Diabetes Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established animal models for studying diabetes, including both T1D and T2D models. These models, such as the STZ-induced model for T1D and db/db mice for T2D, allow for comprehensive evaluations of drug efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action, supporting the preclinical development of new diabetes therapies.
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, resulting from either insufficient insulin production or the body's inability to effectively use the insulin it produces. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes (T2D), on the other hand, is primarily driven by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, often linked to factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after delivery, but it increases the risk of developing T2D later in life.
Disease Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a broad range of well-established animal models for studying diabetes, including models for Type 1 diabetes (T1D), Type 2 diabetes (T2D), gestational diabetes, and other related metabolic disorders. These models are carefully developed to replicate the key features of human diabetes, enabling accurate and reliable preclinical evaluation of therapeutic candidates. Our models, such as STZ-induced models for T1D and db/db mice for T2D, are supported by comprehensive assessments of various metabolic parameters, including glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, and body weight changes. Our team of experienced scientists will work closely with you throughout your project, from experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring high-quality results and efficient progress. To learn more about the diabetes models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
| Diabetes Models | Simulates | Drug Evaluation | Animal species |
| Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Insulin Deficiency | Insulin therapies (e.g., insulin analogs), Insulin sensitizers, Beta-cell regeneration agents, Anti-hyperglycemic drugs | Mouse |
| Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Insulin Deficiency | Insulin therapies (e.g., rapid/long-acting insulin), Insulin mimetics, Beta-cell regeneration agents, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Mouse, Rat |
| Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model | Type 1 Diabetes, Insulin Deficiency | Insulin therapies (e.g., insulin glargine), Insulin sensitizers, Beta-cell protectants, Glucose-lowering agents | Mouse |
| db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance | Insulin sensitizers (e.g., metformin), GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, Anti-obesity drugs, Beta-cell regeneration agents | Mouse |
| Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance, Gestational Diabetes | Insulin sensitizers, Glucose-lowering agents, Anti-hyperglycemic drugs, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Mouse |
| STZ-NA induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance, Beta-cell dysfunction | Insulin sensitizers (e.g., metformin), GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, Anti-obesity drugs, Lipid-lowering agents, Anti-inflammatory drugs | Rat |
| Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Insulin Resistance | Insulin sensitizers (e.g., pioglitazone), GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, Anti-obesity drugs, Beta-cell regeneration agents, Lipid-lowering agents | Rat |
| High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Insulin Resistance | Anti-diabetic drugs (e.g., GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors), Insulin sensitizers (e.g., metformin), Anti-obesity drugs, Lipid-lowering agents | Mouse, Rat, Cat |
| Combined spleen and partial pancreas resection & glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model | Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance, Beta-cell dysfunction | Insulin sensitizers, Anti-hyperglycemic agents, Glucocorticoid antagonists, Anti-inflammatory drugs, Anti-obesity drugs, Beta-cell regenerating agents | Cat |
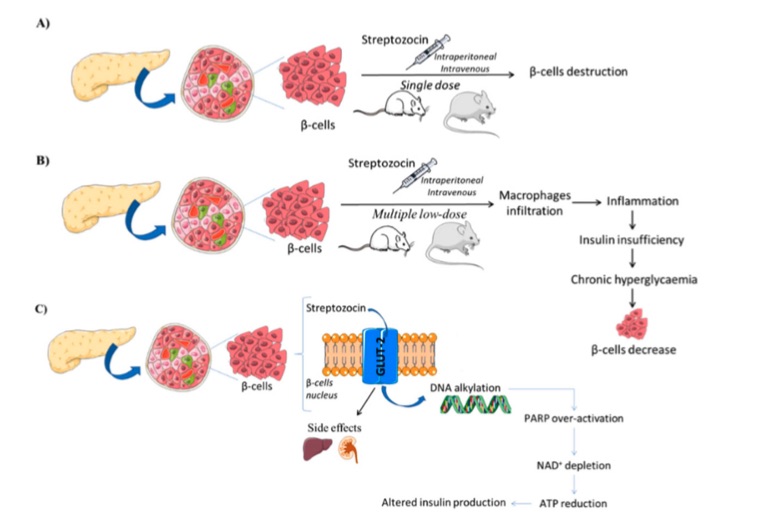 Fig. 1 Streptozocin diabetes induction model.1
Fig. 1 Streptozocin diabetes induction model.1
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in diabetes models, utilizing a range of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, blood glucose levels, food and water intake, and activity levels.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): Assessment of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity by measuring blood glucose levels at various time points after glucose administration.
- Insulin tolerance test (ITT): Measurement of insulin sensitivity through changes in blood glucose levels following insulin injection.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are involved in insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Includes analysis of lipid profiles (e.g., cholesterol, triglycerides), liver enzymes, and kidney function markers (e.g., creatinine, urea) to assess the broader metabolic effects of diabetes.
- Gene/protein expression profiling via RT-qPCR and Western blot: Expression levels of key genes and proteins involved in glucose metabolism, insulin signaling (e.g., GLUT4, IRS-1, PPARγ), and inflammation.
In addition to our established diabetes models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, based on current literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to diabetes models, we also offer a wide range of models for other diseases. These models enable comprehensive evaluation across diverse therapeutic areas.
