Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Introduction
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) constitute a formidable global public health challenge, with millions of new infections reported annually worldwide, underscoring the persistent threat posed by pathogens such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Human Papillomavirus (HPV), and Genital Herpes (HSV). STIs are a leading cause of infertility, mother-to-child transmission, and significantly increase the risk of HIV acquisition and transmission globally. Furthermore, the rapid emergence of Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) strains of bacteria like Neisseria gonorrhoeae threatens to render common treatments ineffective, leading to global health emergencies. Creative Biolabs delivers comprehensive and scientifically rigorous STI infection models, offering essential solutions for in vivo animal modeling and preclinical drug development. The core advantage of these platforms lies in evaluating a drug's mucosal penetration and clearance kinetics, as well as the mechanisms of latent virus reactivation (e.g., HSV), thereby accelerating the discovery and validation of novel antiretroviral therapies, broad-spectrum antibiotics, topical microbicides, and vaccine candidates.
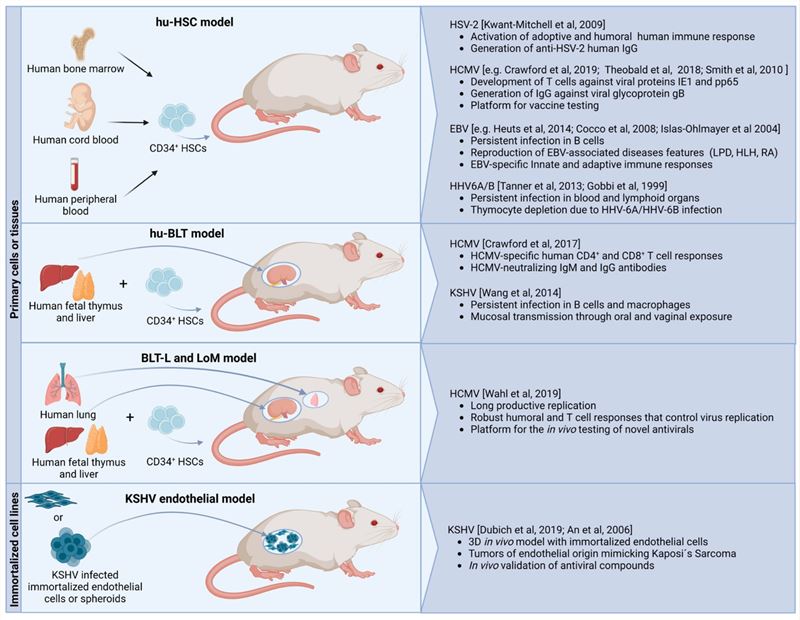 Fig.1 Summary of relevant mouse models for studying herpesviruses.1,4
Fig.1 Summary of relevant mouse models for studying herpesviruses.1,4
Available Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Models
The main pathogens of STIs contain viruses (e.g., HIV, HPV, herpes simplex virus), bacteria (e.g., gonococci, Treponema pallidum), chlamydia, mycoplasma, fungi (e.g., Candida albicans), and parasites (e.g., Trichomonas vaginalis). Based on these pathogens, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of validated STIs animal models, including:
| STIs Models | Related Disease & Drug Evaluation | Animal Species |
| HumanImmunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection Models | HIV/AIDS,Immunodeficiency, Opportunistic Infections; ideally positioned for theadvanced validation of Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) (e.g., Combinationregimens, single-pill), Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), next-generationVaccine candidates, and cutting-edge Cure strategies. | Humanized Mouse, NHPs |
| Genital Herpes(HSV-2) Infection Models | Genital Herpes,Recurrent Ulcerations, Neonatal Transmission; purpose-built for thecomprehensive assessment of Antivirals (e.g., Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Foscarnet),Therapeutic/Prophylactic Vaccines, and novel compounds targetinglatency/reactivation mechanisms. | Mouse, Guinea Pig |
