Inhibitory Immune Checkpoint targeted Reporter Gene Assay Service
Inhibitory Immune Checkpoints are Essential Targets for Cancer Therapy.
Cancer remains a significant global health challenge. Currently, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) lead to advancements in cancer immunotherapy. Targeting co-inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules has shown promising results in treating cancers like melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Normally, these molecules help regulate immune responses by inhibiting cytotoxic T-cell activity, thus preventing autoimmunity. However, in cancer, they allow tumors to evade immune detection. Hence, targeting these inhibitory pathways holds substantial potential for effective cancer treatment.
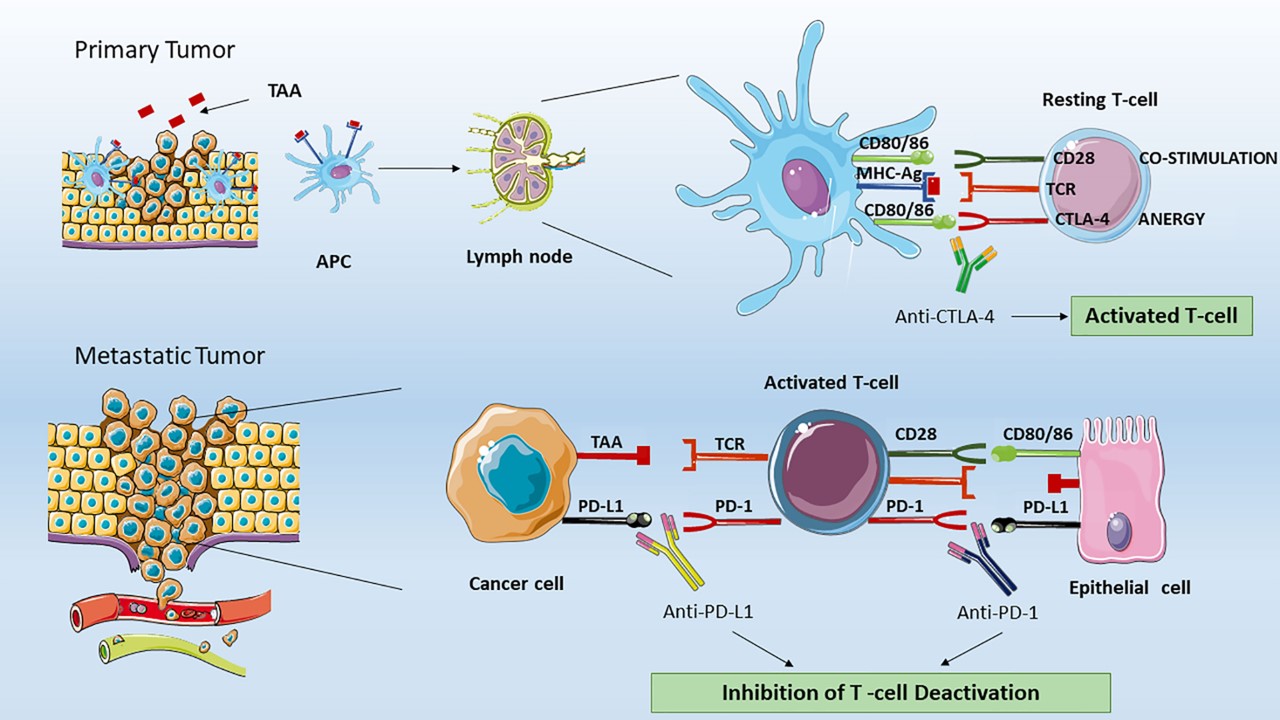 Fig.1 Various ICIs have different effects on T lymphocytes.1, 3
Fig.1 Various ICIs have different effects on T lymphocytes.1, 3
Inhibitory Immune Checkpoint-targeted Reporter Gene Assay at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs offers cutting-edge inhibitory immune checkpoint-targeted reporter gene assay to assess the efficacy of therapeutic compounds. Our cell-based reporter gene assay employed top-tier inhibitory immune checkpoint-expressing reporter cell lines that are engineered or optimized with effective reporter systems, providing quantitative readouts for thorough analysis after treatment. At the same time, we offer ready-to-use reporter cell line products and sensitive report plasmids for global customers to operate in your labs. In addition, we also specialize in tailoring unique solutions to fit your exact research needs. With a skilled team of experts, we guarantee high-quality result delivery with a short turnaround of just 2 weeks.
