Sepsis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established and meticulously developed sepsis models that simulate human disease, enabling researchers to evaluate potential therapies targeting inflammation, immune response modulation, and multi-organ dysfunction. These models provide valuable insights into drug efficacy and disease progression.
Introduction
Sepsis is a severe, life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to an infection becomes dysregulated, leading to widespread inflammation, tissue damage, and potential organ failure. It is typically caused by bacterial infections, but can also result from viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Sepsis can rapidly progress to septic shock, which is characterized by a significant drop in blood pressure, reduced blood flow to vital organs, and failure of one or more organ systems. Due to its complex pathophysiology and high mortality rate, particularly in intensive care settings, sepsis remains a major global health challenge. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial in improving survival outcomes.
Sepsis Models and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of well-established rodent models for sepsis research. These models are carefully designed to replicate the critical stages of sepsis, including systemic inflammation, organ dysfunction, and septic shock, which are characteristic of the disease in humans. Our models are suitable for evaluating a wide range of sepsis therapies, from antimicrobial agents to immunomodulatory drugs and organ protective treatments. These models provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of novel candidates in the preclinical phase. Our team of experienced scientists will collaborate with you throughout your project, from experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring high-quality and reliable results. To learn more about the sepsis models available for preclinical research, explore the links below:
| Sepsis Models | Simulates | Evaluates Drugs | Animal species |
| LPS induced Rodent Sepsis Models | Systemic inflammation and endotoxemia induced by LPS | Antimicrobial agents, immune modulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and therapies targeting the cytokine storm. | Mouse |
| Cecum Ligation and Puncture (CLP) induced Sepsis Models | Polymicrobial infection leading to multi-organ dysfunction | Antibiotics, immune system modulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and therapies for organ protection. | Rat, Mouse |
| 2-HIT Sepsis Models | Two-hit model combining endotoxemia and tissue injury | Anti-inflammatory agents, immune system modulators, organ protective treatments, and novel sepsis therapies. | Mouse |
| Escherichia Coli induced Sepsis Models | Bacterial infection caused by Escherichia coli, resulting in systemic infection and organ failure | Antimicrobials, immune response modulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and treatments aimed at managing sepsis induced organ damage. | Mouse |
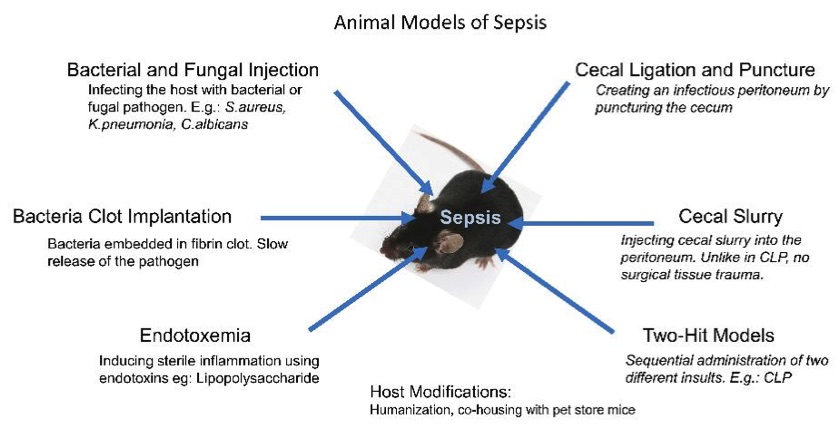 Fig. 1 Methods to develop sepsis models.1,3
Fig. 1 Methods to develop sepsis models.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We provide a range of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in rodent atopic dermatitis and eczema models, using advanced technologies, including but not limited to:- General Observations: Body weight, clinical score for skin lesions (erythema, scaling, edema), pruritus score (itching behavior).
- Histopathology: Skin tissue analysis for inflammation, epidermal thickness, and cell infiltration (e.g., T-cells, eosinophils, mast cells).
- Cytokine Profiling (e.g., ELISA): Quantification of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and TNF-α, which are key in driving inflammation in AD.
- Immunohistochemistry: Immune cell infiltration in skin tissues (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils) and markers of skin barrier integrity (e.g., filaggrin expression).
- Gene/Protein Expression Profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot to analyze the expression of key inflammatory genes and proteins involved in the pathogenesis of AD (e.g., Th2 cytokines, chemokines).
- Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL): Measurement of skin barrier function to assess drug efficacy in improving epidermal permeability.
In addition to our established models, we specialize in the development of novel animal models to address specific research needs. Our team of experts is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized approach to your research.
Our advantages
- Established Protocols: Well-validated models with consistent and reproducible results for sepsis research.
- Customized Services: Tailored drug evaluation services based on specific research goals.
- Advanced Monitoring: Comprehensive assessment tools, from clinical observations to molecular analysis, for thorough evaluation.
- Expert Support: Access to a scientific team to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis.
