Urinary & Genital System Infection Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Urinary and genital tract infections (UGTIs), which include conditions such as urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease, can lead to severe complications such as kidney damage, septicemia, infertility, and vertical transmission from mother to child. Globally, UGTIs are the most common cause of community-acquired sepsis and a leading driver of antibiotic resistance, imposing a significant burden on maternal and neonatal health. These infections commonly involve bacterial, fungal, and parasitic pathogens. Creative Biolabs has developed a broad portfolio of animal models that accurately simulate pathogen ascending infection, intracellular persistence (IBCs), and mucosal immune challenge. These high-fidelity models provide crucial support for the pharmacological and pharmacodynamic studies of traditional pharmaceuticals, novel anti-infective vaccines, biologics, cell/gene therapies, and medical devices, such as localized delivery systems.
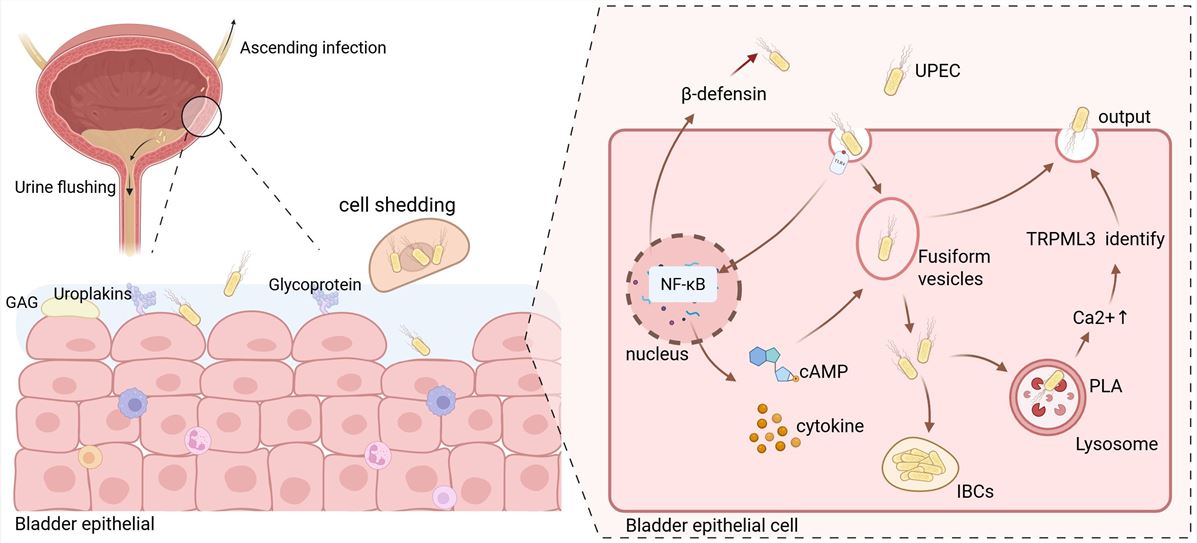 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) invasion into bladder epithelial cells.1
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) invasion into bladder epithelial cells.1
Available Urinary and Genital System Infection Models
Creative Biolabs offers a diverse range of UGTI models induced by various pathogens.
