Non-Cell based Competitive Ligand Binding Assay
Determination of the neutralizing potential of the induced antibodies is an essential element of immunogenicity evaluation. Neutralizing antibody (NAbs) can trigger clinical effects, thus, specific and sensitive in vitro detection methods are needed. Currently, two types of NAb assays are mainly used, a Cell-based Bioassay or a non-cell-based competitive ligand binding (CLB) assay. Creative Biolabs provides immunogenicity assessment services by CLB assay for our worldwide customers.
Non-cell-based CLB NAb Assays
Non-cell-based CLB NAb assays is a simple and useful technique for NAb assessment because they do not suffer from some of the technical limitations of cell-based assays. As for ligand binding assays, any of the available detection systems such as radiochemical, enzymatic, fluorometric, chemiluminescence, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology can be used. However, CLB assays should only be used if the endpoint being measured is reflective of the therapeutic mechanism of action (MOA). For instance, a CLB assay is appropriate in a circumstance where a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) acts by binding to a soluble ligand thereby blocking it from interacting with its receptor thus inhibiting the biological activity of the ligand. Since the assay procedure measures binding to the target and inhibition of the binding activity if NAbs are present, it is reflective of the MOA of the therapeutic.
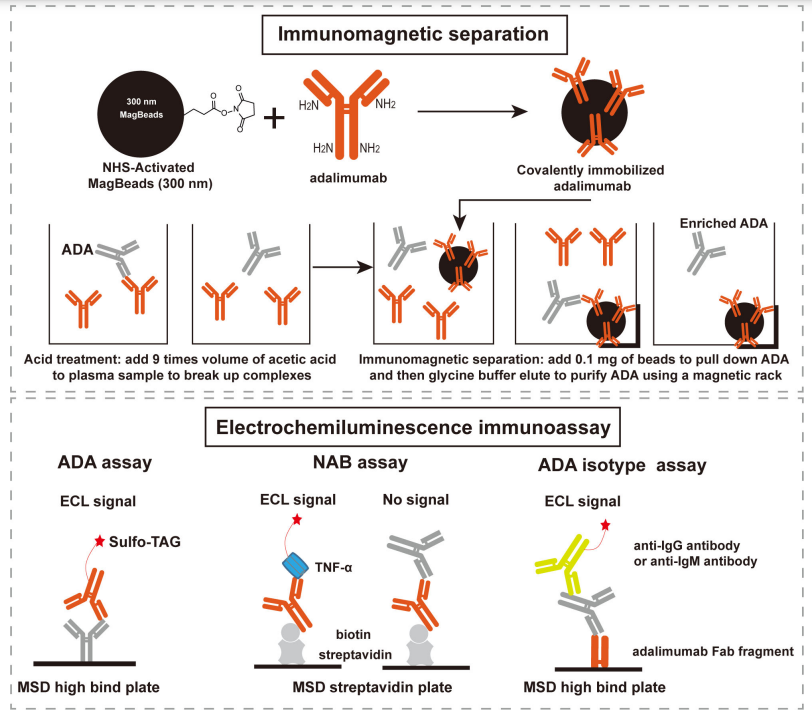 Fig.1 Scheme of the integrated immunoassay platform comprised of immunomagnetic separation and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay.1, 2
Fig.1 Scheme of the integrated immunoassay platform comprised of immunomagnetic separation and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay.1, 2
CLB Assay Formats
Two formats can be used for CLB assays, the simple direct format (Fig.1a) and the complex indirect format (Fig.1b). For the former, the drug molecule is coated on the assay plate as the capture molecule while the labeled target serves as the detection molecule. Interaction of the drug with the target generates an assay signal such as fluorescence. NAb binds to the drug and competitively inhibits the drug-target interaction, resulting in a reduced assay signal.
In the indirect format, the target receptor is immobilized on the assay plate as the capture molecule while the labeled ligand serves as the detection molecule. Binding of the ligand to the target receptor generates an assay signal. Neutralization of the ligand by the drug abrogates the assay signal. In the presence of NAb, it inhibits the drug-ligand interaction and restores the assay signal.
Cell-based Bioassay vs Non-cell-based CLB Assay
Cell-based assays are often employed for agonistic therapeutics and CLB assays are being considered for antagonistic molecules with humoral targets. For antagonists such as mAb therapeutics with effector functions for clinical efficacy, cell-based assays are recommended. Table 1 lists the main advantages and disadvantages of these two methods and their application scope.
Table 1. Methods for Detection of NAbs
| Types of Assay | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cell-based bioassay |
|
|
| Suit for: Agonistic therapeutics. For antagonists such as mAb therapeutics with effector functions for clinical efficacy, cell-based assays are recommended. | ||
| Non-cell based competitive ligand binding (CLB) assay |
|
|
| Suit for: Antagonistic molecules such as anti-IgE. | ||
Biotherapeutic products are the fastest growing medicines in the pharmaceutical market and the immunogenicity of them continues to be a major concern. It is important to monitor the immunogenicity of biological therapeutics throughout the drug product development cycle. Armed with a mature system for NAb analysis, Creative Biolabs provides NAb detection services by non-cell-based CLB assay. If you are interested in our services, please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
References
- Ding, Xiaoliang, et al. "Dynamics and implications of anti-drug antibodies against adalimumab using ultra-sensitive and highly drug-tolerant assays." Frontiers in Immunology 15 (2024): 1429544.
- Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