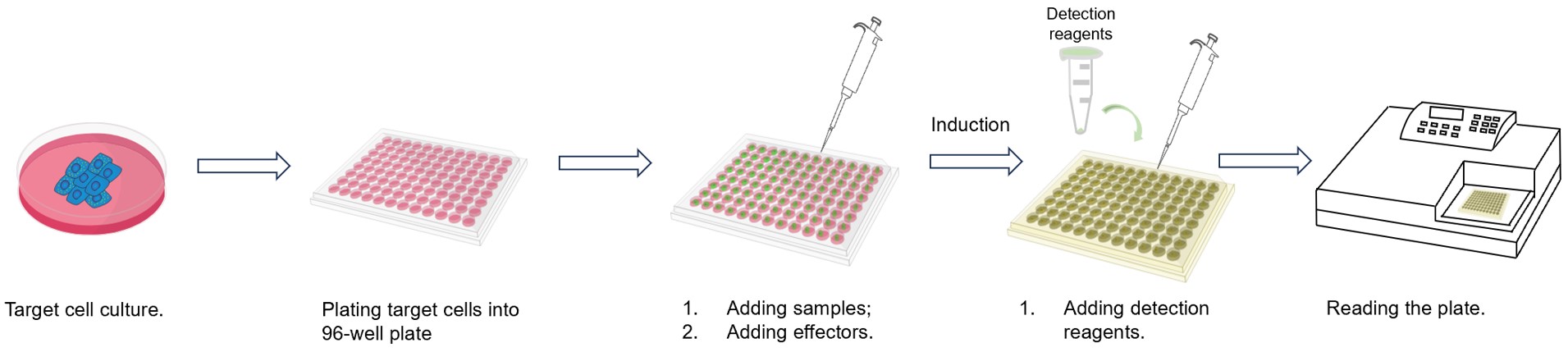 Fig.2 Workflow of our assay.
Fig.2 Workflow of our assay.
Hot Targeted Reporter Gene Assays at Creative Biolabs
The success of inhibitory immune checkpoint targeted therapies in cancer treatment has exerted a positive influence on the research of these checkpoints. Therefore, Creative Biolabs delivers a full range of inhibitory IC-targeted reporter assays to support researchers around the world in discovering and developing more effective targeted therapeutics and therapies. Listed below are several popular targeted reporter gene assays, including:
- PD-1-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
- PD-L1-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
- CTLA-4-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
- TIGIT-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
- LAG3-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
- TIM3-targeted Reporter Gene Assay
Measurable Compounds
- Macromolecular monoclonal antibodies
- Small molecular: chemical compounds and short peptides
Reporter Plasmid Available at Creative Biolabs
We also provide various engineered reporter plasmids for global customers, enabling seamless integration into diverse research projects. Meanwhile, we offer a series of services such as codon optimization and sequence optimization to construct or optimize customized reporter plasmids in accordance with customers' unique research purposes.
- NFAT-Luciferase plasmid
- NFκB-Luciferase plasmid
- pBV-Luciferase plasmid
- pGL4-Luciferase plasmid
- pCMV-Luciferase plasmid
Key Features

- Quantitative: Provides measurable readouts that can be analyzed statistically.
- High-throughput: Suitable for screening large libraries of compounds.
- Robust platforms: Adaptable to different checkpoints and reporter systems.
- Simple and High reproducibility: Streamline protocol makes our assay easy to operate and verify.
- Rapid Timeline: Rapid results delivery within 2 weeks.
Potential Applications
- Drug Screening: Identifying and characterizing new inhibitors of immune checkpoints.
- Mechanistic Studies: Understanding the signaling pathways and mechanisms of immune checkpoint regulation.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identifying potential biomarkers that predict responses to checkpoint inhibitors.
- Cancer Immunotherapy Research: Optimizing existing therapies and developing new therapeutic strategies.
