Immunologically driven Pulmonary Fibrosis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Immunogen-driven pulmonary fibrosis is a severe, progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD) where a dysregulated immune response initiates and perpetuates fibrotic remodeling of the lungs. While idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is primarily caused by connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease and hypersensitivity pneumonitis, new evidence suggests immune dysregulation is a key driver of disease progression. Key pathogenic features of this dysregulation include abnormal T cell polarization, persistent macrophage activation, and heightened cytokine concentrations. Creative Biolabs offers well-designed immunologically-driven pulmonary fibrosis models to accelerate drug R&D, bridge the gap between basic immunology and clinical ILD research, offering validated models, integrated detection, and customized solutions to accelerate therapeutic discovery.
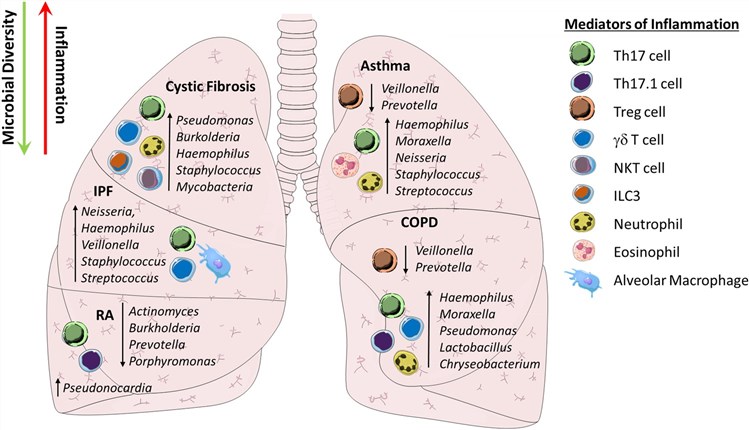 Fig.1 Reduced pulmonary microbial diversity is associated with IL-17-driven inflammation both in the airways and systemically.1,3
Fig.1 Reduced pulmonary microbial diversity is associated with IL-17-driven inflammation both in the airways and systemically.1,3
Available Immunologically driven Pulmonary Fibrosis Models
| Pulmonary Fibrosis Models | Clinical Relevance | Primary Research Applications | Animal Species |
| Adoptive Transfer of Fibrocytes Model | Mimics the accumulation of circulating fibrocytes in human IPF. | Cell-based Therapies (e.g., stem cell therapies), Anti-migratory Drugs (to inhibit fibrocyte recruitment), and agents targeting fibrocyte activation/function. | Mouse |
| IL-13/IL-17 Overexpression Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model | Simulates immune-driven fibrosis mediated by Th2 (IL-13) and Th17 (IL-17) pathways, relevant to some forms of autoimmune or hypersensitivity lung disease. | Biological Agents (e.g., Anti-IL-13 or Anti-IL-17 antibodies), Immunomodulatory Drugs (to rebalance Th2/Th17 responses), and targeted Anti-Cytokine Therapies. | Mouse |
Evaluation Platform
Our multi-dimensional assessment platform facilitates the precise detection of key pulmonary fibrosis indicators, optimizing the quality and reliability of our services.
- Histopathology: Using H&E staining, Masson's trichrome, Sirius red staining, and immunohistochemistry to quantify lung tissue fibrosis.
- Molecular Biology: Employing qPCR, Western blot, and RNA scope to profile gene and protein expression.
- Flow Cytometry: Performing single-cell staining on BALF samples to quantify immune cell dynamics and polarization shifts.
- Biochemical Assay: Using ELISA or hydroxyproline assays to detect cytokines or collagen content in the lung.
- Imaging: Using Micro-CT and high-resolution ultrasound enables non-invasive, longitudinal monitoring of structural lung damage.
- Pulmonary Function: Utilizing whole-body plethysmography and airway resistance and lung compliance provides a functional assessment of respiratory function.
Furthermore, uncovering global immune-fibrotic networks and novel targets via the Transcriptomics/Proteomics Platform.
Applications
- Mechanism Studies: Elucidate immune cell crosstalk and complex immune-fibrotic pathways, such as Th17/IL-17 signaling.
- Drug Development and Biomarker Discovery: Explore diverse therapeutic agents, such as anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and prognostic biomarkers related to pulmonary Fibrosis.
- Combination Therapy Evaluation: Combination of various therapy methods to evaluate multiple disease pathways.