| UGTIModels | Related Disease & DrugEvaluation | Animal Species |
| E.coli Cystitis Models | Acute/Recurrent Cystitis (UTI), Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) infection. Suitablefor evaluating Antibiotics (e.g., Fluoroquinolones, Nitrofurantoin, Fosfomycin),Anti-adhesion therapies, Vaccines, and Anti-biofilm agents. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Pyelonephritis Models | Pyelonephritis (Kidney infection), Upper Urinary Tract Infection. Idealfor assessing systemic Antibiotics (e.g., IV Cephalosporins, Aminoglycosides),Anti-inflammatory agents, and Drugs targeting renal damage/scarring. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Guinea pig |
| Mycoplasma Urethritis Models | Non-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU), Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). Usedto evaluate Antibiotics (e.g., Macrolides, Tetracyclines), Combination therapy, andMicrobicides. | Mouse, Rat |
| Cryptococcal Urinary Tract InfectionModels | Cryptococcal UTI, Disseminated Cryptococcosis. Essential for assessingsystemic and novel Antifungal Drugs (e.g., Fluconazole, Amphotericin B), andCombination therapy regimens. | Mouse, Rat |
| Aspergillus Urinary Tract InfectionModels | Fungal Cystitis, Renal Aspergillosis (often in immunocompromised). Usedto test Antifungal Drugs (e.g., Voriconazole, Amphotericin B), and Local irrigationwith antifungals. | Mouse, Rabbit |
| Adenovirus Cystitis Models | Hemorrhagic Cystitis (especially serotypes 11, 21), Immunocompromisedpatients. For evaluating Supportive care, Antivirals (e.g., Cidofovir insevere cases), and Immunomodulators. | Mouse, Rabbit |
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) UTI Models | CMV Cystitis, CMV Nephritis (transplant recipients). Critical for testingAntivirals (e.g.,Ganciclovir, Valganciclovir, Foscarnet), and Immunosuppression managementstrategies. | Mouse, Guinea Pig |
| Bacterial Vaginosis Models | Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), Increased risk of STIs/preterm birth. Used toassess Antibiotics (e.g.,Metronidazole, Clindamycin), Probiotics (e.g., Lactobacillus replacement), andRecurrence prevention strategies. | Mouse, Rat |
| Trichomoniasis Models (T. vaginalis) | Trichomoniasis (STI), Urethritis, Vaginitis. Ideal for evaluatingAntiprotozoal Drugs (e.g.,Metronidazole, Tinidazole), and New 5-nitroimidazole derivatives. | Mouse, Rat, NHPs |
| Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC) Models | Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Yeast infection), Recurrent VVC. Essential forassessing Antifungal Drugs (e.g., Topical Azoles, Fluconazole), Probiotics, and Immunemodulators (to reduce inflammation). | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit |
| Genital Herpes Models (HSV-1 andHSV-2) | Genital Herpes, Recurrent lesions, Neonatal herpes, Latency. Used toscreen Antivirals (e.g.,Acyclovir, Valacyclovir), Therapeutic/Prophylactic Vaccines, Microbicides,and Latency-reversing agents. | Mouse, Guinea Pig |
| Chancroid Models (Haemophilus ducreyi) | Chancroid (Genital ulcer disease), Lymphadenopathy. Relevant for testingAntibiotics (e.g.,Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone) and Wound care products. | Rabbit, Mouse, NHPs |
| Combined Infection of Escherichia coli, Trichomonas vaginalis,and Candida albicans Models | Mixed UGITI, Synergistic/Polymicrobial Infections, Complex Vaginitis.Critical for evaluating Combination Antibiotic/Antifungal/Antiprotozoaltherapy and Broad-spectrum Microbicides. | Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Guinea pig |
Measurements
Creative Biolabs utilizes multi-dimensional assessment techniques to achieve precise analysis for model identification and pharmacodynamics (PD). To ensure the scientific rigor & reproducibility of results and guarantee the highest quality of service, the primary detection methods include, but are not limited to:
- Infection Colonization Assessment: Pathogen load is detected using quantitative culture or molecular biology techniques (e.g., qPCR, Whole-Genome Sequencing).
- Histopathological Analysis: H&E staining is used for inflammation scoring and tissue damage assessment, focusing on mucosal epithelial integrity and scarring/fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is utilized to evaluate local immune responses and cellular markers.
- Serological Testing: Serum cytokine testing provides insights into the systemic inflammatory status; blood biochemical testing indicates organ damage (e.g., renal function).
- Imaging Techniques: High-frequency ultrasound is employed for the detection of organ lesions (e.g., pyonephrosis, renal abscess). Bioluminescence Imaging (BLI) is used for the real-time, dynamic monitoring of pathogen infection status and drug efficacy. Micro-CT/CT can be utilized to assess models with complex complications (e.g., those accompanied by kidney stones).
Applications
- Disease Modeling: The models simulate the ascending infection pathway of pathogens (like UPEC) from the urethra to the kidneys, and the formation of IBCs within uroepithelial cells, leading to recurrent infection.
- Mechanistic Research: The models are core tools for elucidating the biological mechanisms of infection, including pathogen interaction with mucosal immunity, tissue cells, biofilm formation, and host susceptibility.
- Drug Discovery and Development: The models serve as essential platforms for screening novel antibiotics, antivirals, and topical microbicides, focusing on evaluating effective therapeutic concentrations and penetration into urine and genital secretions.