Published Data
| Summary | This study developed a PD-L1 bioassay using engineered Jurkat T cells (Jurkat/PD-1/NFAT-Luc) and CHO cells expressing TCRA and PD-L1. The bioassay aimed to evaluate the anti-PD-L1 activity of an anti-PD-L1/CD40L bispecific antibody fusion protein (anti-PD-L1/CD40L BsAbFP). Cells were exposed to varying concentrations of anti-PD-L1/CD40L bispecific antibody or anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. Both treatments activated Jurkat/PD-1/NFAT-Luc cells in a dose-dependent manner, demonstrating that the anti-PD-L1 arm of the bispecific antibody fusion protein effectively promotes T cell activation, comparable to the anti-PD-L1 mAb. |
| Sample Type | Anti-PD-L1/CD40L Bispecific Fusion Protein |
| Result: |
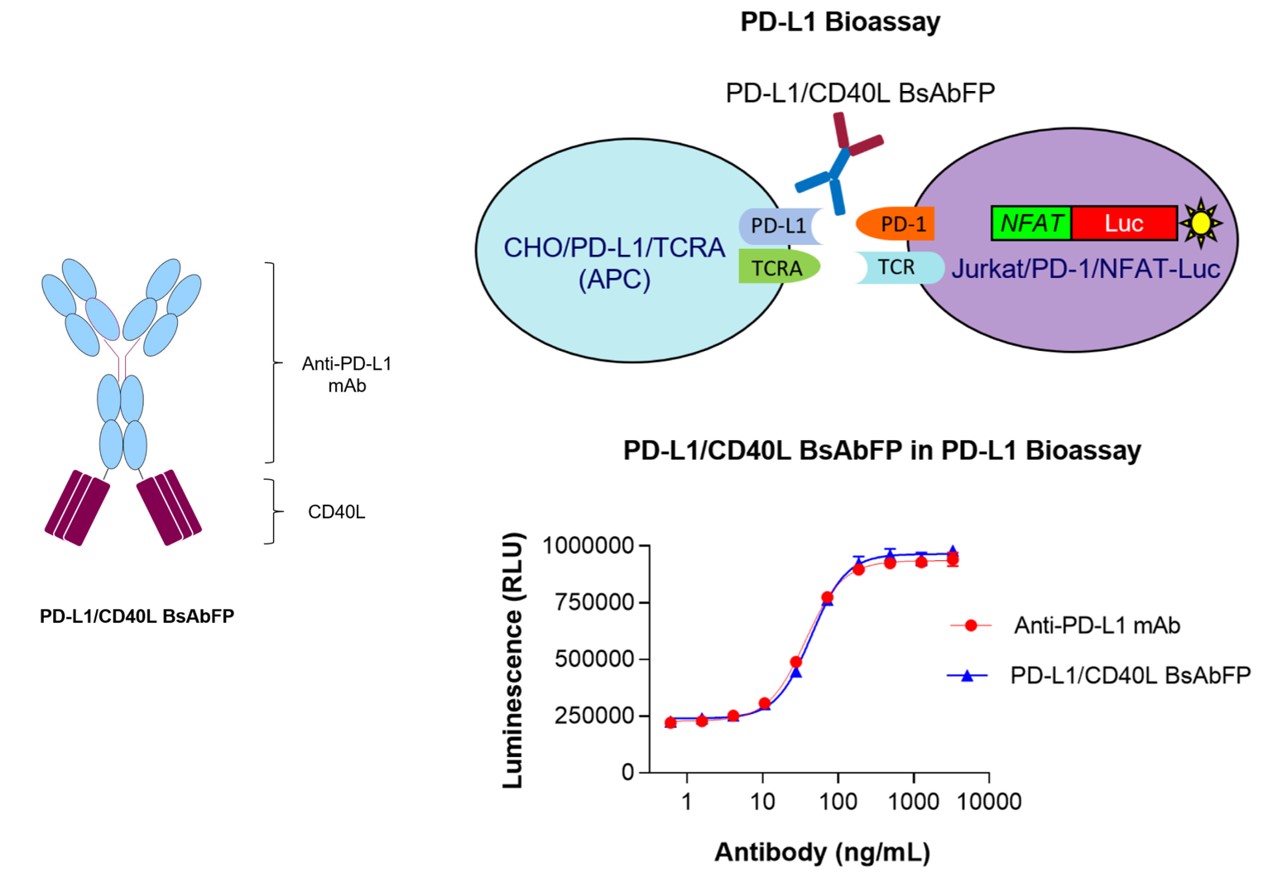 Fig.4 The structure of anti-PD-L1/CD40L BsAbFP (Left) and activity evaluation of anti-PD-L1 arm (Right).2, 4 |
For more information on our inhibitory immune checkpoint-targeted reporter gene assay, feel free to contact us.
References
- Franzin, Rossana, et al. "The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in oncology and the occurrence of AKI: where do we stand?." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 574271.
- Pandey, Madhu S., et al. "Simultaneous inhibition of PD-1 and stimulation of CD40 signaling pathways by anti-PD-L1/CD40L bispecific fusion protein synergistically activate target and effector cells." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.21 (2021): 11302.
- under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- under Open Access License CC BY 4.0. The original image was modified by extracting and regrouping, and the title was changed to " The structure of anti-PD-L1/CD40L BsAbFP (Left) and activity evaluation of anti-PD-L1 arm (Right)".
For Research Use Only.
