Airway Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Airway mucus safeguards the airway epithelium by capturing inhaled foreign pathogens and aiding their removal through mucociliary clearance (MCC). In individuals with respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis (CF), non-CF bronchiectasis, and asthma, the mucus secreted is more viscoelastic than in healthy individuals. This increased viscoelasticity results in mucus accumulation within the respiratory tract, leading to a reduction in lung function. Based on airway responsiveness characteristics, Creative Biolabs has established a set of airway disease models, which empower research into the mechanisms of respiratory diseases and facilitate the development of related therapeutics.
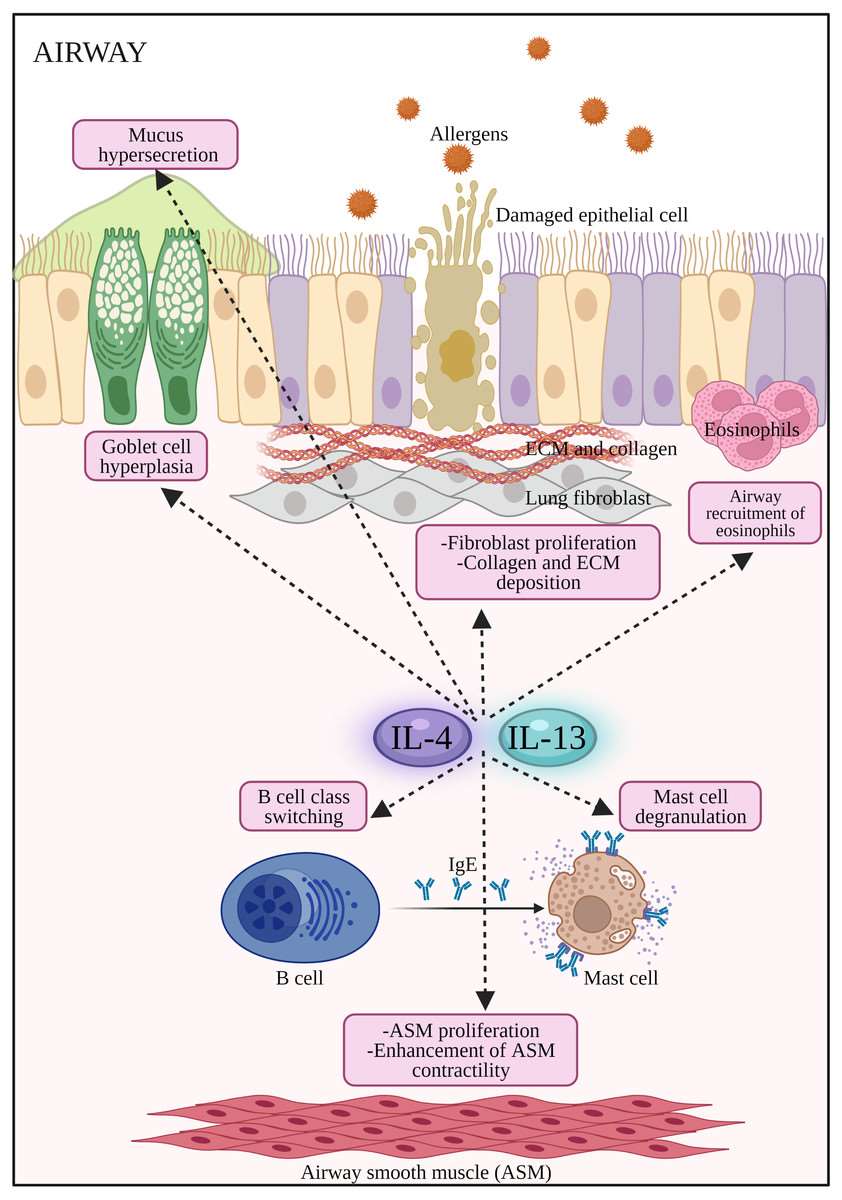 Fig.1 The potential effects of IL-4 and IL-13 on inflammatory cells and structural changes to the epithelial barrier in AR and asthma.1,3
Fig.1 The potential effects of IL-4 and IL-13 on inflammatory cells and structural changes to the epithelial barrier in AR and asthma.1,3
Available Airway Models
| Airway Models | Clinical Relevance | Primary Research Applications | Animal Species |
| IL-13-Induced Airway Mucus Hypersecretion Model | Simulates Th2 inflammation-driven mucus plugging, a key pathology in severe asthma and CF. | Anti-Th2 Biologics (e.g., antibodies, targeting IL-4Rα), Mucolytics (N-acetylcysteine NAC), and Inhibitors of Mucus Hypersecretion (targeting MUC5AC). | Mouse |
| Acetylcholine-Induced Airway Constriction Model | Gold standard for assessing Airway Hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in asthma and COPD. | Bronchodilators (e.g., β2-agonists like Salbutamol or LABAs), Anticholinergics (e.g., Ipratropium), and compounds stabilizing airway smooth muscle function. | Mouse, Rat, guinea pig |
| Pseudomonas Aeruginosa-Induced Bronchiectasis Model | Simulates chronic bacterial infection leading to bronchiectasis and structural damage (e.g., CF infection severe and COPD). | Novel Antibiotics (targeting multi-drug resistant), Anti-inflammatory Agents (e.g., macrolides like Azithromycin), and drugs targeting NETosis (NETs mechanisms) and biofilm destruction. | Mouse, Rat, |
Evaluation Platform
Equipped with cutting-edge technology and highly accurate assays, our platform ensures superior PD service quality.