| Congenital HSVInfection Models | Congenital HerpesSimplex Virus Infection (CNS and systemic); engineered for the criticalevaluation of High-dose Antivirals (e.g., Acyclovir) and prophylactic Vaccinesdesigned to prevent maternal-fetal transmission. | Mouse, Guinea Pig,Rabbit |
| Human Papillomavirus(HPV) Models | Genital Warts,Cervical Dysplasia/Cancer, Anal/Oral Cancers; instrumental for the robustdevelopment of Prophylactic/Therapeutic Vaccines (e.g., L1 VLP, DNA vaccines), targetedAntivirals, and Immuno-oncology approaches. | Mouse, Rabbit |
| Chlamydial InfectionModels | Chlamydia Trachomatis (CT) Urethritis,Cervicitis, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), Trachoma; provides a superiorplatform for the rigorous evaluation of Antibiotics (e.g., Azithromycin,Doxycycline, Rifamycins), next-generation Vaccine candidates, andanti-inflammatory agents (to mitigate scarring). | Mouse, Hamster,Guinea Pig, NHPs |
| Gonorrhea InfectionModels | Gonorrhea (N. gonorrhoeae)Urethritis, Cervicitis, Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI); optimizedfor the accelerated assessment of Novel Antibiotics (critical for combatinghigh drug resistance), combination regimens (e.g., Ceftriaxone plus Azithromycin orDoxycycline), and Vaccines. | Mouse, Guinea Pig |
| Syphilis InfectionModels | Syphilis (Treponema pallidum),Primary, Secondary, Latent, Neurosyphilis; facilitates the definitiveevaluation of Penicillin G (gold standard), specialized Alternative regimens(e.g.,Doxycycline), and optimization strategies for Neurosyphilis treatment. | Rabbit, Mouse |
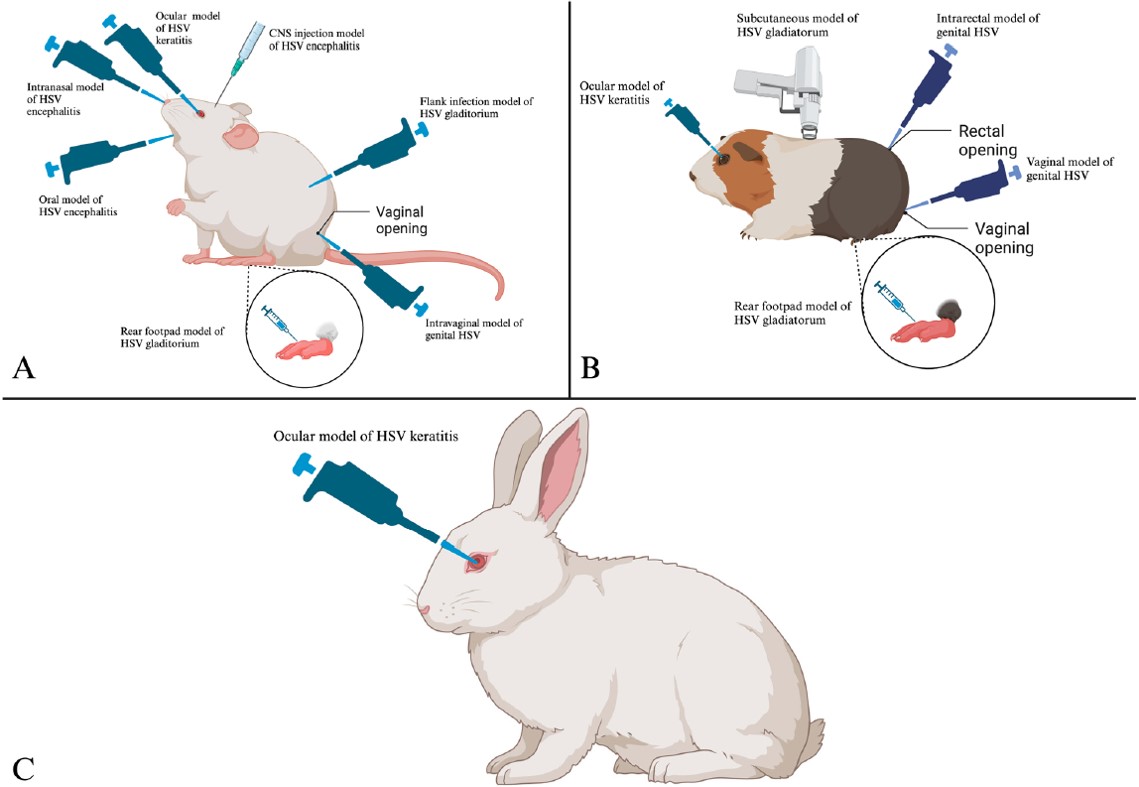 Fig.2 Routes of infection and establishment of HSV disease within mice (A), guinea pigs (B), and rabbits (C).2,4
Fig.2 Routes of infection and establishment of HSV disease within mice (A), guinea pigs (B), and rabbits (C).2,4
Measurements
Creative Biolabs selects assessment metrics of STIs models based on the pathogen types, the species characteristics employed for disease models, and relevant ethical standards. Simultaneously, we leverage the most sophisticated technologies and precision instruments to generate efficacy data of the highest quality, such as Digital Droplet PCR (ddPCR), Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI), Multi-color Flow Cytometry, Multiplex Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy. The primary focus metrics include:
- General Observation Metrics: These include parameters such as body temperature, weight fluctuations, appetite, activity levels, distinctive lesions (e.g., rashes, mucosal ulcers), and pain response.
