Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Alzheimer’s Disease Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Numerous animal models of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) have been described, including chemically-induced, metal-induced, lipid-induced, aging-induced, and transgenic models. Particularly, Creative Biolabs conducts contract studies in a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced AD model, which is based on the intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration of low doses of STZ, to assess the therapeutic potential of various drugs, as well as other non-drug therapeutic strategies.
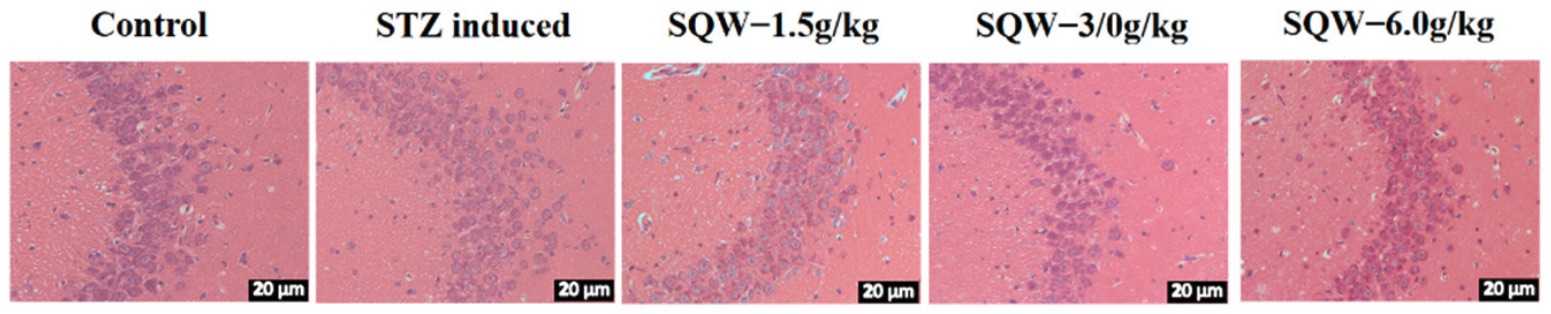 Fig. 1 Pathological images of the hippocampus induced by STZ in rats 1
Fig. 1 Pathological images of the hippocampus induced by STZ in rats 1
Introduction of STZ-Induced AD Model
Streptozotocin (STZ) is a glucosamine nitrosourea compound presented in a strain of the soil microbe Streptomyces achromogenes discovered in 1956. It is an alkylating agent mimicking some properties of nitrosoureas, a class of anticancer agents which are applicable in pancreatic carcinoma. STZ has been widely explored for its diabetogenic potential in animals.
Single or double STZ-ICV injection(s) chronically decrease cerebral glucose uptake and produce multiple other effects that resemble molecular, pathological, and behavioral features of Alzheimer's disease, including memory impairment, progressive cholinergic impairment, neurodegeneration, etc. Thus, it has been explored as a non-transgenic model of AD and used for preclinical testing of pharmacological therapies for this disease.
Features of STZ-Induced AD Model
- ICV application of the STZ has been shown to cause oxidative stress, glucose/energy metabolism alteration, and cholinergic hypo-function accompanied by memory deficit by impairment of the neuronal insulin receptor transduction cascade (including insulin, IR, IRS-1, PI3 K, Akt, and GSK-3).
- The generation of free radicals after ICV STZ injection is an important factor in causing cognitive impairment in rats.
- Histological appearance of Ab and Tau neuropathology takes a long time to develop. Technical expertise is required for ICV infusion.
Assessments
Creative Biolabs utilizes different behavioral tests of cognitive functions to evaluate the effects of novel compounds on AD in animal models. Following the behavioral tests, animals are sacrificed under anesthesia. Blood is collected for biochemical analysis, western blot, and real-time PCR analysis. Brain tissues are isolated for fixation and subsequent histological and immunohistochemical staining. Parameters that can be measured include, but are not limited to:
- Behavioral tests (e.g., motor function, cognition, and social behavior)
- Glucose level measurement
- Biochemical analysis
- Western blot
- Real-time PCR
- Histological & immunohistochemical analysis
Creative Biolabs also offers other AD models that you may be interested in:
Creative Biolabs offers CRO services with extensive expertise in conducting preclinical efficacy, proof-of-concept, and mechanism of action studies in various animal models of neurological diseases. Our comprehensive battery of rodent neurological disease models is listed as follows:
Creative Biolabs works side-by-side with our clients in providing scientific guidance in the model selection, customized study design, end-point analysis, histopathology services, and assist you with professional interpretation of the data. Contact us to discuss your specific needs if you are interested in our services.
Reference
- Huang, Junhao, et al. "Shen Qi Wan ameliorates learning and memory impairment induced by STZ in AD rats through PI3K/AKT pathway." Brain Sciences 12.6 (2022): 758. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using A part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