Advantages
- Expertise and Experience: With years of industry experience, our team of specialists provides high-quality, tailored solutions to meet your research and development needs.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We utilize the latest technologies, ensuring the most advanced and accurate data for your projects.
- Comprehensive Services: From initial consultation to post-project support, we offer a full spectrum of services, including custom experimental setups, precise data collection, and insightful analysis.
- Commitment to Quality: We adhere to the highest standards of quality control, ensuring reliable and reproducible results for all our services.
- Client-Centric Approach: Our focus is on your success. We collaborate closely with clients to understand their specific needs and tailor our solutions accordingly.
- Global Reach with Local Expertise: Whether you are working in global markets or focused on local applications, we bring international standards with in-depth regional knowledge.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What services do you offer?
A: We offer customized solutions to meet the unique needs of your project, with a focus on high-quality data and client satisfaction.
-
Q: How do I get started with a project?
A: We'll work closely with you to design a tailored approach for your project.
-
Q: What makes your models different from others?
A: Our models are developed using advanced technologies and are designed to closely mimic human disease conditions, ensuring high relevance and accuracy for preclinical research.
-
Q: How long does it take to complete a study?
A: The duration of a study depends on the complexity and specific goals of the project. Our team will provide you with a detailed timeline after discussing the project scope.
-
Q: Can you provide customized services for my research?
A: Absolutely! We work closely with clients to understand their specific needs and customize our services accordingly.
Published Data
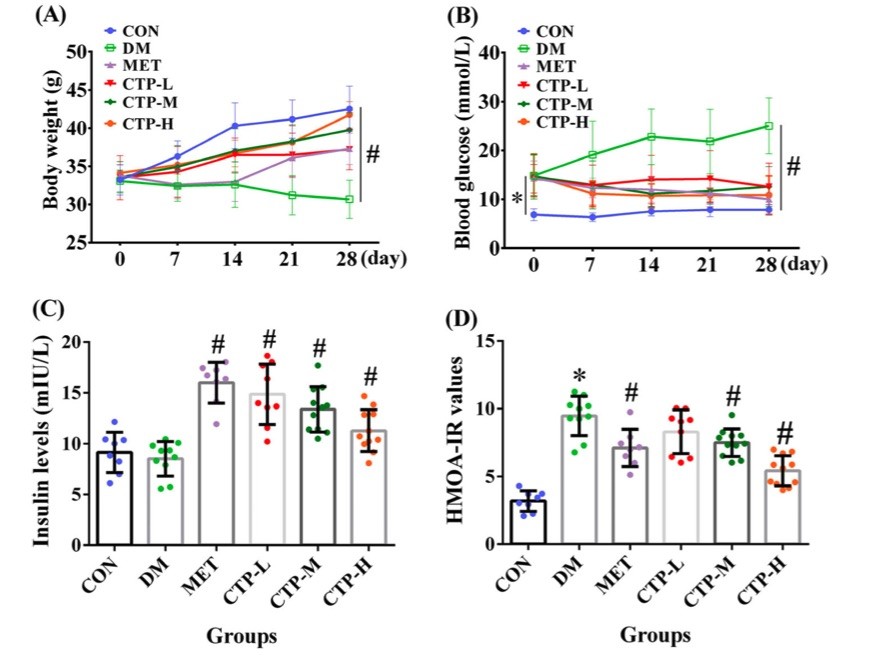 Fig. 2 Effects of CTP on body weight, FBG, insulin level, and HOMA-IR value in STZ-induced diabetic mice.2
Fig. 2 Effects of CTP on body weight, FBG, insulin level, and HOMA-IR value in STZ-induced diabetic mice.2
This study investigated the anti-diabetic effects and mechanisms of action of polysaccharides from C. taii using STZ-induced diabetic mice. During the initial days, no significant differences in body weight were observed among the groups (Fig. 2a). After 7 days, body weights in the DM and MET groups were lower by 10.71% and 10.13%, respectively, compared to the CON group. Over the study period, all groups showed increased glucose levels compared to the CON group (Fig. 2b), but the CTP-L, CTP-M, and CTP-H groups exhibited significant reductions in fasting blood glucose (FBG) at days 7, 14, 21, and 28, with the CTP-H group showing the strongest effect, like that of the MET group. Serum insulin levels and HOMA-IR values (Fig. 2c, d) were also significantly improved, with CTP administration in a dose-dependent manner increasing insulin levels and reducing insulin resistance. The CTP-H group had a stronger effect on reversing the HOMA-IR value compared to the MET group. Overall, CTP treatment lowered FBG, increased insulin levels, and alleviated insulin resistance in diabetic mice, demonstrating its potential as an anti-diabetic agent.
References
- Vieira, Raquel et al. "Sugar-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome-Strategies for In Vivo Administration: Part-II." Journal of Clinical Medicine vol. 8,9 1332. 28 Aug. 2019, DOI:10.3390/jcm8091332. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Liu, Ru-Ming et al. "Glucose-lowering and hypolipidemic activities of polysaccharides from Cordyceps taii in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice." BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine vol. 19,1 230. 23 Aug. 2019, DOI:10.1186/s12906-019-2646-x. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