- Molecular & Pathogen Load Metrics: Key metrics include pathogen nucleic acid quantification (qPCR/RT-PCR) in secretions/tissue biopsies, infectious titers, and dynamic monitoring of viral latency/reactivation status.
- Pathological Metrics: Histopathological examination, immunohistochemical (IHC) localization, and evaluation of tissue scarring/fibrosis (especially for Chlamydia and PID models).
- Pharmacokinetic (PK) Metrics: Local drug concentration determination (e.g., mucosal tissue concentration, cervicovaginal fluid concentration), systemic distribution, and local clearance rates.
- Immunological Metrics: This category encompasses immune cell counts, cytokines and chemokines concentrations, and specific antibody levels.
Applications
- Disease Modeling: The models simulate local mucosal invasion, inflammatory responses in the reproductive tract, the reactivation of latent viruses (like HSV-2), and the impact on HIV susceptibility.
- Mechanism Study: The models elucidate the multifaceted pathogenesis of sexually transmitted infections by reproducing pathogen colonization and transgression across genitourinary mucosal barriers, decoding the modulatory effects of the vaginal microbiome and hormonal microenvironments on susceptibility, and characterizing the chronic inflammatory cascades that drive tissue fibrosis, viral latency, and reproductive sequelae such as pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility.
- Drug Discovery and Development: The models are critical platforms for screening novel antibiotics, antivirals, and topical microbicides, focusing on evaluating their efficacy against resistant pathogens and pharmacokinetics at mucosal sites.
- Infection Treatment: The models are used to optimize combination therapies for drug-resistant strains and latent infections, and to evaluate the effectiveness of preventive interventions in reducing disease transmission and recurrence.
Our Advantages
- Technical Depth and High Translatability: We leverage advanced technologies to create humanized immune system mice and strategically employ non-human primate (NHP) models to precisely simulate complex human infection pathology and immune processes. This multi-species strategy is particularly suitable for evaluating the efficacy of large molecule biologics and complex infections like HIV/SIV, ensuring data reliability.
- Extensive Model Library and Broad Application: The model library not only covers mainstream STIs like HIV and HSV but also possesses the customized capability to develop models for emerging pathogens, co-infections (multiple infections), and drug-resistant strains. This comprehensively supports the efficacy assessment of complex treatment regimens, such as vaccines and long-acting formulations.
- Multi-Dimensional Evaluation System: This system integrates various indicators, such as pharmacodynamics (e.g., lesion scores, viral load), immunology (e.g., neutralizing antibodies, cytokine profiles), and behavioral (e.g., transmission risk assessment) measures. It offers dynamic monitoring of the latency-recurrence cycle.
- One-Stop Solution and Service Advantages: Our services extend from providing pathogen libraries (clinical isolates, WHO recommended strains) to model construction, efficacy evaluation, and ensuring data compliance. We develop specialized models for novel treatment methodologies, such as gene therapy and mucosal vaccines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q. What are the unique advantages of your platform regarding model species and translational capability?
A: Our advantage lies in high translational capability and species diversity. We utilize a panel of models, including Non-Human Primates (NHP), guinea pigs, rabbits, and humanized mice, to accurately mimic the pathogen's natural infection route, mucosal inflammation, and immune responses, ensuring high clinical fidelity to human STIs.
