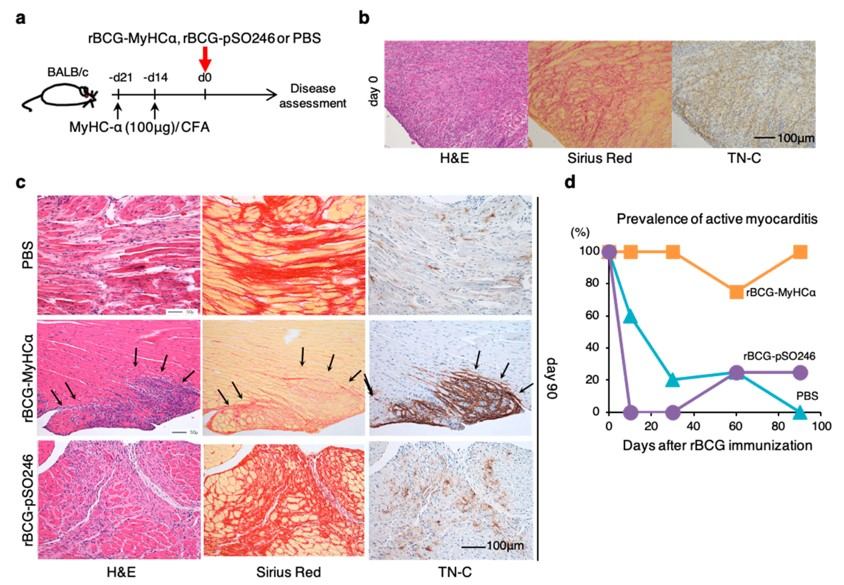 Fig.2 The rBCG-MyHCα-immunization-induced prolonged chronic myocarditis model.2,3
Fig.2 The rBCG-MyHCα-immunization-induced prolonged chronic myocarditis model.2,3
This study utilized a novel MIM model to investigate the progression of chronic myocarditis to dilated cardiomyopathy. The research demonstrated that immunization with recombinant bacille Calmette-Guérin (rBCG) expressing CM heavy chain-α (rBCG-MyHCα) induced chronic myocarditis in mice. This model exhibited ventricular dilation and impaired contraction, closely mirroring human dilated cardiomyopathy, and identified specific CD4+ T cells as key effector cells. This case exemplifies how these models provide robust in vivo evidence to advance drug discovery and understand disease progression.
References
- Čiháková, Daniela et al. "Meeting the Challenges of Myocarditis: New Opportunities for Prevention, Detection, and Intervention-A Report from the 2021 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Workshop." Journal of clinical medicine vol. 11,19 5721. 27 Sep. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195721
- Tajiri, Kazuko et al. "A New Mouse Model of Chronic Myocarditis Induced by Recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guèrin Expressing a T-Cell Epitope of Cardiac Myosin Heavy Chain-α." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 22,2 794. 14 Jan. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020794
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
