db/db Type II Diabetes (T2D) Mouse Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of well-established animal models to evaluate the efficacy of potential Type II Diabetes therapies. These models include both genetic and diet-induced methods to simulate the disease, helping researchers develop and test novel treatments effectively.
Introduction
Type II Diabetes (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired glucose regulation, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Unlike Type I Diabetes, which is primarily caused by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, T2D occurs when the body's cells become less responsive to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin to overcome this resistance. This condition is often linked to obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet, making it prevalent in industrialized societies. Over time, the pancreas may lose its ability to produce insulin altogether, worsening the disease. T2D can lead to a range of serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Early diagnosis and lifestyle interventions, such as diet modification, exercise, and medication, are essential for managing blood glucose levels and preventing these complications.
Disease Models and Applications
The db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model is one of the most widely used models for studying Type II Diabetes. It is constructed by using the db mutation, which leads to leptin receptor dysfunction and results in obesity and insulin resistance. This model mimics key features of human Type II Diabetes, including hyperglycemia, obesity, and impaired glucose tolerance. db/db mice also develop diabetes-related complications such as hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular abnormalities. One advantage of this model is its ability to study the pathophysiological progression of diabetes over time. However, the model has some limitations, such as a lack of complete mimicry of human metabolic syndrome, especially in terms of the cardiovascular system, and its relatively short lifespan compared to humans. Nonetheless, it provides a valuable platform for testing potential diabetes drugs and understanding disease mechanisms.
- Simulates: The db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model simulates human Type II Diabetes by exhibiting metabolic abnormalities, including obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia. It also serves as a platform for studying the progression of associated complications such as cardiovascular diseases and kidney dysfunction.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate anti-diabetic drugs, insulin sensitizers, and therapies targeting metabolic dysfunctions. Drugs that regulate blood glucose levels, reduce insulin resistance, or alleviate obesity are commonly tested using this model. Additionally, it can be used to evaluate the efficacy of combination therapies for diabetes management.
Measurements
For evaluating drug efficacy in the db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model, we offer a variety of measurements using advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Body weight, blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and fasting glucose tolerance.
- Immunohistochemistry: Insulin staining in pancreatic tissues, inflammatory cell infiltration, and adipose tissue analysis.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and adipokines.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Monitoring of lipid profiles, liver enzymes, and kidney function markers.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Quantifying the expression of insulin signaling-related genes, inflammatory mediators, and adipokines via RT-qPCR and Western blot techniques.
These measurements provide a comprehensive assessment of the therapeutic effects on glucose metabolism, inflammation, and diabetic complications.
Related Services
In addition to the db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model, we also offer other models for studying diabetes induced by different methods. These include streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes models, high-fat diet-induced models, and others tailored to specific research needs.
- Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes Model
- Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model
- Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model
- STZ-NA induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Combined Spleen & Partial Pancreas Resection & Glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model
Advantages
- Customized Solutions: We offer tailored animal models and research protocols to meet the specific needs of your study, ensuring the most relevant and accurate results.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced scientists is available to assist with model selection, experimental design, and data analysis, providing you with comprehensive guidance throughout your research.
- High-Quality Models: We provide advanced, reproducible animal models that accurately mimic human diseases, ensuring reliable and consistent results.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Our lab utilizes cutting-edge technologies for measurements and data collection, including advanced imaging, biomarker profiling, and gene expression analysis.
- Extensive Therapeutic Area Experience: With a broad range of expertise in diabetes, oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and more, we are equipped to support studies across diverse therapeutic areas.
- Precision and Reliability: Our commitment to quality control ensures the highest standards in every step of the process, delivering data you can trust.
- Timely and Efficient Execution: We prioritize your timelines, providing fast turnaround times without compromising on the accuracy or quality of results.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of diabetes models do you offer?
A: We provide various models, including db/db Type II Diabetes, STZ-induced Type I Diabetes, and high-fat diet-induced models.
