Cell based Immune Checkpoint Screening Service
The Prospect of Immune Checkpoints in Immune-oncology
Immune checkpoints (ICs) are a bunch of molecules that serve as gatekeepers in immune responses. They are classified into two types: co-stimulatory, which can boost immunological responses, and co-inhibitory, which can suppress immune responses. Their aberrant expression and function are major causes of many illnesses. Targeting these immune checkpoints with new medicines has shown to be a successful therapy strategy for a variety of disorders.
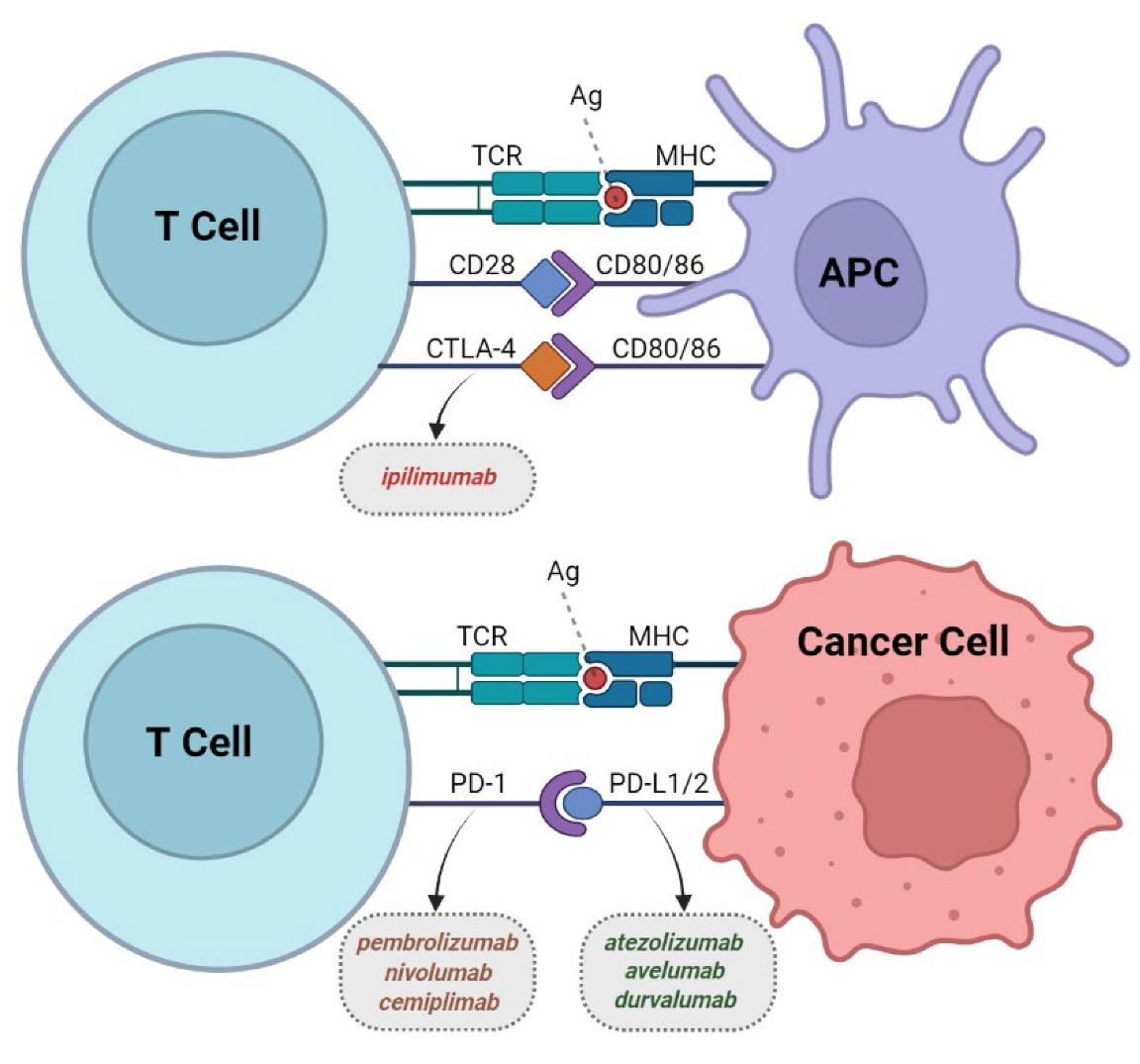 Fig.1 The main immune checkpoint inhibitor classes. 1
Fig.1 The main immune checkpoint inhibitor classes. 1
Our Cell-based Immune Checkpoint Screening Service
Creative Biolabs provides speedy and credible cell-based immune checkpoint screening services to speed up customers' drug discovery. Our cell-based immune checkpoint screening service adopts a cell lines co-culture system. By co-culturing a class of cells expressing immune checkpoint molecules with a class of cells expressing tumor-related antigens followed by samples adding, the endpoint signal will be detected after the reaction occurs. By using the cell-based formats, it is possible not only to identify inhibitors of protein-protein interactions or protein activities, but also to give further information into the environment of live cells.