- Wide Application Range: Models suitable for testing a broad spectrum of drug types, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and immunomodulatory therapies.
- Cost-Effective: A cost-efficient approach for comprehensive drug evaluation and early-stage sepsis research.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What animal models are used to simulate sepsis?
We use several models, including cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection, and bacterial challenge models, depending on the type of infection being studied.
-
2. Can the models be customized to replicate specific infection types?
Yes, our models can be tailored to simulate bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, allowing for a focused investigation of specific pathogens.
-
3. How long do the sepsis models last?
The duration of the model depends on the induction method and the treatment being evaluated. Typically, the models last from 24 to 72 hours, but longer durations are possible.
-
4. Can we assess organ function in these models?
Yes, we provide detailed assessments of organ function, including liver, kidney, and lung damage, through histopathology, biomarkers, and blood analysis.
-
5. What is the survival rate in these models?
Survival rates can vary depending on the severity of the sepsis model and the intervention being tested. Generally, the survival rate is used as a critical endpoint for evaluating drug efficacy.
Published Data
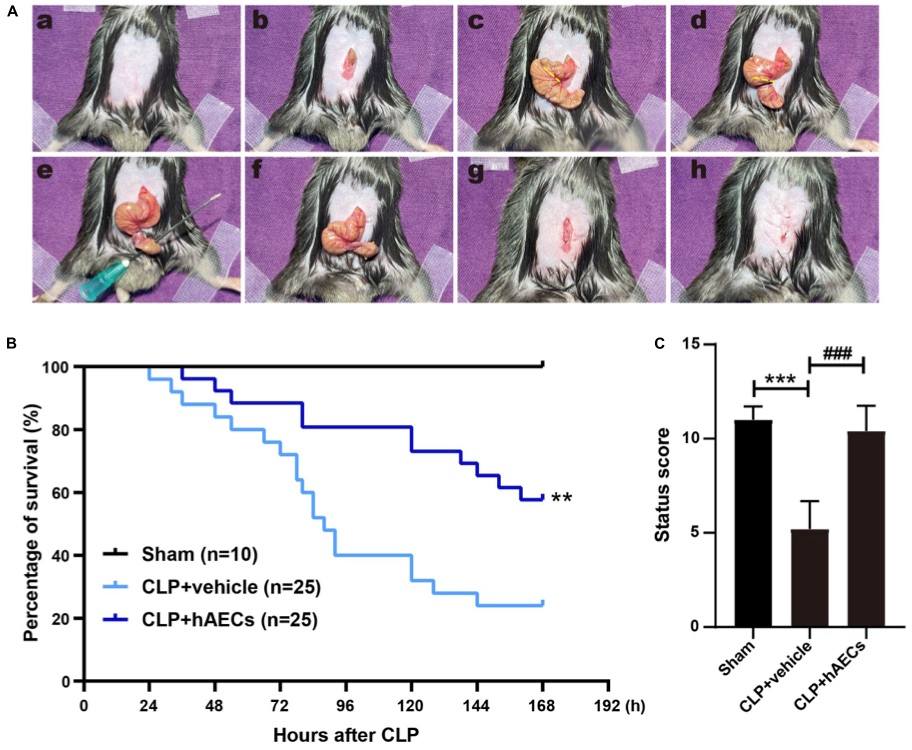 Fig. 2 Establishment of septic mouse model and the effects of human amnion epithelial cells (hAECs) on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) mice.2,3
Fig. 2 Establishment of septic mouse model and the effects of human amnion epithelial cells (hAECs) on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) mice.2,3
To replicate the pathophysiological changes observed in septic patients, a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) procedure was performed on mice, which is the most widely used and recognized gold standard model for experimental sepsis. High-grade sepsis was induced by ligating 75% of the cecum (Figure 2A). Within 7 days (168 hours) of observation, the vehicle control group of CLP mice showed a 76% mortality rate. However, the administration of human amniotic epithelial cells (hAECs) via tail vein injection immediately following the CLP procedure reduced the 7-day mortality rate to 42% (Figure 2B). A scoring system was developed to evaluate the overall health status of the septic mice 16 hours post-CLP, a time point at which no mortality was observed. The scoring system included assessments of mental state, autonomic motor activity, and myodynamia. CLP mice exhibited significantly lower health scores, presenting with symptoms such as low body temperature, listlessness, hunched posture, unsteady gait, muscle weakness, and reduced autonomic reflexes. Administration of hAECs effectively reversed these symptoms, improving the mice's overall condition to levels comparable to the sham-operated group (Figure 2C).
References
- Cai, Lun et al. "Advances in Rodent Experimental Models of Sepsis." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 24,11 9578. 31 May. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119578
- Chi, Dongxuan et al. "Human Amnion Epithelial Cells and Their Derived Exosomes Alleviate Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury via Mitigating Endothelial Dysfunction." Frontiers in Medicine vol. 9 829606. 24 Mar. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.829606
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
