House Dust Mite induced Allergic Asthma Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
For the development of anti-asthma therapeutic intervention, Creative Biolabs provides rodent asthma models induced by ovalbumin, and house dust mite, both of which have become widely used models in asthma studies. Moreover, an extensive range of administration routes and relevant endpoints are also available.
Introduction of Asthma
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the lungs characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), airway remolding and increased infiltration of leukocytes into the airways. Murine models of asthma have provided valuable information on several features of asthma pathogenesis and treatment. Compared to one of the most widely used inducible asthma models, the ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma model, house dust mite (HDM) has in recent years become the allergen of choice to induce airway disease because it is an important environmental aeroallergen that has been identified as a risk factor for persistent asthma in human subjects.
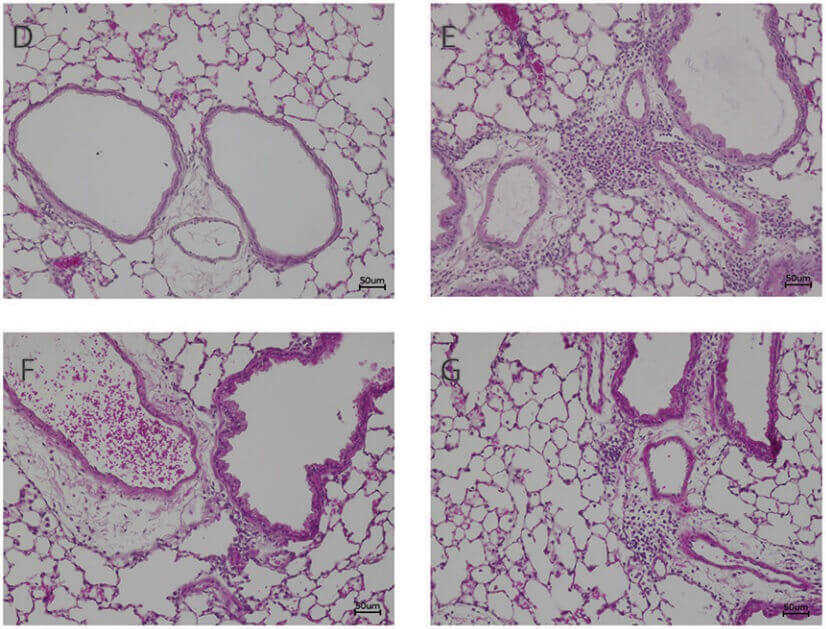 Fig. 1 Photomicrographs of the lungs of HDM-allergic mice stained with H&E. 1
Fig. 1 Photomicrographs of the lungs of HDM-allergic mice stained with H&E. 1
Induction of HDM Model
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are the major source of allergen in house dust. It has been shown to play an important role in asthma and also in the induction of other allergic diseases such as dermatitis and rhinitis. HDM fecal pellets contain various allergens that belong to the major triggers of allergic asthma worldwide, leading to the development of clinically relevant mouse models based on the administration of HDM (extracts). Chronic HDM models can be established by a first-step sensitization followed by consecutive intranasal administration of HDM or HDM extracts. At Creative Biolabs, the induction can be performed in both BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice.
Features of HDM Model
- HDM is an important environmental aeroallergen that has been identified as a risk factor for persistent asthma in human subjects.
- C57Bl/6 mice develop stronger eosinophilia and have higher levels of Th2 cytokines than BALB/c mice, whereas the latter exhibit more pronounced bronchial hyper-reactivity.
- The model is a robust and reproducible model featured by airway eosinophilic inflammation, Th2 cytokine production, the presence of HDM-specific IgE, airway remodeling, and bronchial hyperreactivity, sharing many similarities to human allergic asthma.
Assessments
In testing the therapeutic efficacy of drug candidates, we are capable of conducting all kinds of assessments as well as providing assistance in data interpretation. Our battery of assessments including but not limited to:
- Cytokines in BALF
- IgE levels in serum
- Inflammatory cells measurement
- Cell infiltration and mucus production
- Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR)
- Histopathology
- Protein expression
Additionally, other examples of rodent respiratory disease models that you may be interested include:
- Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma Model
- LPS-induced Pulmonary Neutrophilia Model
- Cigarette Smoke-Induced COPD Model
- Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis
Except for the existing models, Creative Biolabs is willing to share our expertise in project design and model development. We are happy to offer tailor-made experimental models with the highest clinical relevance for our clients to expand the impact of your next project and beyond. If you're interested in our services, contact us for more information.
Reference
- Verheijden, Kim AT, et al. "The combination therapy of dietary galacto-oligosaccharides with budesonide reduces pulmonary Th2 driving mediators and mast cell degranulation in a murine model of house dust mite induced asthma." Frontiers in Immunology 9 (2018): 2419. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using D-G part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