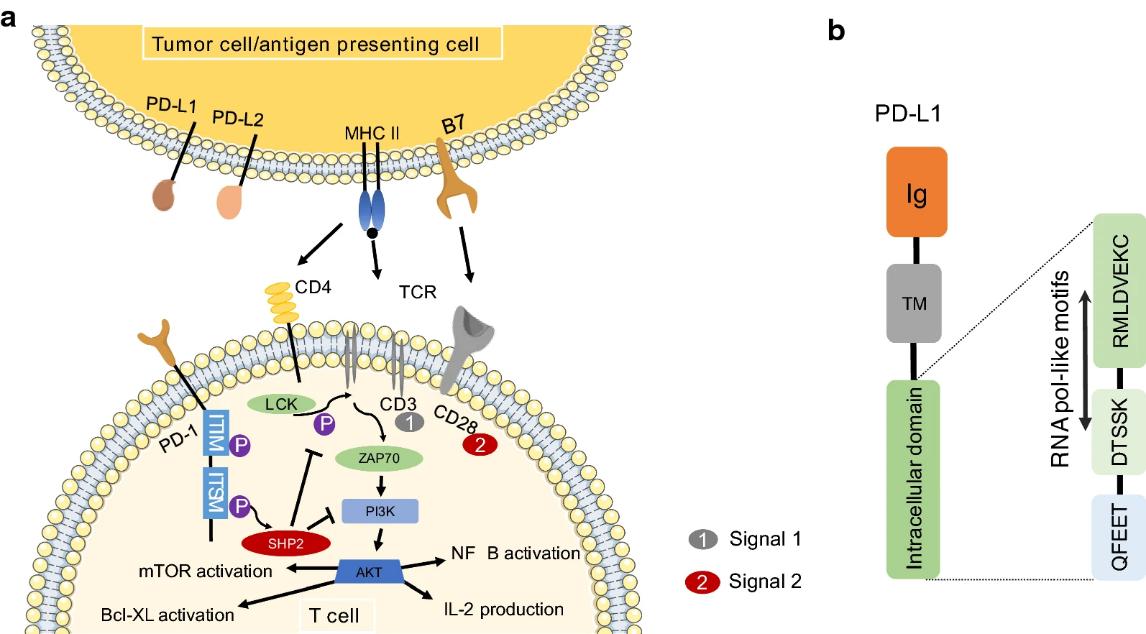 Fig.2 The signaling pathway of PD-1/PD-L1. 2
Fig.2 The signaling pathway of PD-1/PD-L1. 2
Benefit for you
Representative Data
Representative Data 1: The study established an assay, in which an hPD-1 & NFAT luciferase reporter co-transfected Jurkat T cells were incubated with TCR activator-overexpressing HEK293T cells (TCR-HEK293T) or hPD-L1 & TCR activator co-transfected HEK293T cells (hPD-L1-TCR-HEK293T). The luciferase reporter experiment revealed that PDI-1 promotes T cell activation by inhibiting PD-1/PD-L1-mediated suppression of TCR/CD28-mediated signaling cascades.
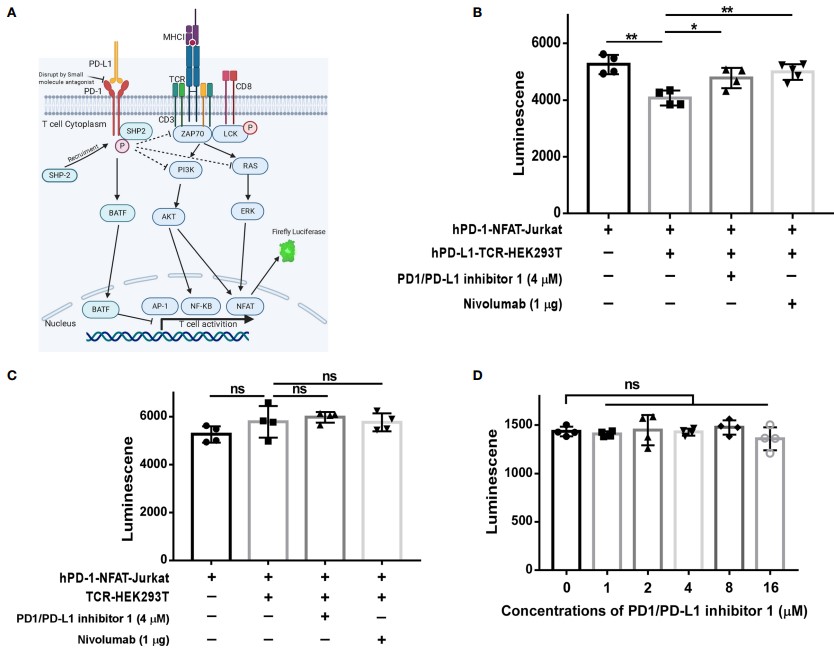 Fig.3 The inhibition of NFAT activity reversed by the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. 3
Fig.3 The inhibition of NFAT activity reversed by the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. 3
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What biomarkers are required for immune checkpoint therapy?
A1: Biomarkers of irAEs originate from the immune system. Immune system biomarkers including neutrophils, lymphocytes, cytokines, tumor-specific antibodies, and antigen-reactive T cells are critical for determining the activation of checkpoint pathway signaling.
Q2: When does the immune checkpoint fail?
A2: Checkpoint mechanisms within cells ensure that the cell is normal enough to progress to the cell cycle. When these mechanisms don't work as some genetic mutations, cells can enter the G1 phase unhindered, eventually leading to cancer.
For more details about our cell-based immune checkpoint screening service, please don't hesitate to contact us.
References
-
Basudan, Ahmed M. "The role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy." Clinics and Practice 13.1 (2022): 22-40.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Liu, Chang, Navindra P. Seeram, and Hang Ma. "Small molecule inhibitors against PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoints and current methodologies for their development: a review." Cancer Cell International 21.1 (2021): 239.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Wang, Yuanyuan, et al. "A small molecule antagonist of PD-1/PD-L1 interactions acts as an immune checkpoint inhibitor for NSCLC and melanoma immunotherapy." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 654463.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
