Chemically induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF), encompassing both idiopathic and secondary types, is a fatal and progressive lung disease driven by environmental and genetic factors, and characterized by alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis, basement membrane damage, abnormal repair responses, and inflammatory dysregulation. While lung transplantation is a necessary intervention for late-stage disease, it's limited by donor availability, and the 5-year post-operative survival rate is only 50%. Current anti-fibrotic drugs like pirfenidone and nintedanib can slow the decline in lung function but cannot cure the disease. Creative Biolabs simulates the pathological process of human pulmonary fibrosis and has established 4 chemically induced PF models. These models provide scientists with crucial platforms to validate therapeutic targets, assess the pharmacodynamics (PD) and safety of lead compounds, and address the heterogeneity of the disease, thereby accelerating the development of treatments for human PF.
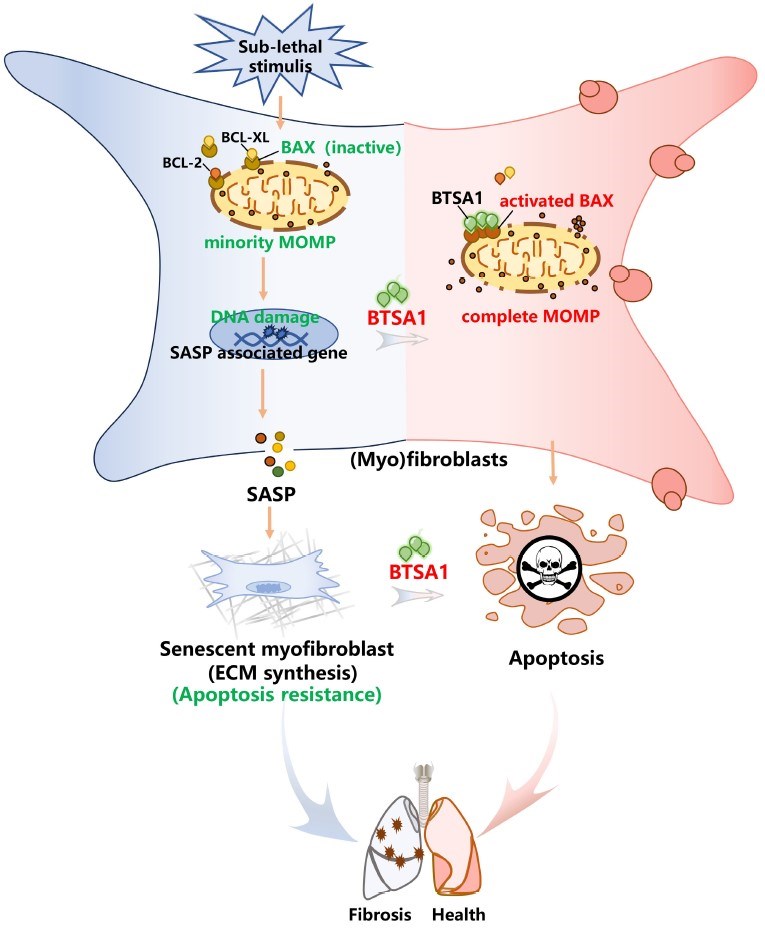 Fig.1 Schematic model illustrating the anti-fibrotic mechanism mediated by BAX activation via the senolytic drug BTSA1.1
Fig.1 Schematic model illustrating the anti-fibrotic mechanism mediated by BAX activation via the senolytic drug BTSA1.1
Available Chemically Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Models
| Pulmonary Fibrosis Models | Clinical Relevance and Primary Research Applications | Animal Species |
| Bleomycin induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model | The gold standard of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), usually used to test novel anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, or immunomodulatory compounds, typically for preventing fibrosis onset. | Mouse, Rat |
| Silica induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model | Silicosis, coal worker's pneumoconiosis, better suited for testing drugs against established, chronic fibrosis, where the goal is to halt or reverse the existing pathology. | Mouse, Rat |
| Paraquat induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model | Toxic pulmonary fibrosis, post-ARDS fibrosis, especially used to study oxidative stress and apoptosis-mediated mechanisms, to test specific antagonists against chemical induced injury, and multi - organ toxicity. | Rat |
| Asbestos induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model | Malignant mesothelioma, Asbestosis, applied to study the mechanisms of fibrosis induced by specific environmental particulates. | Mouse, Rat, Guinea pig |
Evaluation Platform
Our advanced detection platforms and precise instrumentation ensure the accuracy of all pharmacodynamic evaluations.
- Inflammatory Response Indicator Detection: This platform enables the quantification of inflammatory cells using methods like blood cell analysis or flow cytometry. Inflammatory mediators are detected through techniques such as ELISA, multiplex cytokine assays, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) / immunofluorescence (IF).
- Pulmonary Function Testing: We dynamically monitor early changes in lung function to assess ventilation parameters and perform blood gas analysis to evaluate gas exchange capabilities.
- Pathological Damage Assessment: This platform involves histomorphological analysis of lung tissue sections and the examination of lung ultrastructure via techniques such as transmission electron microscopy.
- Molecular Mechanism-Related Indicator Detection: We employ various methods, including assay kits, Western blot, RT-qPCR, and immunofluorescence, to detect indicators related to molecular mechanisms, such as oxidative products, antioxidant enzymes, and signaling pathways associated with fibrosis.