- Molecular Biology: Leverages PCR, WB, RNA-seq, ELISA, Luminex, and MSD for high-throughput quantification. The primary purpose is the precise measurement of cytokine/chemokine levels, gene expression, and protein levels to support inflammatory gene profiling, target validation, and PD assessment.
- Immunology: Focuses on understanding the immune landscape in the lungs/airways using Flow Cytometry and Immunofluorescence. Performs detailed immune cell profiling (phenotyping, counting) and analyzes epithelial marker expression/localization to gain insights into inflammation and immune modulation.
- Histology & Imaging: Provides critical structural and morphological assessments using H&E staining, Masson's trichrome, PAS, and confocal microscopy. Quantifies airway structure integrity, collagen deposition/fibrosis, and mucus, and visualizes the 3D architecture of lung tissues.
- Functional Physiology: Employs specialized instruments like FlexiVent to provide quantitative functional data. Measures airway resistance and lung compliance in rodents, assesses Airway Hyperresponsiveness (AHR), and determines ciliary beat frequency and mucus transport rate.
- Omics: Encompasses proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptome profiling (RNA-seq). Generates large-scale, comprehensive datasets of proteins, metabolites, and genes, essential for target discovery, biomarker identification, and understanding complex drug mechanism of action (MoA).
- Inhalation Pharmacology: Utilizes technologies like nebulizer-coupled ALI models to optimize drug delivery. The primary purpose is to refine inhaled drug formulations and ensure optimal delivery efficiency to target tissues.
Applications
- Depth of Mechanism Research: Models target key drivers like the STAT6-SPDEF axis, neuroreceptors, and the infection-inflammation cascade to accelerate therapeutic target validation. This targeted approach accelerates the validation of specific therapeutic targets.
- Translational Medicine Value: Our advanced airway models directly translate to clinical therapeutic optimization, such as biologics, optimizing bronchodilator treatment regimens, and antibacterial strategies.
- New Trends in Compound Models: Based on the models mentioned above, we can establish compound airway models to accelerate the simulation of complex disease pathologies, such as severe asthma, bronchiectasis, and virus-induced asthma exacerbations, through synergistic co-stimulation (e.g., IL-13 + Acetylcholine or Elastase + Infection).
Our advantages
- Cutting-edge platforms: We integrate conventional methods for drug efficacy testing, co-culture, transcriptomics, and real-time imaging, an inhalation pharmacology platform, to comprehensively evaluate the model and drug efficacy.
- Cross-disciplinary expertise: Our team comprises respiratory disease modeling experts, pharmacologists, and biologists, all possessing years of experience in model development. We also excel at providing customized models tailored to meet specific client needs.
- High success rate: Our skilled technical operators meticulously follow standardized protocols and rigorous quality control (QC) measures, ensuring a model success rate exceeding 90%.
- One-stop service: Beyond our Airway Models, we also establish oncology models, metabolic disease models, and conduct toxicology studies. We offer one-stop services to streamline your research and minimize time spent coordinating across multiple platforms.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What types of airway disease models can we construct? What research directions are they applicable to?
A: We offer a comprehensive portfolio of advanced airway models, ranging from fundamental allergic inflammation and bronchoconstriction models to highly translational human-relevance models. Our capabilities span fungal allergen-induced asthma models (mimicking eosinophilia and AHR) and IL-13 transgenic models (simulating Th2-driven fibrosis and mucus pathology). This integrated platform ensures robust model validation and functional assessment (via carbachol/methacholine challenges) to accelerate target identification and preclinical efficacy testing for a broad spectrum of obstructive and inflammatory airway diseases.
