Gouty Arthritis (GA) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs offers a range of well-established models for simulating gouty arthritis, designed to evaluate drug efficacy in preclinical studies. These models can be tailored to assess the effectiveness of urate-lowering therapies and anti-inflammatory agents, providing valuable insights into disease mechanisms and treatment options.
Introduction
Gouty arthritis (GA) is an inflammatory arthritis primarily caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in joints, which triggers an intense immune response and inflammation. It is characterized by sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness, commonly affecting the big toe but can also involve other joints such as the knees, ankles, and wrists. The condition is often linked to hyperuricemia, where elevated levels of uric acid in the blood lead to the formation of MSU crystals. Gout attacks are typically acute but can become recurrent if left untreated, leading to joint damage, tophi formation, and chronic pain. GA is one of the oldest known diseases, with a well-documented history in medical literature. However, effective treatment remains a challenge, as current therapies primarily focus on managing acute attacks and preventing further flare-ups. Traditional treatments include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and uric acid-lowering agents like allopurinol and febuxostat. Biologic therapies targeting inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β are also emerging as potential options for managing acute attacks and preventing long-term joint damage.
Gouty Arthritis (GA) Model and Applications
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established rodent models for Gouty Arthritis (GA). These models are carefully designed to simulate the acute inflammatory response caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which is the key pathological feature of gouty arthritis in humans. The models are ideal for evaluating therapeutic candidates aimed at treating both the acute and chronic phases of gout, providing detailed insights into the effectiveness of urate-lowering drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and cytokine-targeting biologics. Our team of experienced scientists will collaborate with you through every stage of your project, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring high-quality and reliable results. To learn more about our Gouty Arthritis models and how they can support your research, explore the links below.
| Gouty Arthritis Models | Simulates | Evaluates Drugs | Animal species |
| Monosodium Urate induced Air-Pouch GA Rat Model | Acute inflammatory response caused by urate crystal deposition, including edema, leukocyte infiltration, and cytokine release. | Anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs, colchicine, urate-lowering agents, and novel therapeutics targeting crystal induced inflammation. | Rat |
| Monosodium Urate induced Gouty Arthritis Rat Model | Joint inflammation, pain, and swelling resulting from monosodium urate crystal deposition. | Analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, urate-lowering therapies, and biologics targeting IL-1β and other inflammatory mediators. | Rat |
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the Gouty Arthritis model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:- General Observations: Joint swelling, body weight, and signs of pain or discomfort.
- Histopathology: Infiltration of inflammatory cells, particularly neutrophils, into the joint tissues; crystal deposition in joint synovial tissues.
- Cytokine Profiling: Serum levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
- X-ray or MRI Imaging: Detection of joint damage, bone erosion, or changes in joint structure.
- Gene/Protein Expression: RT-qPCR and Western blot to assess the expression of inflammatory markers, immune cell activation, and matrix metalloproteinases involved in joint degradation.
- Pain and Mobility Assessment: Mechanical allodynia or joint sensitivity tests, as well as gait analysis to evaluate functional impairment.
In addition to the established GA models, we also specialize in developing custom models tailored to your specific research needs. Our team of experts is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis to ensure a robust approach to your project at every stage.
Our advantages
- Tailored Models: Customizable to simulate different stages of gout, from acute attacks to chronic disease.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A broad range of measurements from histopathology to pain assessment, offering a detailed understanding of drug effects.
- Expert Guidance: Our experienced scientists will assist you with model design, data interpretation, and troubleshooting throughout your project.
- Preclinical Research Expertise: Proven success in drug efficacy testing and development for gout and related conditions.
- Accelerated Timelines: Rapid model generation and data collection to help speed up your research and bring treatments to market faster.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. How does this model simulate gouty arthritis?
The model is induced by the administration of monosodium urate crystals, which trigger an acute inflammatory response in the joints, mimicking the pain and swelling associated with gout attacks.
-
2. Can this model be used to study chronic gout?
This model primarily simulates acute gout attacks. For chronic gout, additional long-term studies are needed to observe repeated flares and joint damage.
