Vincristine induced Neuropathy Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Various anti-cancer chemotherapeutic agents including vincristine, oxaliplatin, paclitaxel, and cisplatin are well reported to produce peripheral neuropathic pain as their main side effect. Models induced with these agents mimic the peripheral neuropathy that often results from chemotherapy treatments. Creative Biolabs conducts contract studies in the vincristine-induced neuropathy models of both rats and mice to evaluate the efficacy of analgesic drugs.
Introduction of Vincristine-Induced Neuropathy Model
Vincristine is a purified alkaloid extracted from the periwinkle plant Vinca rosea Linn. of the family Apocynaceae. It has been extensively used as chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of several malignancies including breast cancer, leukemia, lymphomas, and primary brain tumors. However, clinical use of vincristine has been associated with the development of neurotoxicity of peripheral nerve fibers with resultant sensory-motor neuropathy.
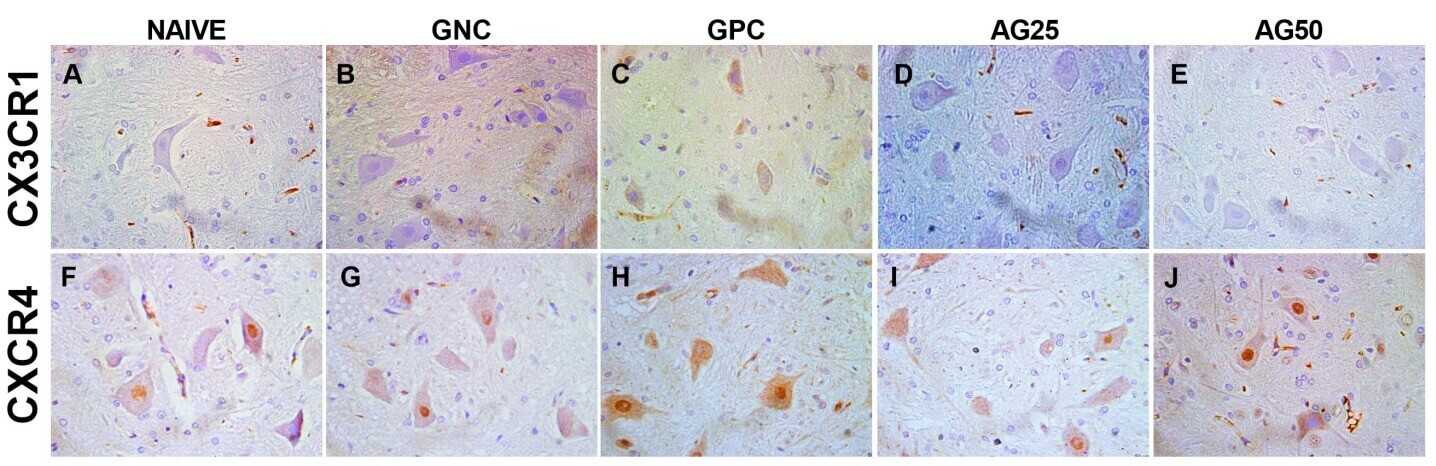 Fig. 1 Photomicrographs of immunostaining expression in rat spinal cord of CX3CR1 and CXCR4.1
Fig. 1 Photomicrographs of immunostaining expression in rat spinal cord of CX3CR1 and CXCR4.1
Models of vincristine-induced neuropathy have been developed for studying the pathogenic mechanisms involved in the development of neurotoxicity and used to study electrophysiological and histopathological changes due to chemotherapeutic agents. The treatment typically involves consecutive administrations of vincristine (intravenous infusion or intraperitoneal injection) to gradually produce in the animals (rats or mice) a significant mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity to both warm and cold stimuli, providing consistent and long-lasting neuropathic pain states mimicking vincristine-induced pain conditions in human patients.
Assessments
To evaluate the efficacy of analgesic drugs in neuropathic pain, Creative Biolabs conducts different behavioral tests to quantify the resulting neuropathic pain symptoms. Usually, mechanical hyperalgesia is measured with von Frey filaments and cold hyperalgesia is assessed with the acetone test. Other behavioral assays, such as the pin-prick test and hot-plate test are also used for testing vincristine-induced pain hypersensitivity. Briefly, Creative Biolabs provides assessments including but not limited to:
- Mechanical hyperalgesia (Randall-Selitto paw pressure test; Pin-prick test)
- Thermal hyperalgesia (paw-flick test; Hargreaves test)
- Mechano-tactile allodynia (Von Frey fiber test)
- Cold allodynia (the acetone test)
- Motor nerve conduction velocity (MNCV)
- Behavioral tests for motor function
- Behavioral tests for cognitive function
- Immunohistochemistry and histology
Meantime, Creative Biolabs offers other pain models to study different pain-related conditions and to evaluate the analgesic activity of novel drugs:
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema
- Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis (AIA) Rodent Model
- Monosodium Iodoacetate (MIA)-Induced Osteoarthritis Model
- Formalin-induced Pain Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Diabetic Neuropathy Model
- Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model
- Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (PSL) Rat Model
- Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI) Model
Creative Biolabs has abundant experience in advancing the innovations of our clients through the preclinical efficacy phases. We provide open communications and flexible study protocols to minimize the use of resources while maximizing the information obtained. With a wide range of behavior, cognitive, and motor function tests, coupled with the complementary ex vivo analyzing tools, Creative Biolabs is capable of providing a comprehensive battery of services, with the best quality and highest clinical relevance. The extensive range of rodent neurological disease models available at Creative Biolabs is listed in the following chart:
For more information please contact us or send us an inquiry below.
Reference
- Drummond, Isabela Santana Albertazzi, et al. "Evaluation of the Therapeutic Potential of Amantadine in a Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Model in Rats." Animals 14.13 (2024): 1941. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using A-J part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
