Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established animal models designed to evaluate the efficacy of drugs targeting diabetes-related complications. These models are tailored to simulate the various aspects of diabetes, including hyperglycemia, wound healing impairment, and neuropathy, providing a reliable platform for therapeutic development.
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or poor insulin response. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications, including diabetic foot ulcers, nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. Diabetic foot ulcers are one of the most common and debilitating complications, often resulting from a combination of factors such as nerve damage, poor circulation, and immune dysfunction. These ulcers can lead to infections, gangrene, and, in severe cases, amputations. Diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are other common complications, often leading to kidney failure and blindness, respectively. Neuropathy, the nerve damage associated with diabetes, can result in chronic pain, loss of sensation, and difficulty with mobility.
Disease Models and Applications
The Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model is a widely used preclinical model for studying the pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. In this model, diabetes is induced in rodents via a single injection of streptozotocin, which selectively destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to hyperglycemia. Subsequently, foot ulcers are induced by creating controlled wounds on the animals' feet. This model mimics the chronic, non-healing nature of diabetic foot ulcers, allowing for the investigation of therapeutic interventions targeting wound healing and diabetes management. The model's advantages include its reproducibility, reliability, and ability to assess a wide range of treatment approaches. However, limitations include the stress imposed on animals and the lack of certain human-specific diabetic complications.
- Simulates: The Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model simulates the chronic complications of diabetes, particularly focusing on diabetic foot ulcers. This model is ideal for investigating how hyperglycemia affects wound healing, immune response, and tissue regeneration, which are key factors in managing diabetes-related complications.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate drugs aimed at enhancing wound healing, such as growth factors, antimicrobial agents, and anti-inflammatory drugs. It is also suitable for testing treatments that aim to improve glycemic control, modulate the immune response, or enhance blood circulation to prevent ulcer formation and promote recovery.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model, utilizing an array of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General Observations: Body weight, ulcer size, wound healing rate, foot inflammation, and mortality rate.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of immune cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in foot tissues to assess immune response and tissue repair processes.
- Cytokine Profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and growth factors like VEGF, to understand inflammation and angiogenesis in wound healing.
- Hematology Analysis and Serum Biomarkers: Monitoring of blood glucose levels, insulin levels, and markers of systemic inflammation and infection.
- Gene/Protein Expression Profiling via RT-qPCR and Western Blot: Analyzing key genes and proteins involved in wound healing, collagen synthesis, and the immune response to better understand the molecular mechanisms of treatment.
Related Services
In addition to the STZ induced diabetic foot ulcer model, our company offers other models induced by different methods to simulate diabetes complications. These models include high-fat diet (HFD) or genetically modified animal models. With our range of services, we ensure that each model fits the specific requirements of your research.
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Skin Defect/Burn Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetic Cataract Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- db/db Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Model
Advantages
- Scientifically Validated Models: We offer reliable, reproducible models that simulate various diabetic complications, including foot ulcers, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy, ensuring high-quality research results.
- State-of-the-Art Technologies: Our advanced measurement techniques and technologies, such as immunohistochemistry, cytokine profiling, and gene expression analysis, provide comprehensive and accurate data.
- Customization: We tailor our models and experimental designs to meet the specific needs of your research, ensuring the most relevant and effective approach for your study.
- Expert Support: Our scientific team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, offering personalized guidance throughout your project.
- Reliability and Reproducibility: Our models have been thoroughly validated, ensuring consistent and reliable results across studies for accurate therapeutic evaluations.
- Innovation and Flexibility: We continuously improve our models and services to meet the evolving needs of the scientific community, providing cutting-edge solutions to advance diabetes research.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What is the STZ induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model?
A: The STZ induced Type I Diabetic Foot Ulcer Model is a widely used preclinical model to simulate diabetic foot ulcers in rodents, created by inducing diabetes using streptozotocin and generating foot ulcers through controlled injuries.
-
Q: What drugs can be evaluated using this model?
A: This model is used to evaluate drugs targeting wound healing, glucose regulation, and inflammation, such as growth factors, anti-inflammatory agents, and antibiotics.