-
3. What types of drugs can be tested in this model?
The model is suitable for evaluating uric acid-lowering drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and biologic therapies targeting cytokines involved in the inflammatory process.
-
4. What types of measurements are available in the Gouty Arthritis model?
We offer a range of measurements, including joint swelling, inflammatory cell infiltration, cytokine profiling, pain assessment, and joint imaging, among others.
-
5. How long does it take to observe results?
Acute effects can typically be observed within 24-48 hours of MSU crystal administration, while longer-term studies can assess the effectiveness of treatments over several weeks.
Published Data
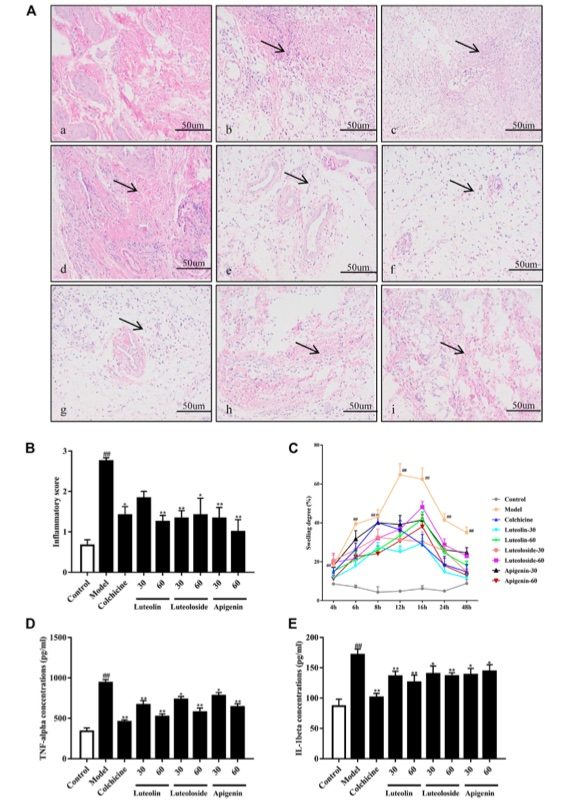 Fig. 1 The effects of the active flavonoids luteolin, luteoloside, and apigenin attenuated monosodium urate (MSU) crystal induced gouty arthritis of rats.1
Fig. 1 The effects of the active flavonoids luteolin, luteoloside, and apigenin attenuated monosodium urate (MSU) crystal induced gouty arthritis of rats.1
As depicted in Figure 1A, the synovial tissue of the normal group showed no signs of infiltration, with cells appearing intact. In contrast, the synovial tissue of the model group exhibited significant infiltration of inflammatory cells, accompanied by vesicular-like changes in the surrounding cells. Administration of colchicine and active flavonoids notably reversed these inflammatory pathological changes in the synovial tissue of the ankle joint. As shown in Figure 1B, the active flavonoids significantly reduced the cell infiltration induced by MSU crystals, as indicated by the inflammatory score and the results from histopathological analysis. Figure 1C illustrates that, compared to the control-vehicle group, rats injected with MSU crystals displayed significant ankle joint swelling at all time points from 4 to 48 hours post-injection, with the peak swelling occurring at 12 hours. The swelling gradually subsided between 12 and 24 hours but remained significantly higher than in the control rats. Notably, both colchicine and active flavonoids significantly reduced ankle joint swelling from 6 to 48 hours post MSU crystal injection, compared to the model group. Figures 1D and 1E demonstrate that MSU crystal injection resulted in a marked increase in the serum levels of TNF-α and IL-1β. However, both colchicine and active flavonoids significantly reduced the levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines in the serum, relative to the model group, following MSU crystal injection.
Reference
- Ouyang, Xiang et al. "Active Flavonoids From Lagotis brachystachya Attenuate Monosodium Urate induced Gouty Arthritis via Inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Expression." Frontiers in Pharmacology vol. 12 760331. 5 Nov. 2021. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.760331
For Research Use Only.
