Pulmonary Hypertension Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Introduction
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a precapillary form of pulmonary hypertension caused by complex endothelial dysfunction and vascular remodeling. It affects about 1% of the global population, and various underlying conditions can lead to it; for example, over half of heart failure patients may be affected. If left untreated, this progressive disease can cause debilitating fatigue, a significant decline in quality of life, and ultimately lead to heart failure and death, with a high mortality rate.
 Fig.1 Classification of PH.
Fig.1 Classification of PH.
 Fig.2 Pathogenesis related to PH.
Fig.2 Pathogenesis related to PH.
Available Pulmonary Hypertension Models
Creative Biolabs employs rigorous strategies and has established a comprehensive set of PH Models, ensuring high fidelity and translational relevance for research into pathogenesis and drug development, including small molecules, gene therapies, and biopharmaceuticals.
| Pulmonary Hypertension Models | Clinical Simulation | Primary Research Applications | Animal Species |
| Monocrotaline (MCT)-Induced PH Model | Specifically simulates drug-induced and idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), characterized by significant endothelial injury and vascular remodeling. | Vasodilators (e.g., Endothelin Receptor Antagonists ERA, PDE5 Inhibitors like Sildenafil), Anti-proliferative Drugs, and Anti-remodeling Drugs. | Mouse, Rat |
| Hypoxia-Induced PH Model | Simulates PH associated with chronic lung disease (PH-ILD), such as PH resulting from COPD and Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Characterized by Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction (HPV). | Adjuvant Drugs for Oxygen Therapy, Specific Vasodilators, and novel agents targeting vascular remodeling and hypoxia-driven mechanisms. | Mouse, Rat |
Evaluation Platform
At Creative Biolabs, we offer the highest quality services using state-of-the-art technology platforms. These include:
- Hemodynamic Assessment: Measurements of Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP), mean Pulmonary Arterial Pressure (mPAP), and Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR) are the gold standards for directly quantifying the severity of pulmonary hypertension and the resulting cardiac strain (Cardiac Output, RVEDP).
- Histopathological Analysis: This involves assessing pulmonary vascular remodeling (e.g., medial wall thickness), observing myocardial tissue sections, and performing immunofluorescence/confocal imaging to evaluate cellular proliferation, fibrosis, and the degree of right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH).
- Molecular and Biochemical Assays: Using gene expression analysis, protein detection (Western blot/ELISA), cytokine/metabolite measurement, and omics analysis, researchers delve into the molecular mechanisms of vascular remodeling, endothelial dysfunction, and RVH at the gene, protein, and functional levels.
- Imaging Evaluation: Non-invasive techniques such as echocardiography, MRI, and small animal PET are used to assess right ventricular function (e.g., size, wall thickness, ejection fraction), cardiac morphology, and pulmonary perfusion status in vivo and longitudinally.
- Behavioral and Survival Analysis: Continuous body weight monitoring and survival curve analysis serve as essential, high-level indicators of overall disease progression, systemic health, and the long-term efficacy and toxicity of therapeutic interventions.
Applications
- Pathological Mechanism Elucidation: Analyze pathological mechanisms such as endothelial dysfunction, vascular remodeling, and inflammatory pathways. Interpret the associations between genes, environment, and metabolic abnormalities and PH.
- Therapeutic Target and Drug Efficacy Validation: This involves analyzing the action targets of anti-vascular remodeling drugs, evaluating the efficacy of PH-related drugs, and validating the in vivo activity of candidate molecules.
Our advantages
- Comprehensive and precise model construction: Covering Diverse PH Models. Our approach closely mirrors the multifactorial nature of human PH, meeting various research objectives such as vascular remodeling, right heart function, and inflammatory mechanisms.
- Rigorous quality control and standardized procedures: We adhere to standardized experimental protocols for every step, from animal selection and reagent dosing to the modeling cycle, ensuring model stability and reproducibility.
- Expert technical team with in-depth analytical capabilities: Our team boasts cross-disciplinary technical expertise in PH model operations, gene editing, and indicator analysis, allowing us to navigate the technical challenges of different models.
- Efficient project management and flexible service models: We recommend the most suitable model based on the client's research phase and drug characteristics, establish reasonable timelines, and implement personalized project designs.
- Enhancing model value for clinical translation: Acknowledging that no single model can fully replicate human PH, we offer clients multi-model simultaneous testing services for parallel validation.
- Integration of cutting-edge technologies: We incorporate emerging methods to provide clients with a deeper analysis of model characteristics.
- Full data traceability and after-sales support: We provide complete experimental records and assist with data interpretation after project completion.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of pulmonary hypertension animal models does your company offer? Do they cover different WHO classifications?
A: We offer a variety of animal models covering WHO group 1-3 PH. These include genetic mutation models, chronic hypoxia models, cigarette smoke exposure models, bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis models, and pulmonary artery banding (PAB) models related to right ventricular failure, among others. This allows us to meet research needs for various etiologies and pathological characteristics.
-
Q: How do you ensure data reliability?
A: We validate model effectiveness through multi-dimensional analyses, including hemodynamic measurements, histopathological analysis, and molecular indicator detection, to provide clients with reliable foundational data.
-
Q: Can you construct complex models induced by multiple factors? What are the advantages of such models?
A: Yes, we can. Complex models simulate the synergistic effects of gene and environment or multiple injuries, more closely resembling the multifactorial nature of human PH. This approach significantly enhances the clinical translational value of drug development.
Published Data
Lycopene can reverse increased vascular wall thickness and smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by hypoxia. The potential of this model for preclinical PH research and development was confirmed through the inhibitory effect of lycopene on the hypoxia-induced PH model.
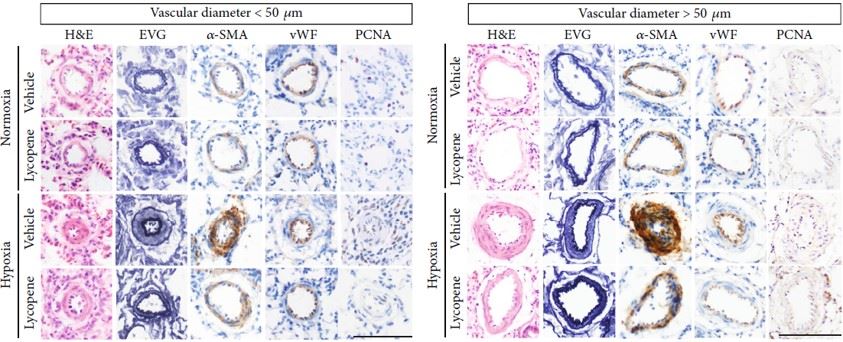 Fig.3 H&E staining, EVG staining, and immunohistochemistry results for α-SMA, vWF, and PCNA in pulmonary arterioles.1
Fig.3 H&E staining, EVG staining, and immunohistochemistry results for α-SMA, vWF, and PCNA in pulmonary arterioles.1
Reference
- Wang, Dingyou et al. "Lycopene Ameliorates Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension via Suppression of Oxidative Stress." Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity vol. 2022 9179427. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9179427. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
