LPS induced Neuroinflammation Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Neuroinflammation is a process that results primarily from the presence of chronically activated glial cells (astrocytes and microglia) in the brain and has a proved common feature of several neurodegenerative conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, Multiple sclerosis, and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Research articles have reported that targeting neuroinflammation might present a promising method to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Creative Biolabs conducts contract studies in LPS-induced neuroinflammation model (both rats and mice) to evaluate the efficacy of potential anti-neuroinflammation drugs.
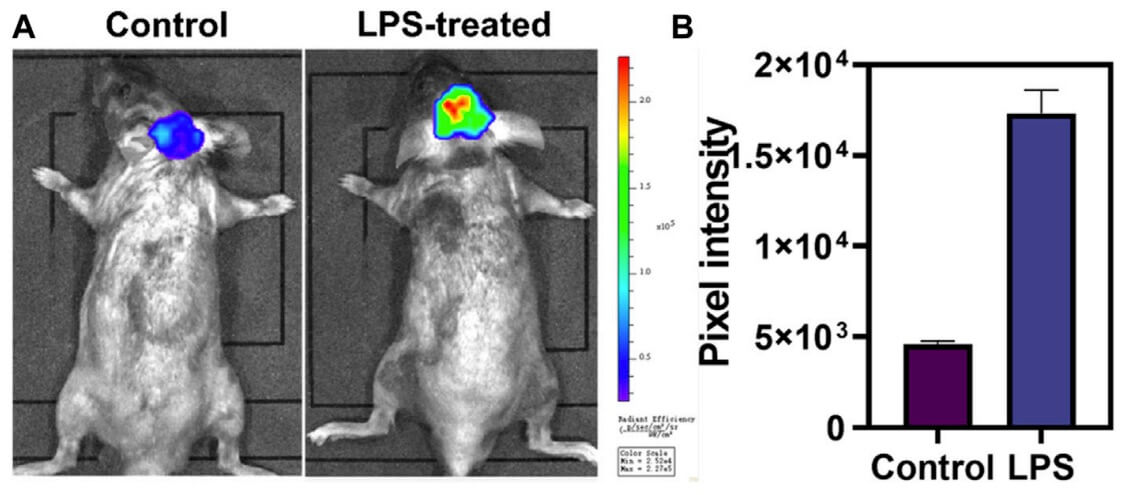 Fig. 1 Evaluation of HOCl in LPS-induced neuroinflammation mice with a responsive far-red fluorescent probe, DCI-H. 1
Fig. 1 Evaluation of HOCl in LPS-induced neuroinflammation mice with a responsive far-red fluorescent probe, DCI-H. 1
Introduction of Neuroinflammation
Microglial cells, as the resident immune cells in the CNS, play critical roles in host defense and tissue repair in the brain. When activated, they show macrophage-like capabilities including phagocytosis, inflammatory cytokine production, and antigen presentation. Normally, these neuroinflammatory changes are transient with microglia returning to a resting state as the immune stimulus is resolved. However, chronically activated microglia in a diseased brain brings an amplified or excessive inflammatory response in the brain, leading to complications such as cognitive dysfunctions, prolonged sickness behavior, and depressive-like behavior.
Model Description
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a classic inflammatory agent, is the main component of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. Peripheral or central administration of LPS has been used to produce neuroinflammation in animals. LPS triggers an array of microglial response by interacting with the membrane receptor Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), leading to the production of pro-inflammatory mediates (e.g., cytokines and interleukins, TNFα, and IFNγ) and the self-activation of the nuclear factor-κB system. Usually, mice can receive intraperitoneal injections of LPS to model neuroinflammation while rats receive intracerebral injections of LPS.
Assessments
For the evaluation of drug efficacy, various parameters can be determined at Creative Biolabs, including behavioral test, inflammatory cytokine measurement, immunostaining of brain sections for neuron loss assessment, etc. Creative Biolabs provides assessment including, but not limited to:
- Behavioral tests (e.g., motor function, cognition, social behavior)
- Pro-inflammatory and inflammatory mediator assessment
- Immunohistochemical staining of brain tissues
- mRNA and protein expression analysis
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to improving the understanding of human central nervous system (CNS) disorders and developing effective and efficient therapeutic interventions. Our preclinical service section is one of the most experienced in the world for screening and testing of experimental therapeutics of CNS disorders. The comprehensive list of rodent neurological disease models is placed below for your review:
If you are interested in our services, contact us to discuss your neuroinflammation study requirements today.
Reference
- Mi, Long, et al. "Development of an activatable far-red fluorescent probe for rapid visualization of hypochlorous acid in live cells and mice with neuroinflammation." Frontiers in Chemistry 12 (2024): 1355238. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using A, B parts of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