-
Q. Why are in vivo models indispensable for STI drug development, and what is the core value?
A: STI drugs must effectively penetrate the genital tract mucosal barriers. The in vivo model is the only reliable tool capable of assessing the drug's tissue penetration, clearance efficiency, and local/systemic toxicity. Our core value is providing this critical local, targeted PK/PD data to accelerate preclinical decision-making.
-
Q. How does your efficacy assessment system quantify STI outcomes, especially for viral latency and recurrence?
A: We use a multi-dimensional quantitative approach. We base our assessment on microbial/viral load quantification at the infection site, combined with histopathological analysis and immunological markers (e.g., antibody titers, cytokine levels). Crucially, we possess the capability for dynamic monitoring of HSV latency and reactivation.
-
Q. How do your models evaluate the efficacy and safety of prophylactic drugs (e.g., PrEP) and complex formulations?
A: We focus on local assessment. For PrEP drugs, we precisely evaluate the drug's local concentration and duration of effective exposure in target tissues. For complex dosage forms like long-acting injectables or local rings, we provide specialized local PK/PD analysis and assess the impact on genital epithelial integrity and local microbiome to ensure local tolerability.
-
Q. How does your data directly support clinical translation and regulatory submissions?
A: Our reports provide precise PK/PD targets and dosing recommendations that directly support IND submission and mitigate clinical failure risks. The provided highly translational pharmacological evidence, particularly demonstrating the drug's effectiveness in site-specific clearance and prophylactic effect, satisfies the scientific depth required by regulatory bodies for STI drug development.
Published Data
Using a mouse HSV-2 genital herpes model, it was clearly demonstrated that the interferon vaginal tablet exhibited a dose-dependent therapeutic effect against HSV-2 infection. The tablet significantly improved survival rate, alleviated clinical symptoms, and suppressed viral replication, with the high-dose effect being comparable to Acyclovir.
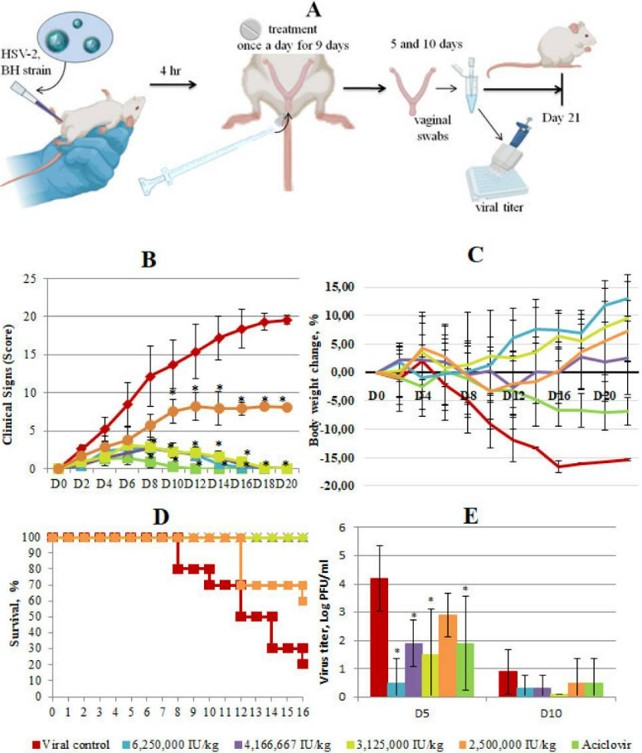 Fig.3 In vivo efficacy of Interferon Vaginal Tablets as a treatment for HSV-2 infection.3,4
Fig.3 In vivo efficacy of Interferon Vaginal Tablets as a treatment for HSV-2 infection.3,4
References
- Kutle, Ivana et al. "Mouse Models for Human Herpesviruses." Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 12,7 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070953
- Hussain, Mohammed Tanveer et al. "Small Animal Models to Study Herpes Simplex Virus Infections." Viruses vol. 16,7 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16071037
- Ivanina, Anna et al. "The Topical Novel Formulations of Interferon α-2в Effectively Inhibit HSV-1 Keratitis in the Rabbit Eye Model and HSV-2 Genital Herpes in Mice." Viruses vol. 16,6 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060989
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