-
Q: How do you choose experimental animals when building airway models, and what are the advantages of different species?
A: Optimal animal selection is crucial and tailored to specific research goals: For detailed mechanistic studies and the generation of transgenic models, strains like C57BL/6J and BALB/c mice are utilized. Conversely, for reliable physiological measurements such as airway resistance and respiratory rate, Wistar rats and other suitable species are employed to ensure superior stability and data quality.
-
Q: What are the core detection indicators for airway models?
A: Our core detection platform utilizes a multi-layered approach to ensure robust pharmacodynamic evaluation, encompassing Pathological Indicators (e.g., eosinophil/neutrophil infiltration, Masson's staining for fibrosis, and cytokine analysis like IL-5/IL-13), Physiological Function (e.g., AHR and airway resistance via plethysmography, including human-relevant FEV1 assessment), and Molecular Indicators (e.g., critical chemokines, receptor expression, and signaling pathway activity). This comprehensive suite provides the precision necessary to accelerate your drug pipeline through mechanism-based validation.
-
Q: How do you ensure data reliability?
A: We ensure superior data reliability and statistical rigor through an uncompromised experimental design: Each study mandates robust sample sizes (5-8 animals per group, repeated 2-3 times) and adheres strictly to Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs) for all critical parameters, including aerosol administration and precise detection time points. The incorporation of both negative and positive controls, combined with the application of appropriate statistical methods like ANOVA and paired t-tests, guarantees the statistical significance and reproducibility of all preclinical results.
-
Q: Can you customize specific airway models?
A: Yes, we offer highly customized models leveraging advanced gene editing and manipulation techniques, including cell-specific knockout/overexpression models (e.g., the RoraCre+ ChatLoxP mouse model) and molecular modulation models (e.g., ACh depletion via aerosolized AChE or transgenic IL-13 overexpression to mimic airway fibrosis). We support your specific research objectives with preliminary validation data, though custom model construction typically requires a 4-8 week adjustment period.
Published Data
The P. aeruginosa-induced Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) rabbit model successfully recapitulates the pathological features of human VAP, ranging from early injury to severe inflammation. Furthermore, the accompanying severe pulmonary edema and the degree of lung injury are positively correlated with the infection duration. This confirms the model's significant application potential in research concerning respiratory system diseases.
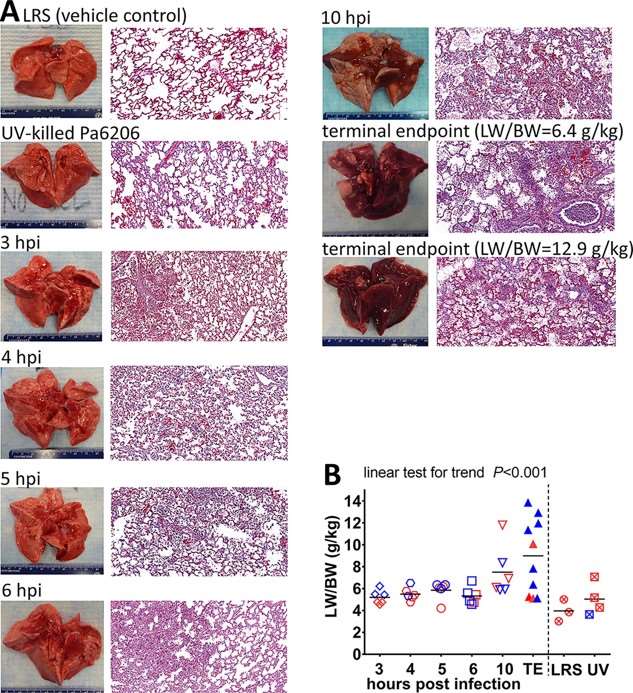 Fig.2 Natural history of P. aeruginosa-induced ventilator-associated pneumonia in rabbits.2,3
Fig.2 Natural history of P. aeruginosa-induced ventilator-associated pneumonia in rabbits.2,3
References
- Nur Husna, Siti Muhamad et al. "IL-4/IL-13 axis as therapeutic targets in allergic rhinitis and asthma." PeerJ vol. 10 e13444. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13444.
- Roberts, Luke B et al. "Differential Regulation of Allergic Airway Inflammation by Acetylcholine." Frontiers in immunology vol. 13 893844. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.893844.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
