In Vitro Antibody dependent Enhancement (ADE) Assay
Based on the unrivaled expertise and experiences in antibody discovery and development, Creative Biolabs has developed a novel in vitro antibody-dependent enhancement assay service for global clients to speed up the project's development.
Introduction of Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE)
Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), known as immune enhancement, involves a cascade of events whereby viruses may infect susceptible cells via interaction between virions complexed with antibodies (or complement components) and, respectively, Fc (or complement receptors), leading to the amplification of their replication increasing the infectivity and virulence.
ADE functions in viral infection with two distinct mechanisms: by enhancing antibody-mediated viral absorption into phagocytes expressing Fc gamma receptor IIa (FcγRIIa), leading to increased viral infection and replication, or by excessive antibody-mediated FC-mediated effector function or immune complex formation, causing enhanced inflammation and immunopathology.
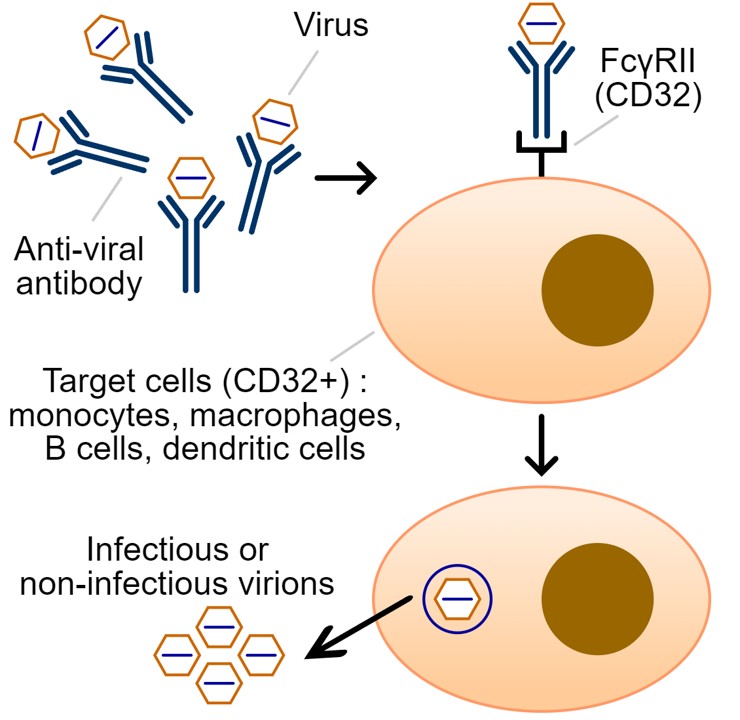 Fig. 1 Antibody-dependent enhancement assay.1
Fig. 1 Antibody-dependent enhancement assay.1
The Importance of ADE study
During the past years, ADE has been reported for several viruses such as dengue virus, yellow fever virus, zika virus, and more importantly in the content of COVID-19, coronaviruses (CoVs), and so on. More importantly, ADE has been linked to the development of cytokine storm, which occurs in the most severe cases of MERS, SARS, and COVID-19 infection. Therefore, antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of disease is a particularly important consideration for the development of vaccines and antibody therapies. In vitro ADE assay is a valuable tool to assess the capacity of antibodies to enhance secondary infection with related viruses and provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis of virus infections in the development of vaccines.
In Vitro ADE Assay Service at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs is a world-leading services provider in the field of antibody discovery and development. Experienced in antibody function assays development, we are dedicated to supporting custom high-quality in vitro ADE assay service based on the immunostaining and flow cytometry analysis, greatly improving the accuracy and sensitivity of the detection. In addition, we are devoted to designing comprehensive research practices and handling high-quality studies to support your biopharmaceutical development pipeline.
Advantages of Our In Vitro ADE Assay Service
- Excellent analytical performance.
- Low reagent, short reaction time, and power consumption.
- Excellent quality and timely feedback.
Support Data
Gaining insight into the molecular mechanisms that drive antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for crafting safe and effective therapeutic interventions. This study demonstrates that the neutralizing monoclonal antibodies MW01 and MW05 have the potential to increase the infection rate of a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus in B cells expressing the FcγRIIB receptor.
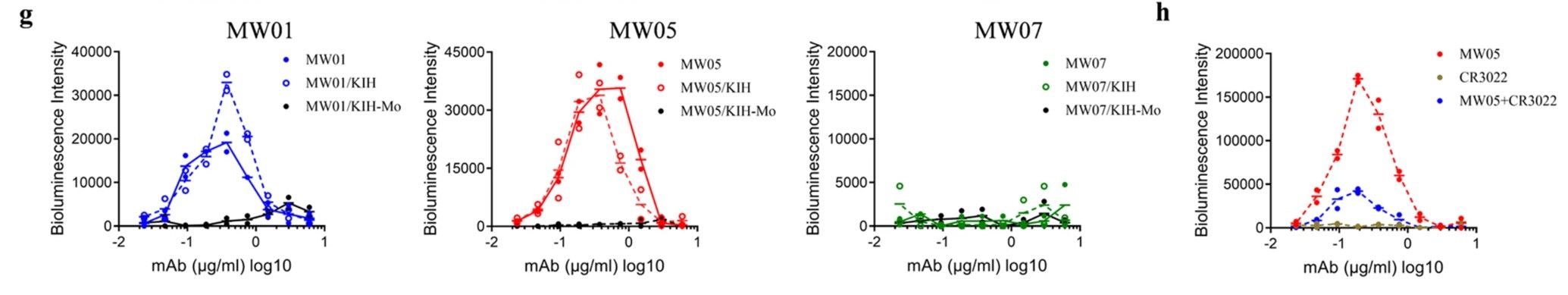 Fig.2 Comparative analysis of ADE in SARS-CoV-2 infection using Raji cells.2
Fig.2 Comparative analysis of ADE in SARS-CoV-2 infection using Raji cells.2
Creative Biolabs' scientists are dedicated to bringing together years of valuable experience to help our clients shorten the project journey. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
References
- From Wikipedia: By Jmarchn - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Antibody_dependent_enhancement-en.svg
-
Wang, Shuang, et al. "Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviral infection requires FcγRIIB and virus-antibody complex with bivalent interaction." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 262.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0. The original image was modified by extracting and using parts g & h, and the title was changed to "Comparative analysis of ADE in SARS-CoV-2 infection using Raji cells".
For Research Use Only.
