Nervous System Infection Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Infectious diseases of the nervous system, such as meningitis and encephalitis, lead to an estimated 1.7 million deaths annually on a global scale. Significant sequelae such as cognitive deficits, epilepsy and limb paralysis, often remain even after treatment. In response to the varied onset of these diseases, Creative Biolabs has established advanced animal models (mice, rats, NHPs) to provide reliable tools for disease treatment and prevention. The core value of these models lies in evaluating the efficiency of drug candidates to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and their ability to achieve therapeutic concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and brain parenchyma. This capability accelerates the Investigational New Drug (IND) application process for novel anti-infective agents, vaccines, and advanced drug delivery systems.
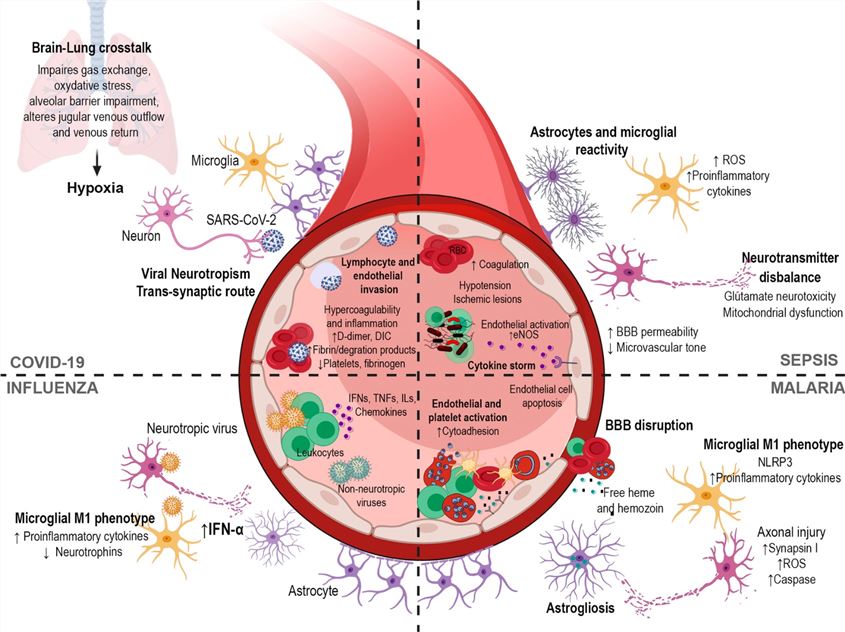 Fig.1 Mechanisms implicated in neurological complications after infection.1
Fig.1 Mechanisms implicated in neurological complications after infection.1
Available Nervous System Infection Models
Creative Biolabs offers Central Nervous System (CNS) Infection Models induced by a variety of pathogens. These sophisticated models are tailored for the pharmacological and pharmacodynamic evaluation of novel antiviral drugs, antibiotics, antifungals, and immune-modulatory agents. Please review the table below to learn how we can accelerate your preclinical drug development against neurological infections such as meningitis and encephalitis.
| Nervous System Infection Models | Related Disease | Relevant Drug Evaluation | Animal Species |
| Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSE) Models | HSE, Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) CNS infection | Antivirals (e.g., Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Foscarnet), Immunomodulators. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Japanese Encephalitis (JEV) Models | JEV, Viral Encephalitis | Antivirals (e.g., Ribavirin, Interferons, novel candidates), Vaccines. | Mouse, Rat, Guinea pig, Pig |
| Poliomyelitis (Polio) Models | Poliomyelitis, Paralytic Poliomyelitis, Viral Meningitis | Antivirals (e.g., Vaxart's VAX-A101), Vaccines (e.g., Inactivated Polio Vaccine - IPV, Oral Polio Vaccine - OPV). | Mouse, Rat, Hamster, NHPs |
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Encephalitis Models | CMV Encephalitis, Congenital CMV infection, AIDS-related CNS disease | Antivirals (e.g., Ganciclovir, Valganciclovir, Foscarnet), Immunomodulators. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)/Polyomavirus CNS Models | PML, Polyomavirus JC (JCV) infection | Antivirals (e.g., Mefloquine, Maraviroc), Immune checkpoint inhibitors, Immune reconstitution strategies. | Mouse, NHPs |
| Acute Bacterial Meningitis Models | Acute Bacterial Meningitis (e.g., S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, H. influenzae) | Antibiotics (e.g., Ceftriaxone, Vancomycin, Dexamethasone adjunct therapy), New-generation antibiotics. | Mouse, Rat, Guinea pig, Rabbit |
| Tuberculous Meningitis (TBM) Models | TBM | Anti-Tuberculosis drugs (e.g., Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide), Adjunctive corticosteroids, Novel drug penetration studies. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Listeria Meningitis Models | Listeria Meningitis, Meningoencephalitis | Antibiotics (e.g., Ampicillin, Penicillin G, Gentamicin synergy), Immunomodulators. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Neurosyphilis Models (Treponema pallidum) | Neurosyphilis (Treponema pallidum CNS infection) | Antibiotics (e.g., High-dose Penicillin G), Ceftriaxone. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Dog, NHPs |
| Brain Abscess Models | Brain Abscess (Polymicrobial, e.g., Staph, Strep, Anaerobes) | Antibiotics (e.g., Metronidazole, Cephalosporins, Vancomycin), Surgical intervention/aspiration. | Mouse, Rat |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis Models | Cryptococcal Meningitis (Cryptococcus neoformans) | Antifungal drugs (e.g., Amphotericin B, Flucytosine, Fluconazole), Combination therapy. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Guinea pig |
| Candidal Meningitis Models | Candidal Meningitis/Disseminated Candidiasis (CNS involvement) | Antifungal drugs (e.g., Amphotericin B, Echinocandins, Azoles), Combination therapy. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Aspergillosis (Cerebral Aspergillosis) Models | Cerebral Aspergillosis (Aspergillus spp.), Fungal Brain Abscess | Antifungal drugs (e.g., Voriconazole, Amphotericin B), Combination therapy. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Mucormycosis (Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis) Models | Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis (Mucorales fungi), Orbital/CNS involvement | Antifungal drugs (e.g., High-dose Amphotericin B, Posaconazole), Hyperbaric oxygen, and surgical debridement. | Mouse, Rabbit |