-
Q: How long does it take to see results from the db/db Type II Diabetes model?
A: Results typically emerge within 4-6 weeks, depending on the study's parameters and treatment timeline.
-
Q: Can the db/db Type II Diabetes model be used for long-term studies?
A: Yes, this model can be used for chronic studies, allowing for the observation of disease progression and therapeutic effects over time.
-
Q: What measurements are available for monitoring drug efficacy?
A: We offer a range of tests, including glucose tolerance tests, insulin sensitivity assays, and various biomarker analyses.
-
Q: Can you tailor models to specific research needs?
A: Yes, we can customize models and protocols to meet the specific requirements of your research, ensuring the most relevant outcomes for your study.
Published Data
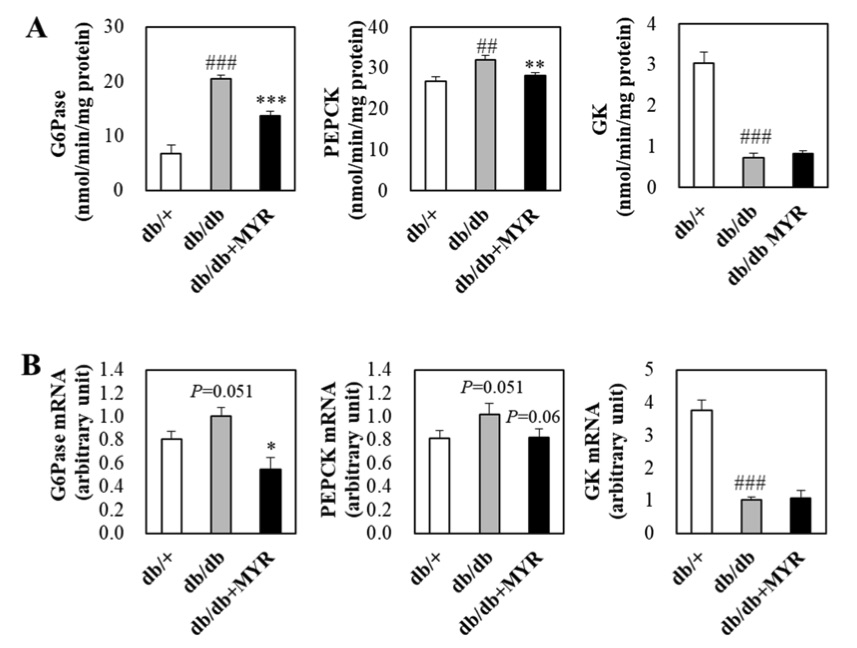 Fig. 1 Effects of myricitrin on hepatic glucose-regulating enzyme activity and mRNA expression in db/db mice.1
Fig. 1 Effects of myricitrin on hepatic glucose-regulating enzyme activity and mRNA expression in db/db mice.1
In an experiment using db/db mice, the activities of key glucose-regulating enzymes were measured. The results revealed that gluconeogenic enzymes, glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), exhibited significantly higher activity in db/db mice compared to db/+ control mice (Figure 1A). In contrast, the activity of the glycolytic enzyme glucokinase (GK) was significantly lower in db/db mice. When db/db mice were supplemented with myricitrin, the elevated activities of hepatic G6Pase and PEPCK were significantly inhibited. However, no significant change in hepatic GK activity was observed following supplementation with myricitrin (Figure 1A). Correspondingly, myricitrin supplementation also led to a down-regulation of the mRNA expression levels of G6Pase and PEPCK in db/db mice, while GK mRNA expression remained unaffected (Figure 1B). These findings suggest that myricitrin has a selective effect on gluconeogenesis-related enzymes without altering glycolytic enzyme activity in db/db mice.
Reference
- Kim, Sang Ryong et al. "Therapeutic Potential of Myricitrin in a db/db Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes." Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 30,7 1460. 25 Mar. 2025, DOI:10.3390/molecules30071460. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