-
Q: How long does it take to see results in this model?
A: Results can typically be observed within 3-4 weeks, depending on the specific interventions and endpoints measured.
-
Q: Can I customize the model to suit my research?
A: Yes, we offer customization options based on specific research needs, from different diabetic induction methods to variations in wound severity and treatment protocols.
-
Q: What measurements are included in the evaluation process?
A: We provide a comprehensive range of measurements, including general observations, immunohistochemistry, cytokine profiling, hematology analysis, and gene/protein expression analysis.
Published Data
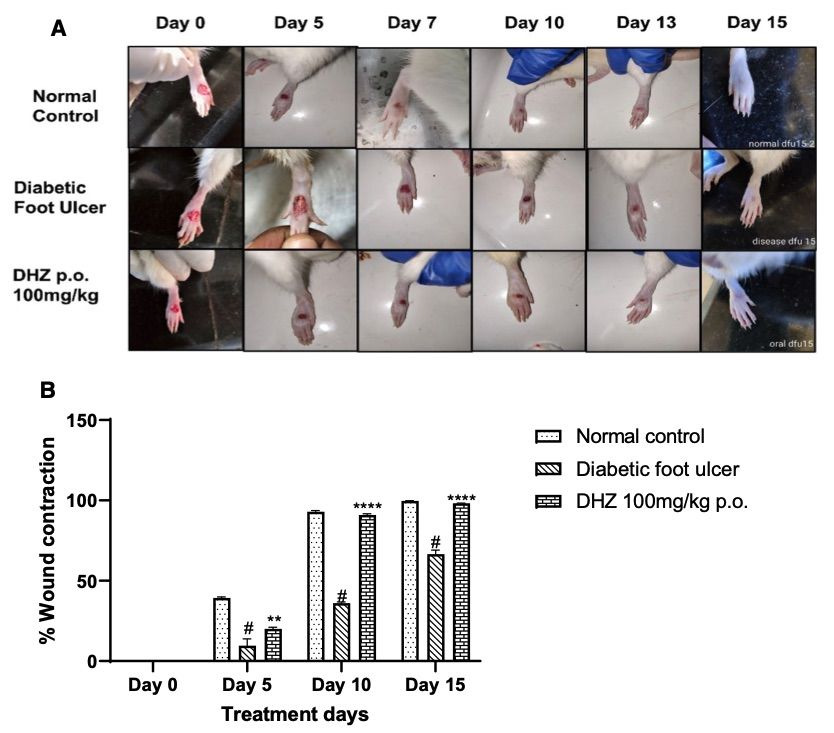 Fig. 1 The effect of DHZ on wound healing was evaluated in a foot ulcer model in Wistar rats.1
Fig. 1 The effect of DHZ on wound healing was evaluated in a foot ulcer model in Wistar rats.1
Rats were treated with dehydrozingerone (DHZ) for 15 days, and the wound area was measured on days 5, 10, and 15. On day 5 post-wounding, animals treated with DHZ showed accelerated healing, with a wound area of 20 ± 0.94, compared to the disease group, which exhibited a wound area of 39.2 ± 0.83 (p < 0.001). On day 10, DHZ-treated animals demonstrated 90.23 ± 0.68% re-epithelialization, compared to 92.91 ± 0.78% in the normal control group and 36.02 ± 0.79% in the disease control group, with the difference between DHZ and the disease control being statistically significant (p < 0.0001). By day 15, re-epithelialization reached nearly 100% in the normal control group and 98.16 ± 0.10% in DHZ-treated animals, which was significantly higher than the 66.51 ± 2.55% re-epithelialization observed in the disease group (p < 0.0001). These findings demonstrate that DHZ treatment significantly accelerated wound healing compared to the disease control group.
Reference
- Begum, Farmiza et al. "Dehydrozingerone promotes healing of diabetic foot ulcers: a molecular insight." Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling vol. 17,3 (2023): 673-688. DOI:10.1007/s12079-022-00703-0. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