| Neurocysticercosis Models | Neurocysticercosis (Taenia solium larval stage in CNS) | Antihelminthic drugs (e.g., Albendazole, Praziquantel), Adjunctive steroids, Surgery. | Mouse, Rat, Guinea pig |
| African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness) Models | Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), CNS stage disease | Anti-protozoal drugs that cross the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) (e.g., Fexinidazole, Melarsoprol). | Mouse, Rat, Guinea Pig, NHPs |
| Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) Models | Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) (Naegleria fowleri) | Antiprotozoal drugs (e.g., Miltefosine, Amphotericin B combination). | Mouse, Rabbit |
| Neurotrichinosis Models | Neurotrichinosis (Trichinella larvae in CNS) | Antihelminthic drugs (e.g., Albendazole, Mebendazole), Corticosteroids. | Mouse, Rat, Guinea Pig |
| Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) Models | Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD), Sporadic Prion Disease | Supportive care, Experimental anti-prion compounds. | Mouse, Rat, Hamster, NHPs |
| Variant CJD (vCJD) Models | Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD) | Supportive care, Experimental anti-prion compounds. | Mouse, Bovine, NHPs |
Measurements
To deliver scientifically rigorous and mechanistically rich data, our Nervous System Infection Model assessments integrate a range of advanced, multi-dimensional detection technologies and critical endpoints, including:
- Pathogen Detection: Molecular biology techniques are employed to quantify the pathogen nucleic acid/CFU load in brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Serological and Immunological Detection: Methods such as ELISA/MSD are implemented to detect inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in the CSF and serum, along with performing immune cell phenotyping analysis.
- Pathological and Histological Analysis: Pathological assessment is conducted using H&E and Luxol Fast Blue (LFB) staining. The focus includes Immunohistochemistry (IHC) to evaluate the activation level of glial cells (microglia/astrocytes) and neuronal apoptosis.
- Imaging and Biochemical Indicators: Dynamic monitoring of brain damage (e.g., edema/abscess). This includes drug concentration determination in the CSF and brain parenchyma, and the detection of biochemical indicators such as neurotransmitters.
- Behavioral and functional assessment: Performing motor function tests, including gait analysis, and scoring neurological symptoms.
Applications
- Disease Modeling: The models are used to reproduce complex central nervous system pathology, including pathogen invasion, blood-brain barrier (BBB) breach, and the subsequent neural damage and inflammation.
- Drug Discovery and Development: The models serve as critical platforms for evaluating new antimicrobial agents' ability to traverse the BBB, achieve therapeutic concentrations in the CNS, and assess their neurotoxicity safety profiles.
- Therapeutic Strategy Optimization: The models are utilized to optimize combination and adjunctive therapeutic regimens for complex CNS infections and to validate specialized drug delivery techniques like intrathecal administration.
- Mechanism Study: The models delineate the intricate pathogenesis of neuroinvasive infections by replicating pathogen traversal across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and retrograde axonal transport, elucidating the neuroinflammatory cascades driven by microglia and astrocyte activation, and characterizing the specific pathways of synaptic dysfunction and neuronal apoptosis that precipitate meningoencephalitis and long-term neurological sequelae.
Our Advantages
- Professional Team: Our multidisciplinary group consists of senior specialists in neurobiology, microbiology, and veterinary medicine, offering extensive proficiency in developing animal models for nervous system infectious diseases, exploring disease mechanisms, and advancing drug R&D across various modalities, such as small molecules, biologics, and vaccines.
- Advanced Facilities: We employ cutting-edge equipment, such as animal behavior analysis systems, high-throughput sequencing, and small animals in vivo imaging systems, to guarantee successful project completion.
