Isolation by Acid Elution of Cell Surface
The myriad of peptides presented at the cell surface by class I and class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are of great importance for basic research and translational science. With access to advanced instruments, fit-for-purpose laboratories, and professional knowledge, Creative Biolabs has developed a wide variety of methods to isolate and analyze MHC-associated peptides to support the immunotherapies for cancer and autoimmune diseases, vaccines development, as well as improvement of protein therapies. Amongst, acid elution of cell surfaces is one of the well-studied methods with simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Introduction of MHC-associated Peptides
MHC-associated peptides, referred to as the collection of peptides associated with and presented by MHC molecules, can be divided into two classes: MHC class I and class II peptides. These peptides are recognized by T lymphocytes and then stimulate the immune responses to eliminate abnormal cells such as pathogen-infected and cancer cells.
- MHC class I peptides predominantly consist of 9-12 amino acids that are generated mainly following the degradation of intracellular proteins by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and are recognized by cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. In addition, class I peptides are presented on virtually any nucleated cell.
- MHC class II peptides mainly consist of 10-25 amino acids, derived mainly from protease-mediated degradation of endocytosed proteins of extracellular origin, and are recognized by helper CD4+ T cells. Different from class I peptides, class II peptides are presented on a subset of specialized immune cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B lymphocytes.
There are two main methods normally used for the isolation of MHC peptides, namely immunoaffinity chromatography and acid stripping of cell surfaces.
What Is Acid Elution?
Traced back to 1993, the acid elution method is based on the release of MHC class I peptides from the cell surface by a short (15-300 s) acid treatment at pH 3.3 with a mixed citrate-phosphate buffer. Now, this method has been extended to MHC class II peptides isolation. Compared to immunoaffinity chromatography, acid elution shows several prominent advantages, such as simplicity (fewer purification steps), no detergents, cost-effectiveness, and the outlook to obtain mainly cell surface MHC peptides that are the relevant part for T-cell recognition.
However, acid elution has never been used for high-throughput sequencing of MHC peptides repertoire, mainly because that the eluted peptides are always contaminated by non-MHC peptides and proteins (e.g., proteolytic fragments, cytoplasmic peptides, peptides from other peptide receptors). To overcome this challenge, Creative Biolabs has used MHC-deficient cells as a negative control. For instance, β2-microglobulin (β2m)-deficient cells are MHC I deficient, because β2m is essential for the formation of stable peptide-MHC I complexes.
Up to date, acid elution method has been successfully employed, e.g., to identify T-cell epitopes from melanoma cells and an immunogenic peptide deriving from the BCR-ABL fusion protein (the product of the Philadelphia chromosome, Ph’). Usually, there are two acid elution techniques have been developed to extract MHC-associated peptides:
- Strong acid elution of MHC class I and II peptides from the whole-cell lysate using trifluoroacetic acid.
- Mild acid elution (MAE) of MHC class I peptides from the cell surface. Until recently, MAE has been used to isolate MHC class I peptides from various cell lines, bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells, and primary thymocytes.
Schematic Overview of Acid Elution Method
The rationale of MAE is to use 10% acetic acid buffer at pH 3.3 to extract MHC-associated peptides by denaturation of MHC class I molecules on the surface of cells. After elution, the peptides are mostly concentrated on cation exchange or reversed-phase cartridges for further purification (HPLC) and analyses (MS).
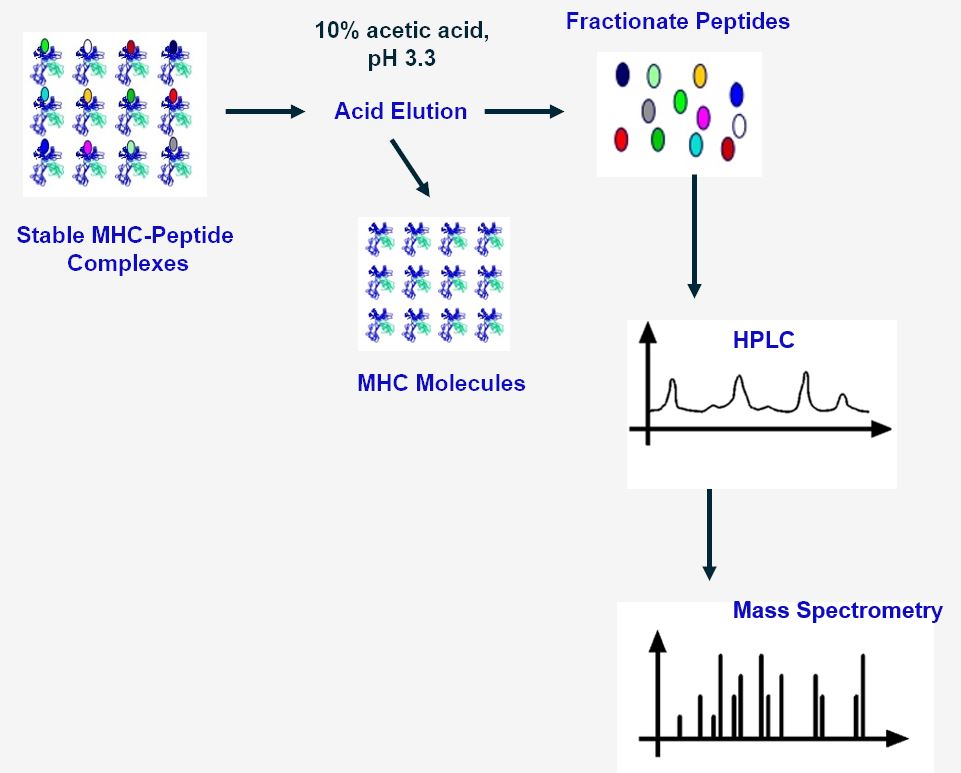 Fig.1 Workflow of MHC-associated peptides isolation by acid elution at Creative Biolabs.
Fig.1 Workflow of MHC-associated peptides isolation by acid elution at Creative Biolabs.
As critical components of the immune system, MHC-associated peptides can directly fuel and guide the development of next-generation vaccines and immunotherapies against autoimmunity, infectious diseases, and cancers. As an excellent pharmaceutical company and CRO service provider, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing comprehensive services about MHC-associated peptides isolation. If you are interested in our acid elution services, please feel free to contact us. We can also customize other drug target discovery services to address your specific demand.
For Research Use Only.