Applications
- Mechanistic Studies: These models are indispensable for dissecting the complex and dynamic progression of lung fibrosis, focusing on the analysis of inflammation and injury pathways, the stages of fibrotic progression, and the critical intercellular crosstalk between pulmonary epithelial cells, immune cells, and fibroblasts.
- Drug Screening: Due to their rapid induction and high reproducibility, they are ideal for high-throughput screening of lead compounds to determine their potential in reversing or halting PF.
- PD Studies: These models serve as the cornerstone for evaluating the efficacy and pharmacodynamics of novel anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory agents.
Our advantages
- Professional model development and optimization capabilities: We have established four chemically induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and developed standardized operating procedures (SOPs) to ensure model reproducibility. We also have the capability to develop customized models, covering diverse pathogenic mechanisms and satisfying specific customer needs, such as those related to drug targets and mechanisms.
- Advanced detection and analysis techniques: We combine advanced multi-dimensional detection platforms, such as molecular and cell biology, imaging techniques, immunology, pathology, and high-throughput screening, to meet customers' high-standard requirements for data delivery.
- Strict quality control and compliance: To ensure experimental data is traceable and repeatable, we conduct a full-process review of experimental design, data collection, and reporting.
- Rich project experience and interdisciplinary team: We have successfully completed numerous projects related to respiratory disease models, accumulating significant industry experience that helps customers rapidly evaluate drugs. Our team comprises experts in respiratory medicine, biologists, and statistical analysis specialists.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: To what extent does the chemically induced pulmonary fibrosis model mimic the actual clinical condition of the disease?
A: Our models undergo rigorous validation processes. They consistently align with clinical patient manifestations across pathological features (e.g., alveolar structure destruction and collagen fiber deposition, biochemical indicators (e.g., changes in cytokines like TGF-β, TNF-α), pulmonary function tests (e.g., decreased vital capacity and reduced lung compliance). This enables effective simulation of disease progression, providing a reliable basis for efficacy evaluation.
-
Q: Can I choose specific modeling inducers and methods according to my needs?
A: Absolutely. We offer various modeling protocols tailored to your research objectives. Our expert team will recommend the most suitable and personalized modeling approach based on your research direction.
-
Q: What is the typical project timeline?
A: Project timelines vary depending on the experimental content and complexity. Typically, a basic pulmonary fibrosis model construction and efficacy evaluation project takes 6-8 weeks. If the project includes special assays or multiple comparative experiments, the timeline might be extended accordingly. We will clearly specify the exact timeframes in the proposal.
-
Q: What does the experimental report include?
A: The experimental report includes the background and objectives, materials and methods, experimental results including data charts, pathological analysis, statistical test outcomes, conclusions, and discussion, while also supplying raw data such as original measurement values and image files to ensure data completeness and traceability.
-
Q: Is the data kept confidential?
A: We prioritize client data security and privacy, strictly adhering to confidentiality agreements and ensuring no disclosure of experimental data or related information to third parties without written authorization.
Published Data
The therapeutic potential of protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK; Eif2ak3) inhibitors (GSK2656157): In mice with established fibrosis, induced by 13 days of exposure to asbestos or bleomycin, GSK2656157 significantly suppressed eIF2α phosphorylation in pulmonary macrophages, reduced collagen deposition, and hydroxyproline content. This example effectively demonstrates the application potential of the Bleomycin and Asbestos induced fibrosis models in the R&D of pulmonary fibrosis drugs.
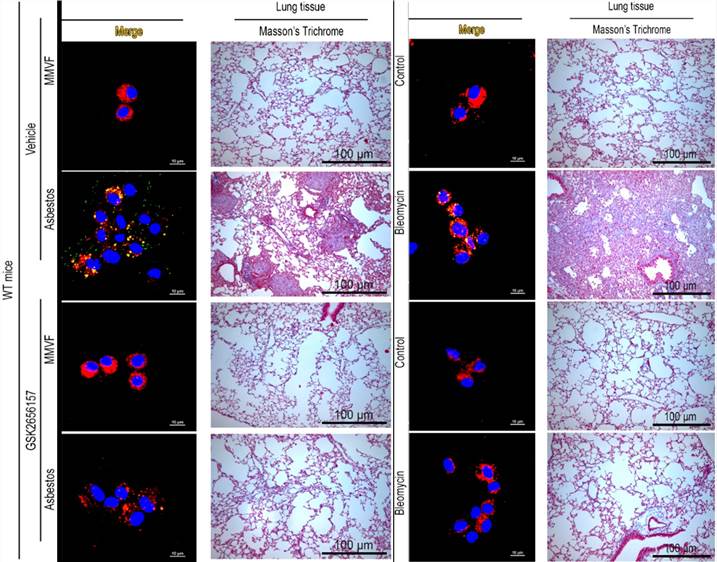 Fig.2 PERK reverses established lung fibrosis.2
Fig.2 PERK reverses established lung fibrosis.2
References
- Shen, Mengxia et al. "A novel senolytic drug for pulmonary fibrosis: BTSA1 targets apoptosis of senescent myofibroblasts by activating BAX." Aging cell vol. 23,9 (2024): e14229. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.14229. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Pandey, Jyotsana et al. "The PERK/ATF4 pathway is required for metabolic reprogramming and progressive lung fibrosis." JCI insight vol. 10,10 e189330. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.189330. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, with modification.
For Research Use Only.