Our advantages
- Diverse, Mechanism-Covering Models: We offer a broad range of models, from chemically induced to genetically engineered, precisely simulating various immune-driven scenarios to meet specific research needs.
- High Model Success Rate: Our standardized modeling procedure, featuring rigorous control over inducer dosage, administration routes, and environmental factors, ensures a success rate of over 90% and significantly reduces experimental variability.
- Integrated Multi-Platform Detection: We provide seamless integration of detection at the molecular, cellular, and whole-organism levels, offering comprehensive data support.
- Customization Capability: We can customize models, such as specific immune cell knockout or overexpression, humanized modifications, and detection combinations to flexibly adapt to your unique research goals.
- Rigorous Data Scientificity: Our experimental design incorporates controls, blinded assessments, and sample size power analysis. Data undergoes cross-validation across multiple platforms to ensure scientific rigor.
- Experienced Expert Team: Our team members have more than 10 years of experience in project development, comprising multidisciplinary experts in molecular biology, pathology, and pharmacology.
- One-Stop Service: We offer one-stop service, covering everything from model construction and sample collection to data analysis and report generation, which significantly shortens research cycles.
- Human Relevance Validation: The immunopathological features of our models, such as cytokine profiles, immune cell infiltration, and lung histopathology, are validated against patient sample databases from IPF/CTD-ILD, enhancing their translational value.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: Can models be tailored to specific immunological pathways?
A: Yes. We customize models by adjusting inducers (e.g., anti-IL-17 neutralizing antibodies) or genetic modifications (e.g., Il17a gene knockout in mice) to target pathways of interest.
-
Q: How can you define the success of a model?
A: Success is confirmed by ≥3 readouts, including: histopathological fibrosis (Ashcroft score ≥3), elevated hydroxyproline (>50% vs. control), and immune cell infiltration (BALF Th17 cells >10% of CD4+ T cells).
-
Q: How is data reproducibility ensured?
A: We perform technical replicates (n≥3 per group) and biological replicates (n≥6 mice per group) with centralized protocol execution to determine the details of the technical solution. All data undergo statistical analysis and are reported with 95% confidence intervals.
-
Q: Do you offer long-term fibrosis monitoring?
A: Yes. We track fibrosis progression up to 12 weeks post-induction, with serial Micro-CT and lung function tests (mimicking human IPF).
-
Q: Are negative controls included?
A: All experiments include sham controls (vehicle-only) and naive controls to exclude non-specific effects.
Published Data
A case demonstrates the potential of the IL-13/IL-17 overexpression induced pulmonary fibrosis model for preclinical pulmonary fibrosis R&D, highlighting IL-17, predominantly produced by γδ T cells, and its effect on the development of acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis.
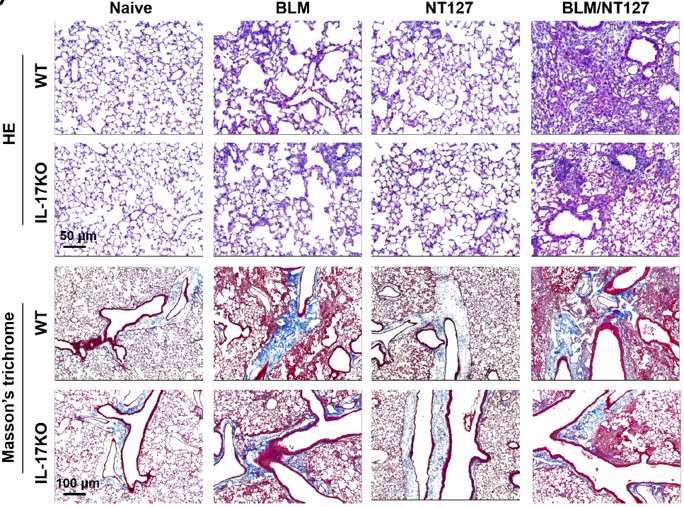 Fig.2 H&E and Masson's trichrome staining of lung sections from WT and IL-17 KO mice.2,3
Fig.2 H&E and Masson's trichrome staining of lung sections from WT and IL-17 KO mice.2,3
References
- Mannion, Jenny M et al. "The Airway Microbiome-IL-17 Axis: a Critical Regulator of Chronic Inflammatory Disease." Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology vol. 64,2 (2023): 161-178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-022-08928-y
- Chen, Shengsen et al. "Essential role of IL-17 in acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis induced by non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae." Theranostics vol. 12,11 5125-5137. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.74809
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