- Infection Treatment: The models are used to optimize combination therapies targeting IBCs and drug-resistant strains, and to assess the role of probiotics and local interventions in preventing infection recurrence.
Our Advantages
- Frontier Technology Reserves: Our team comprises biostatisticians, biologists, pathologists, and pharmacologists, all possessing extensive scientific research experience.
- Model Diversity: Our models encompass a wide range of pathogens, including common bacterial infection models, as well as fungal, parasitic, and immunodeficient host infection models, and even pregnancy infection models. These models cover over 95% of urinary and genital tract infection pathogens, supporting scenarios from single-bacterium infections to complex drug-resistant cases.
- Advanced Technical Platforms and Detection Capabilities: We are equipped with a microbiology detection platform for pathogen quantification and whole-genome sequencing, facilitating the analysis of mechanisms. The pathology and immunology detection platform offers H&E and special staining for histopathological evaluations, alongside immunological function analysis and in vivo dynamic monitoring technology platforms.
- Full-Process Service System: We provide comprehensive services for the development of early-screening models, IND application models, and mechanism research models, thereby expediting project implementation.
- Flexible and Customized Services: We offer customized services tailored to specific client needs and model characteristics. Throughout project implementation, we can adjust protocols to achieve optimal pharmacodynamic outcomes.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: Why is your in vivo platform indispensable, and what is its core value?
A: Our platform is the only tool that overcomes the urogenital system's tissue barriers to accurately provide PK/PD data in urine and target tissues (e.g., kidney, prostate). We ensure high clinical fidelity using diverse models (e.g., acute/chronic cystitis, pyelonephritis).
-
Q: How do you assess efficacy in refractory/recurrent infections?
A: We use multi-site quantitative assessment: microbial load quantification, histopathological scoring, and anti-biofilm activity analysis. For hard-to-penetrate tissues, we precisely measure interstitial fluid concentration and model chronic/recurrent infections to assess deep tissue clearance.
-
Q: How does your service accelerate IND filing and commercial translation?
A: We provide precise PK/PD targets to support First-in-Human (FIH) dose selection, reducing clinical failure risk. Simultaneously, we deliver regulatory-compliant in vivo efficacy data, especially for complex/recurrent infections, enhancing regulatory confidence.
-
Q: Does your platform support novel local delivery systems?
A: Yes. We specialize in supporting novel complex formulations like local controlled-release systems and suppositories. We provide precise analysis of local drug exposure and clearance kinetics to validate their pharmacodynamics.
Published Data
The mouse mpox virus model validated the vaccine's protective efficacy. Secondary immunization significantly boosted vaccinia virus-neutralizing antibody titers, confirming potent direct neutralization. Post-challenge analysis revealed no inflammation or pathological damage in vital organs (heart, liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys), demonstrating robust systemic safety and organ protection from the induced immune response.
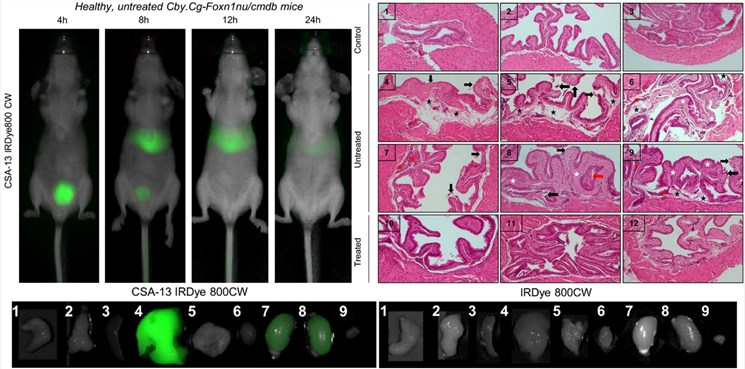 Fig.2 Antibacterial effect and biodistribution of CSA-13.2
Fig.2 Antibacterial effect and biodistribution of CSA-13.2
References
- Hou, Yilin et al. "The immune mechanisms of the urinary tract against infections." Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology vol. 15 1540149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1540149. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Wnorowska, Urszula et al. "Ceragenin CSA-13 displays high antibacterial efficiency in a mouse model of urinary tract infection." Scientific Reports vol. 12,1 19164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23281-y. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, with modification.
For Research Use Only.