- Comprehensive Services: We deliver customized, one-stop solutions, covering from experimental design and animal model construction to sample test and data analysis, meeting a broad spectrum of pharmacology and pharmacodynamic requirements.
- Efficient and Reliable: We have implemented standardized experimental procedures and a rigorous project management system to guarantee the efficient project progression and the timely delivery of high-quality data.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: What are the advantages of your CNS infection models in terms of species and translatability?
A: We utilize multi-species models, including NHP, rabbits, and rodents, to simulate the CNS invasion pathways of various pathogens. These models ensure high clinical fidelity to human neurological pathology.
-
Q: What is your core value, and how do you address the significant challenge of BBB penetration?
A: The CNS has the unique structure of the BBB. In vivo models are the only tools capable of assessing a drug's BBB penetration efficiency and its ability to achieve effective concentrations in the CSF/brain parenchyma. Our core value is providing precise CNS PK/PD data (e.g., measuring CSF/MIC ratio) to guide dose optimization and ensure the drug reaches and maintains the minimum effective concentration.
-
Q: Which core indicators do you use to evaluate CNS therapeutic efficacy and neuroinflammation/sequelae?
A: We adopt a multi-modal assessment: quantitative detection of pathogen load in the CSF and brain parenchyma; evaluation of survival rate/disease progression scores; performing histopathological analysis (e.g., neuronal damage, glial cell activation); and conducting neurofunctional/behavioral tests. Concurrently, we quantify inflammatory cytokines in the CSF/brain tissue to evaluate the drug's protective effects against neuroinflammation and long-term sequelae.
-
Q: How do your services accelerate IND submission and support novel delivery systems?
A: We provide highly translatable BBB penetration data and precise PK/PD targets that directly support Investigational New Drug (IND) applications. The platform professionally supports the evaluation of advanced delivery methods such as nanocarriers, shuttle peptide-modified drugs, and local delivery methods like intrathecal (IT) injection, verifying the efficacy and safety of these advanced systems through accurate CSF PK analysis.
Published Data
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV)-S3 infection destroys the mouse Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and triggers cerebral pathological lesions highly consistent with human JEV encephalitis. This model successfully recapitulates the pathological state involving the virus breaking through the central barrier, establishing residence and replicating in the brain, and inducing inflammation and necrosis. This validates the clinical relevance and effectiveness of the mouse model.
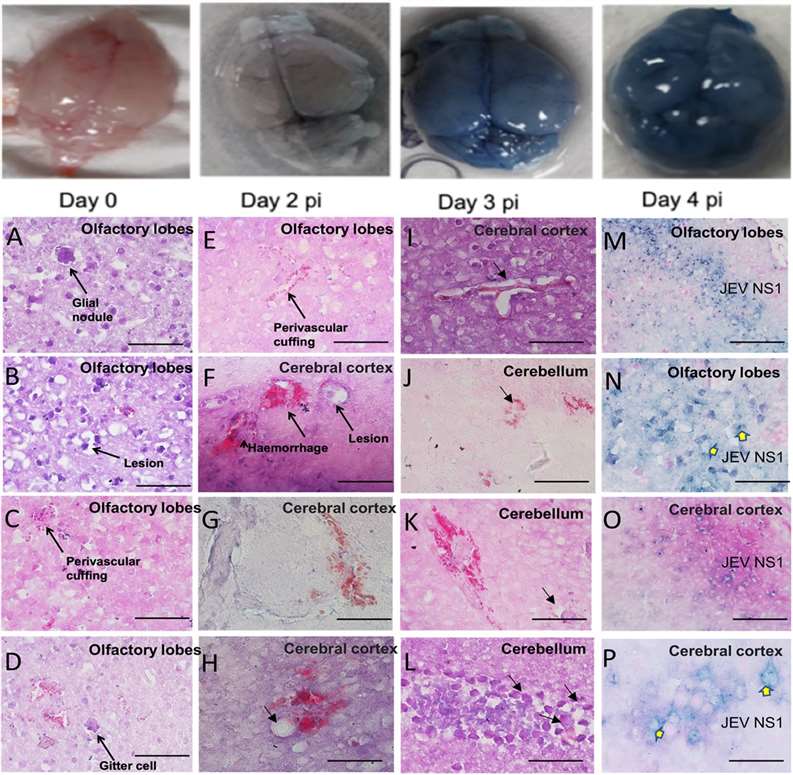 Fig.2 Evans Blue dye-stained brain tissue and brain tissue pathology of JEV in the C57BL/6 mouse model.2
Fig.2 Evans Blue dye-stained brain tissue and brain tissue pathology of JEV in the C57BL/6 mouse model.2
References
- Barbosa-Silva, Maria C et al. "Infectious disease-associated encephalopathies." Critical care (London, England) vol. 25,1 236. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-021-03659-6. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Tripathi, Aarti et al. "Development and characterization of an animal model of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in adolescent C57BL/6 mouse." Disease models & mechanisms vol. 14,10 (2021): dmm049176. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.049176. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, with modification.
For Research Use Only.
